Clin Endosc.
2023 Jan;56(1):100-106. 10.5946/ce.2022.058.
Role of interventional endoscopic ultrasound in a developing country
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia–Cipto Mangunkusumo National General Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
- KMID: 2538757
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.058
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) has become an essential diagnostic and therapeutic tool. EUS was introduced in 2013 in Indonesia and is considered relatively new. This study aimed to describe the current role of interventional EUS at our hospital as a part of the Indonesian tertiary health center experience.
Methods
This retrospective study included all patients who underwent interventional EUS (n=94) at our center between January 2015 and December 2020. Patient characteristics, technical success, clinical success, and adverse events associated with each type of interventional EUS procedure were evaluated.
Results
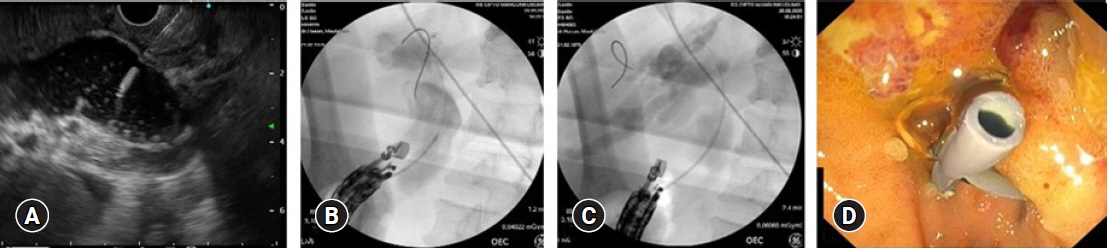
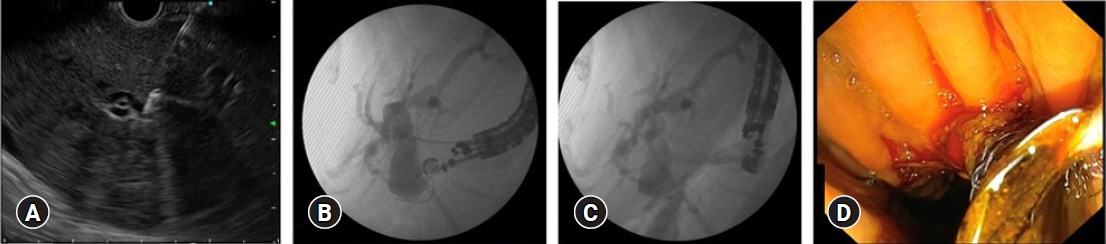
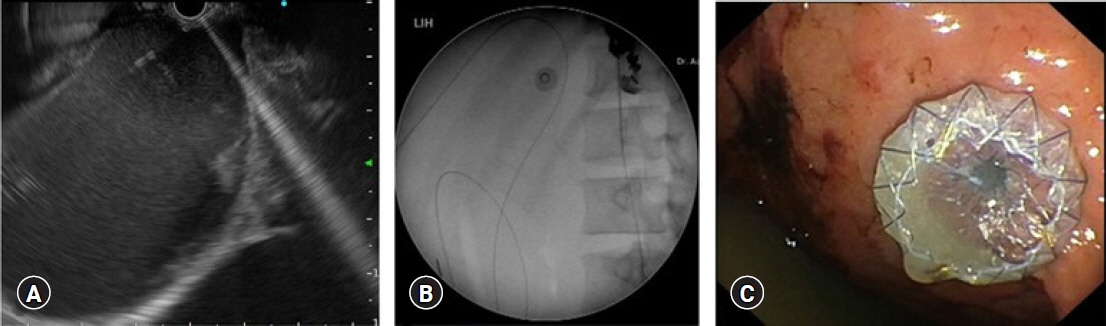
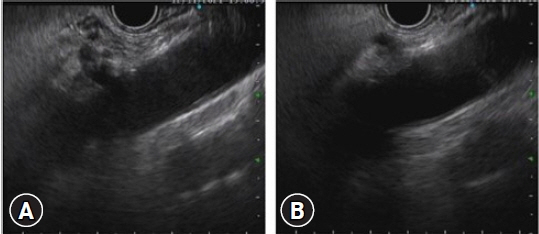
Altogether, 94 interventional EUS procedures were performed at our center between 2015 and 2020 including 75 cases of EUS-guided biliary drainage (EUS-BD), 14 cases of EUS-guided pancreatic fluid drainage, and five cases of EUS-guided celiac plexus neurolysis. The technical and clinical success rates of EUS-BD were 98.6% and 52%, respectively. The technical success rate was 100% for both EUS-guided pancreatic fluid drainage and EUS-guided celiac plexus neurolysis. The adverse event rates were 10.6% and 7.1% for EUS-BD and EUS-guided pancreatic fluid drainage, respectively.
