J Rheum Dis.
2023 Apr;30(2):99-105. 10.4078/jrd.22.0053.
The effect of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on sleep and quality of life in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Faculty of Medicine, Aydin Adnan Menderes University, Aydın, Turkey
- KMID: 2541053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.22.0053
Abstract
Objective
The sleep quality is worse in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients than in healthy controls and it is more difficult to achieve a satisfactory quality of life after treatment with age. Our aim is to assess the quality of life and sleep in elderly onset RA patients and to analyze the effect of disease-modifying agents on sleep and quality of life.
Methods
Thirty-four older patients with RA patients and 30 healthy controls are included in the study. Sleep quality was evaluated with the Pittsburg sleep quality index and quality of life with Short Form-36. Parametric/non-parametric tests and Spearman/ Pearson correlation analysis were applied for the data according to the distribution.
Results
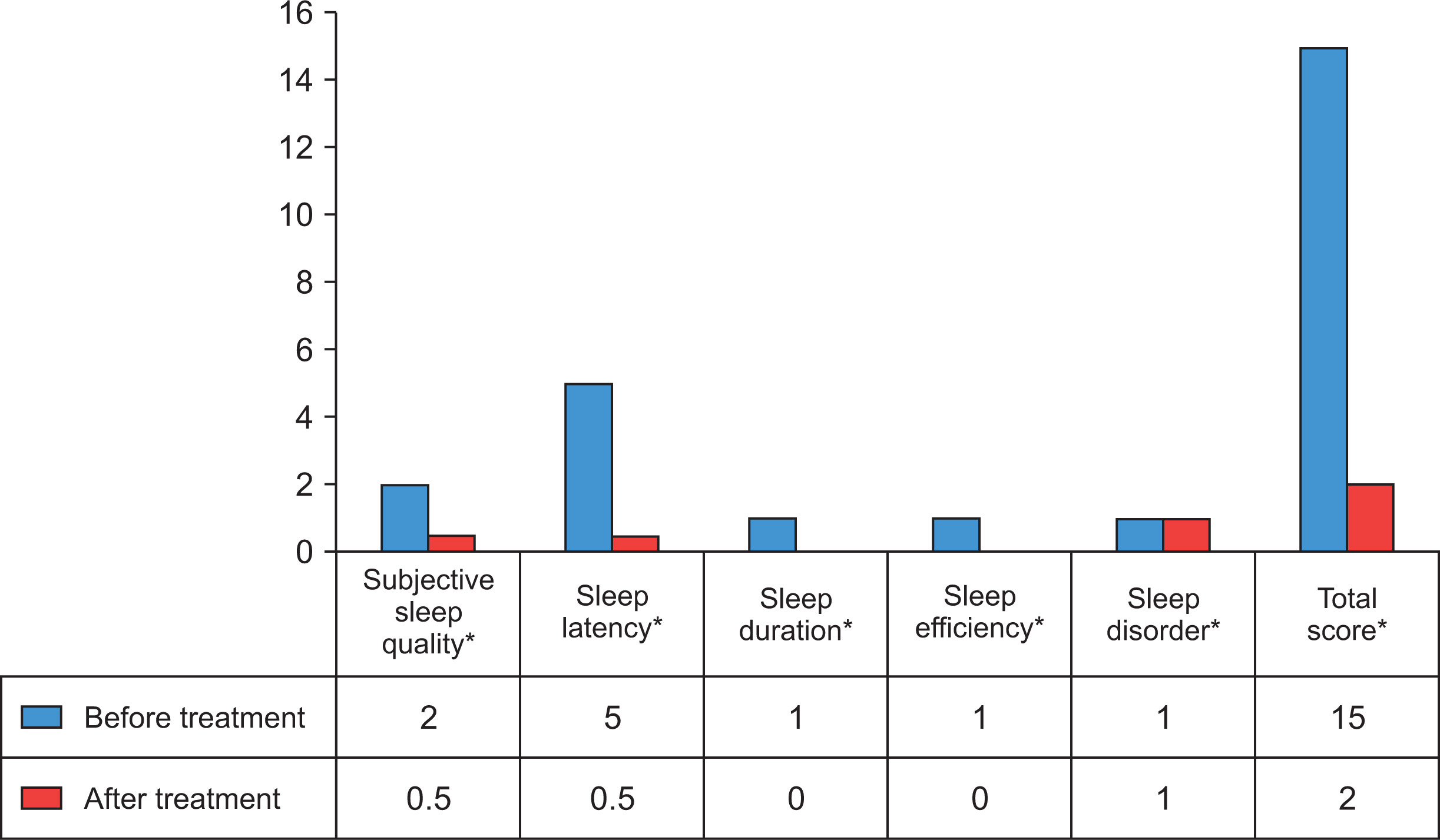
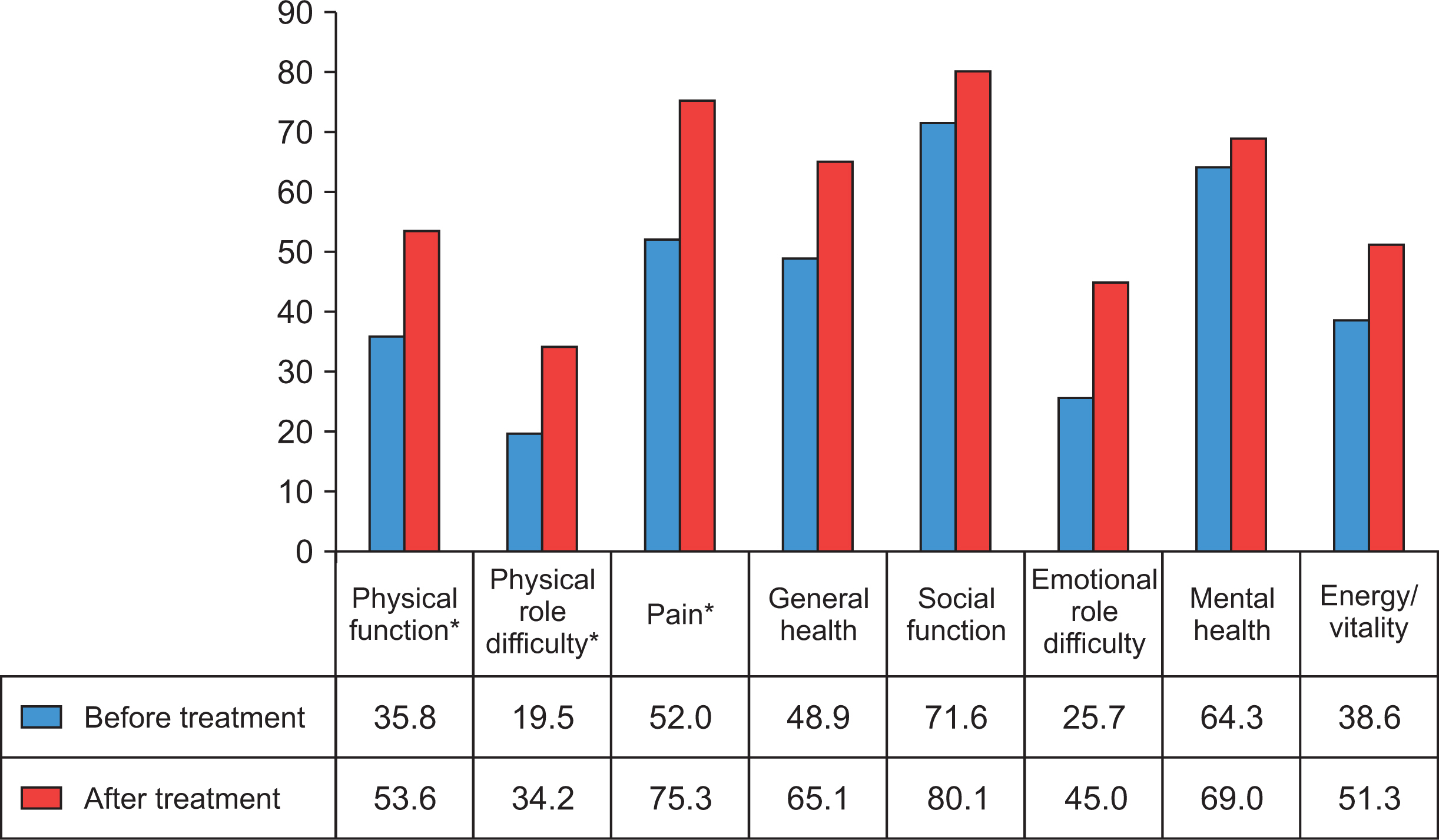
While the rate of poor sleep quality before treatment was 67.6%, the rate was 26.5% after treatment. There was a statistically significant difference before and after treatment in terms of subjective sleep quality, sleep latency, sleep duration, sleep efficiency, and scores for sleep disturbance. The mean steroid dose and Disease Activity Score-28 were higher in patients with poor sleep quality than in patients with good sleep quality. Patients with poor sleep quality had lower mean physical function, pain, general health, social function, emotional role difficulties, and energy/vitality values than patients with good sleep quality.
