Yonsei Med J.
2008 Jun;49(3):451-458. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.3.451.
A Comprehensive Prognostic Stratification for Patients with Metastatic Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. sjhong346@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Urology, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Urology, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 724262
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.3.451
Abstract
- PURPOSE
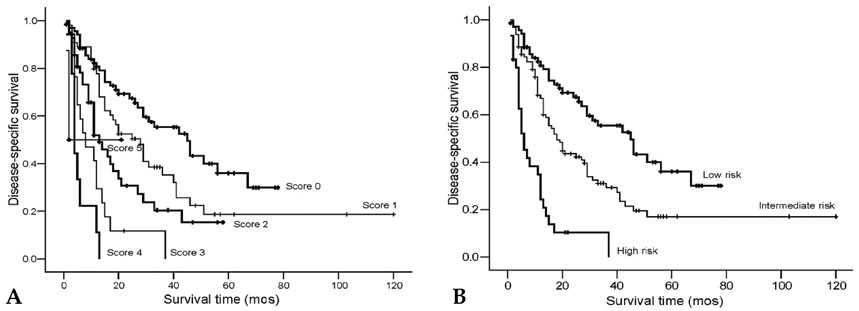
To develop a reliable prognostic model for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) based on features readily available in common clinical settings. PATIENTS AND METHODS: A total of 197 patients with RCC who underwent nephrectomy and immunotherapy from 1995 to 2004 were retrospectively reviewed. Their mean age was 55.1+/-11.8 yrs (24-83yrs) and mean survival time from metastasis was 22.6+/-20.2mos (3-120mos). The impact of 24 clinicopathological features on disease specific survival was investigated. RESULTS: On univariate analysis, constitutional symptoms, sarcomatoid differentiation, tumor necrosis, multiple primary lesions, liver metastasis, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG-PS), thrombocytosis, alkaline phosphatase, hematocrit, T stage, N stage, and nuclear grade had significant influence on survival (p<0.05). Multivariate analysis revealed the following features associated with survival: sarcomatoid differentiation [hazard ratio (HR)=2.99, p<0.001], liver metastasis (HR=2.09, p=0.002), ECOG-PS (HR=1.95, p= 0.005), N stage (HR=1.94, p=0.002), and number of metastatic sites (HR=1.76, p=0.003). An individual prognostic score was defined as the sum of the weight of these features. According to prognostic scores, patients could be subdivided into 3 groups: low risk (score 0), intermediate risk (score 1 or 2), and high risk (score> or =3). CONCLUSION: A comprehensive prognostic stratification model was developed to predict survival and stratify patients for prospective clinical trials.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Carcinoma, Renal Cell/pathology/*therapy
Combined Modality Therapy
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Humans
Immunotherapy/methods
Kidney Neoplasms/pathology/*therapy
Male
Middle Aged
Multivariate Analysis
Neoplasm Metastasis
Neoplasm Staging
Nephrectomy/methods
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Trends of Presentation and Clinical Outcome of Treated Renal Angiomyolipoma
Kyo Chul Koo, Won Tae Kim, Won Sik Ham, Jin Sun Lee, Hee Jeong Ju, Young Deuk Choi
Yonsei Med J. 2010;51(5):728-734. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.5.728.
Reference
-
1. Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1996. 335:865–875.
Article2. Pantuck AJ, Zisman A, Belldegrun AS. The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2001. 166:1611–1623.
Article3. Flanigan RC, Salmon SE, Blumenstein BA, Bearman SI, Roy V, McGrath PC, et al. Nephrectomy followed by interferon alfa-2b compared with interferon alfa-2b alone for metastatic renal-cell cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:1655–1659.
Article4. Mickisch GH, Garin A, van Poppel H, de Prijck L, Sylvester R. Radical nephrectomy plus interferon-alfa-based immunotherapy compared with interferon alfa alone in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001. 358:966–970.
Article5. Bellmunt J, Montagut C, Albiol S, Carles J, Maroto P, Orsola A. Present strategies in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an update on molecular targeting agents. BJU Int. 2007. 99:274–280.
Article6. Atzpodien J, Royston P, Wandert T, Reitz M. Metastatic renal carcinoma comprehensive prognostic system. Br J Cancer. 2003. 88:348–353.
Article7. Leibovich BC, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, Frank I, Kwon ED, et al. A scoring algorithm to predict survival for patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a stratification tool for prospective clinical trials. J Urol. 2005. 174:1759–1763. discussion 1763.
Article8. Leibovich BC, Han KR, Bui MH, Pantuck AJ, Dorey FJ, Figlin RA, et al. Scoring algorithm to predict survival after nephrectomy and immunotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a stratification tool for prospective clinical trials. Cancer. 2003. 98:2566–2575.
Article9. Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Murphy BA, Russo P, Mazumdar M. Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:289–296.
Article10. Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Bacik J, Berg W, Amsterdam A, Ferrara J. Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:2530–2540.
Article11. Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Dorey F, Said JW, Shvarts O, Quintana D, et al. Improved prognostication of renal cell carcinoma using an integrated staging system. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:1649–1657.
Article12. Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Wieder J, Chao DH, Dorey F, Said JW, et al. Risk group assessment and clinical outcome algorithm to predict the natural history of patients with surgically resected renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:4559–4566.
Article13. Frank I, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Weaver AL, Zincke H. An outcome prediction model for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with radical nephrectomy based on tumor stage, size, grade and necrosis: the SSIGN score. J Urol. 2002. 168:2395–2400.
Article14. de Forges A, Rey A, Klink M, Ghosn M, Kramar A, Droz JP. Prognostic factors of adult metastatic renal carcinoma: a multivariate analysis. Semin Surg Oncol. 1988. 4:149–154.
Article15. Lopez Hänninen E, Kirchner H, Atzpodien J. Interleukin-2 based home therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: risks and benefits in 215 consecutive single institution patients. J Urol. 1996. 155:19–25.
Article16. Jones M, Philip T, Palmer P, von der Maase H, Vinke J, Elson P, et al. The impact of interleukin-2 on survival in renal cancer: a multivariate analysis. Cancer Biother. 1993. 8:275–288.
Article17. Palmer PA, Vinke J, Philip T, Negrier S, Atzpodien J, Kirchner H, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with recombinant interleukin-2. Ann Oncol. 1992. 3:475–480.
Article18. Elson PJ, Witte RS, Trump DL. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with recurrent or metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1988. 48:7310–7313.19. Fosså SD, Kramar A, Droz JP. Prognostic factors and survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with chemotherapy or interferon-alpha. Eur J Cancer. 1994. 30A:1310–1314.20. Amin MB, Amin MB, Tamboli P, Javidan J, Stricker H, de-Peralta Venturina M, et al. Prognostic impact of histologic subtyping of adult renal epithelial neoplasms: an experience of 405 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002. 26:281–291.
Article21. Berndt SI, Carter HB, Schoenberg MP, Newschaffer CJ. Disparities in treatment and outcome for renal cell cancer among older black and white patients. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:3589–3595.
Article22. Tripathi RT, Heilbrun LK, Jain V, Vaishampayan UN. Racial disparity in outcomes of a clinical trial population with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2006. 68:296–301.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma to the Gallbladder
- A Case of Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to the Right Zygoma
- A Case of Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to the Scalp
- Perineal Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report
- Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma to the Thyroid Gland