Conclusions
EUS is an effective and safe tool for the treatment of gastrointestinal and biliary diseases. It has a low rate of adverse events, even in developing countries.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Friedberg SR, Lachter J. Endoscopic ultrasound: current roles and future directions. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 9:499–505.2. Sharma V, Rana SS, Bhasin DK. Endoscopic ultrasound guided interventional procedures. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:628–642.3. Saumoy M, Kahaleh M. Safety and complications of interventional endoscopic ultrasound. Clin Endosc. 2018; 51:235–238.4. Makmun D, Fauzi A, Abdullah M, et al. The role of EUS-BD in the management of malignant biliary obstruction: the Indonesian perspective. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2017; 2017:4856276.5. Kanno Y, Koshita S, Ogawa T, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage for unresectable malignant biliary obstruction: 10-year experience of 99 cases at a single center. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019; 50:469–477.6. Paik WH, Lee TH, Park DH, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage versus ERCP for the primary palliation of malignant biliary obstruction: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018; 113:987–997.7. Baars JE, Kaffes AJ, Saxena P. EUS-guided biliary drainage: a comprehensive review of the literature. Endosc Ultrasound. 2018; 7:4–9.8. Park SW, Lee SS. Which are the most suitable stents for interventional endoscopic ultrasound? J Clin Med. 2020; 9:3595.9. Ramirez-Luna MA, Tellez-Avila FI, Giovannini M, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliodigestive drainage is a good alternative in patients with unresectable cancer. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:826–830.10. Kawakubo K, Isayama H, Kato H, et al. Multicenter retrospective study of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage for malignant biliary obstruction in Japan. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014; 21:328–334.11. Kumta NA, Tyberg A, Bhagat VH, et al. EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections using lumen apposing metal stents: an international, multicenter experience. Dig Liver Dis. 2019; 51:1557–1561.12. Hao SJ, Xu WJ, Di Y, et al. Novel and supplementary management of pancreatic fluid collections: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 9:486–493.13. Xie LT, Zhao QY, Gu JH, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided versus percutaneous drainage for the recurrent pancreatic fluid collections. Med Sci Monit. 2019; 25:5785–5794.14. Keane MG, Sze SF, Cieplik N, et al. Endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage of symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections: a 14-year experience from a tertiary hepatobiliary centre. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:3730–3740.15. Kato S, Katanuma A, Maguchi H, et al. Efficacy, safety, and long-term follow-up results of EUS-guided transmural drainage for pancreatic pseudocyst. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2013; 2013:924291.16. Puli SR, Reddy JB, Bechtold ML, et al. EUS-guided celiac plexus neurolysis for pain due to chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer pain: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54:2330–2337.17. Kaufman M, Singh G, Das S, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided celiac plexus block and celiac plexus neurolysis for managing abdominal pain associated with chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 44:127–134.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Procedures: A Review
- Recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage
- Role of endoscopic ultrasound in non-small cell lung cancer
- New Scopes, New Accessories, New Stents for Interventional Endoscopic Ultrasound
- Present status and perspectives of endosonography 2017 in gastroenterology