Conclusion
Both sleep and quality of life improved after treatment in older patients with RA patients. In older patients, it should be regularly evaluated in terms of sleep and quality of life and appropriate treatment should be provided.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sparks JA. 2019; Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 170:ITC1–16. DOI: 10.7326/AITC201901010. PMID: 30596879.
Article2. Guo Q, Wang Y, Xu D, Nossent J, Pavlos NJ, Xu J. 2018; Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 6:15. DOI: 10.1038/s41413-018-0016-9. PMID: 29736302. PMCID: PMC5920070.
Article3. Bullock J, Rizvi SAA, Saleh AM, Ahmed SS, Do DP, Ansari RA, et al. 2018; Rheumatoid arthritis: a brief overview of the treatment. Med Princ Pract. 27:501–7. DOI: 10.1159/000493390. PMID: 30173215. PMCID: PMC6422329.4. Kobak S, Bes C. 2018; An autumn tale: geriatric rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 10:3–11. DOI: 10.1177/1759720X17740075. PMID: 29290762. PMCID: PMC5724645.5. Tan TC, Gao X, Thong BY, Leong KP, Lian TY, Law WG, et al. TTSH Rheumatoid Arthritis Study Group. 2017; Comparison of elderly- and young-onset rheumatoid arthritis in an Asian cohort. Int J Rheum Dis. 20:737–45. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.12861. PMID: 27135312.6. Zhang JF, Ye XL, Duan M, Zhou XL, Yao ZZ, Zhao JX. 2020; [Clinical characteristics of elderly and younger onset rheumatoid arthritis]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 100:3788–92. Chinese.7. Kłodziński Ł, Wisłowska M. 2018; Comorbidities in rheumatic arthritis. Reumatologia. 56:228–33. DOI: 10.5114/reum.2018.77974. PMID: 30237627. PMCID: PMC6142024.8. Martinec R, Pinjatela R, Balen D. 2019; Quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis - a preliminary study. Acta Clin Croat. 58:157–66. DOI: 10.20471/acc.2019.58.01.20. PMID: 31363338. PMCID: PMC6629210.9. Roma I, Almeida ML, Mansano NS, Viani GA, Assis MR, Barbosa PMK. 2014; [Quality of life in adults and elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis]. Rev Bras Reumatol. 54:279–86. Portuguese. DOI: 10.1016/j.rbre.2014.03.025.
Article10. Worley SL. 2018; The extraordinary importance of sleep: the detrimental effects of inadequate sleep on health and public safety drive an explosion of sleep research. P T. 43:758–63.11. Grabovac I, Haider S, Berner C, Lamprecht T, Fenzl KH, Erlacher L, et al. 2018; Sleep quality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and associations with pain, disability, disease duration, and activity. J Clin Med. 7:336. DOI: 10.3390/jcm7100336. PMID: 30304765. PMCID: PMC6210607.12. MacDonald IJ, Huang CC, Liu SC, Tang CH. 2020; Reconsidering the role of melatonin in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:2877. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21082877. PMID: 32326031. PMCID: PMC7215432.13. Mangoni AA, Jackson SH. 2004; Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 57:6–14. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.02007.x. PMID: 14678335. PMCID: PMC1884408.14. Son CN, Choi G, Lee SY, Lee JM, Lee TH, Jeong HJ, et al. 2015; Sleep quality in rheumatoid arthritis, and its association with disease activity in a Korean population. Korean J Intern Med. 30:384–90. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2015.30.3.384. PMID: 25995669. PMCID: PMC4438293.15. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. 1989; The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 28:193–213. DOI: 10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4. PMID: 2748771.16. Matcham F, Scott IC, Rayner L, Hotopf M, Kingsley GH, Norton S, et al. 2014; The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on quality-of-life assessed using the SF-36: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 44:123–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.05.001. PMID: 24973898.17. Song BW, Jeong HJ, Kim BY, Cho YW, Son CN, Kim SS, et al. 2021; Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index is associated with the quality of sleep in ankylosing spondylitis patients. J Rheum Dis. 28:143–9. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.3.143.18. Ağargün MY, Kara H, Anlar Ö. 1996; [The validity and reliability of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index]. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 7:107–15. Turkish.19. Sohn SI, Kim DH, Lee MY, Cho YW. 2012; The reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Sleep Breath. 16:803–12. DOI: 10.1007/s11325-011-0579-9. PMID: 21901299.20. Lee J, Kim SS, Jeong HJ, Son CN, Kim JM, Cho YW, et al. 2017; Association of sleep quality in Behcet disease with disease activity, depression, and quality of life in Korean population. Korean J Intern Med. 32:352–9. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2016.367. PMID: 28192886. PMCID: PMC5339476.21. Faulkner S, Sidey-Gibbons C. 2019; Use of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index in people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders: a mixed methods study. Front Psychiatry. 10:284. DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00284. PMID: 31143131. PMCID: PMC6520598.22. Goes ACJ, Reis LAB, Silva MBG, Kahlow BS, Skare TL. 2017; Rheumatoid arthritis and sleep quality. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed. 57:294–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.rbr.2016.06.002. PMID: 28743355.23. Guo G, Fu T, Yin R, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Xia Y, et al. 2016; Sleep quality in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: contributing factors and effects on health-related quality of life. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 14:151. DOI: 10.1186/s12955-016-0550-3. PMID: 27852301. PMCID: PMC5111274.24. Zamarrón C, Maceiras F, Mera A, Gómez-Reino JJ. 2004; Effect of the first infliximab infusion on sleep and alertness in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:88–90. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.007831. PMID: 14672898. PMCID: PMC1754718.25. Taylor-Gjevre RM, Gjevre JA, Nair BV, Skomro RP, Lim HJ. 2011; Improved sleep efficiency after anti-tumor necrosis factor α therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 3:227–33. DOI: 10.1177/1759720X11416862. PMID: 22870481. PMCID: PMC3383532.26. Sariyildiz MA, Batmaz I, Bozkurt M, Bez Y, Cetincakmak MG, Yazmalar L, et al. 2014; Sleep quality in rheumatoid arthritis: relationship between the disease severity, depression, functional status and the quality of life. J Clin Med Res. 6:44–52. DOI: 10.4021/jocmr1648w. PMID: 24400031. PMCID: PMC3881989.27. Westhovens R, Van der Elst K, Matthys A, Tran M, Gilloteau I. 2014; Sleep problems in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 41:31–40. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.130430. PMID: 24293569.28. Walker EA, Keegan D, Gardner G, Sullivan M, Katon WJ, Bernstein D. 1997; Psychosocial factors in fibromyalgia compared with rheumatoid arthritis: I. Psychiatric diagnoses and functional disability. Psychosom Med. 59:565–71. DOI: 10.1097/00006842-199711000-00002. PMID: 9407573.29. Belt NK, Kronholm E, Kauppi MJ. 2009; Sleep problems in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 27:35–41.30. Doğan A, Ceceli E, Okumuş M, Gökkaya NKO, Kutsal YG, Borman P, et al. 2011; [Identifying the characteristics of geriatric patients who referred to outpatient clinics of physical medicine and rehabilitation: a multicenter descriptive study]. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 57:143–9. Turkish.31. Bulut İ, Deveci SE. 2017; [The life quality of women aged 15-49 living in Elazig city centre and the factors affecting it]. Firat Üniv Sağlık Bilim Tıp Derg. 31:61–9. Turkish.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Rheumatoid Artritis
- Medical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (I): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, disease modifying antirheumatic drugs and glucocorticoids
- Cementless Total Knee Arthroplasty and Effects of Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis