Lab Med Online.
2022 Oct;12(4):269-277. 10.47429/lmo.2022.12.4.269.
Performance Evaluation of the Mindray BC-6200 Hematology Analyzer; Comparison with Sysmex XE-2100 and Manual Microscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Catholic University of Korea Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Konkuk University Chungju Hospital, Chungju, Korea
- KMID: 2538614
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2022.12.4.269
Abstract
- Background
Complete blood count (CBC) and white blood cell (WBC) differential are essential tests for various diseases. Related to this, the Mindray BC-6200 automated hematology analyzer (BC-6200, Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd, China) was recently launched in clinical laboratories. This study aimed to evaluate the analytical and flagging performance of BC-6200.
Methods
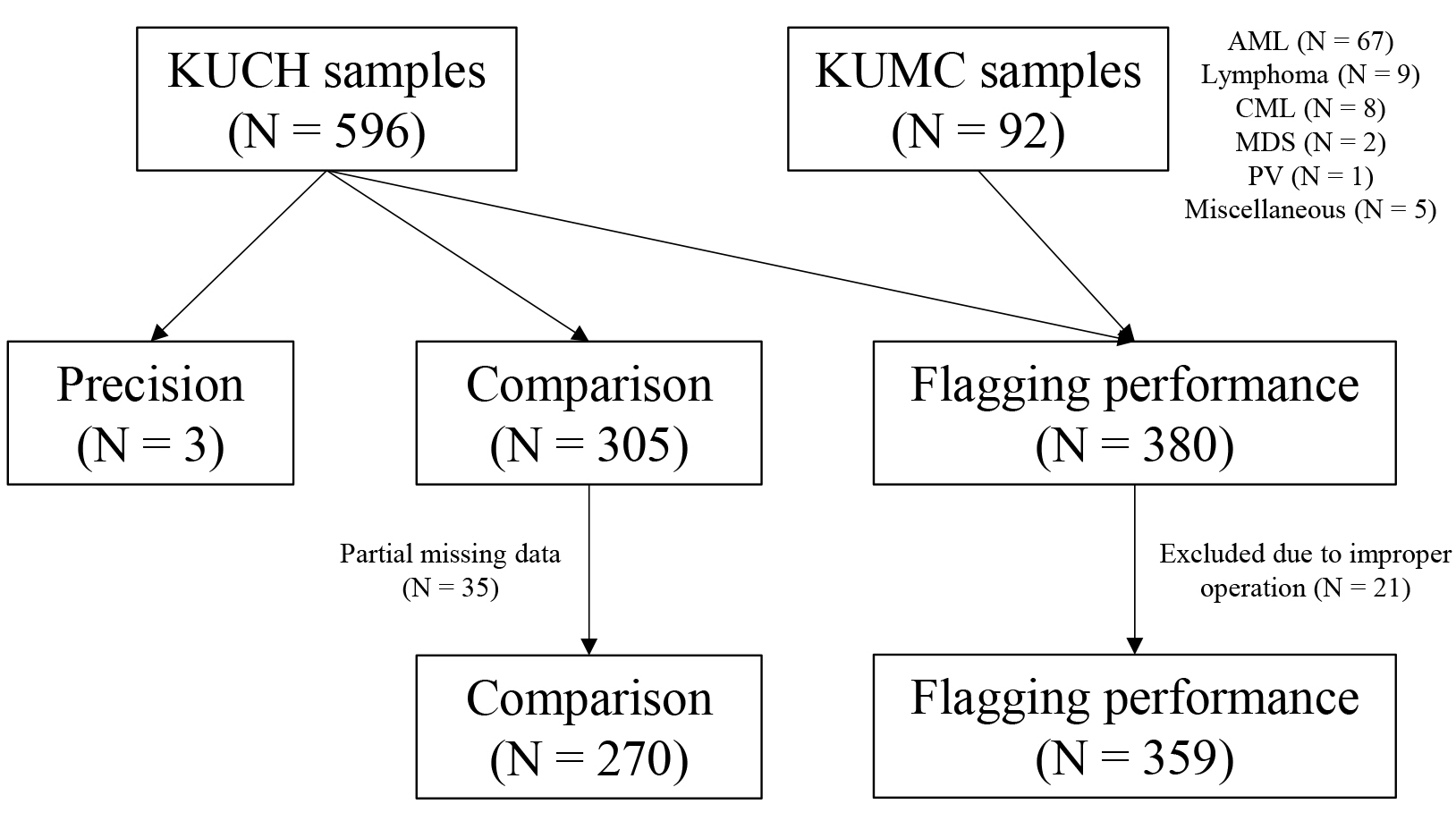
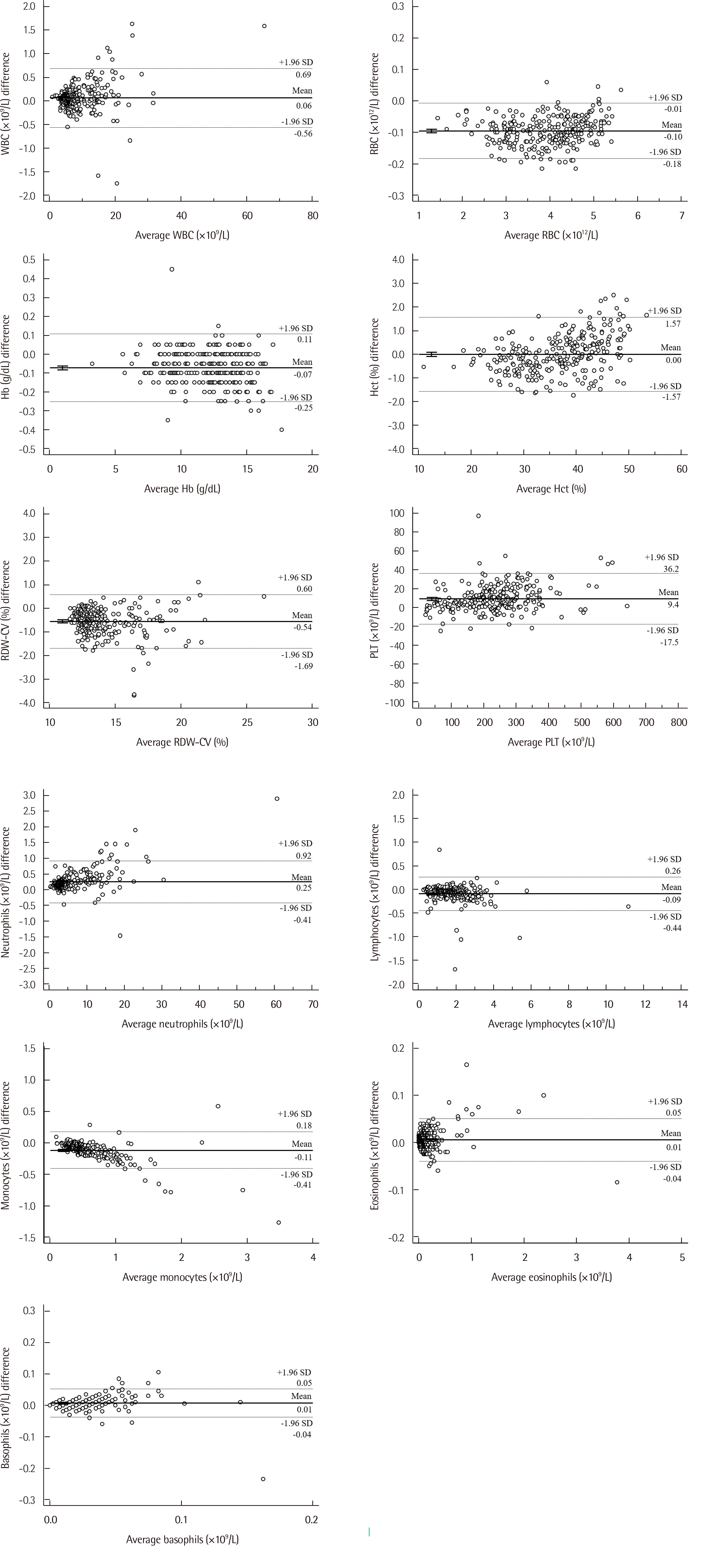
Using 688 whole blood samples, the precision and carryover of 12 CBC parameters were evaluated with BC-6200 according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines EP15-A3 and H26-A2, respectively. 11 CBC parameters of BC-6200 were compared with Sysmex XE-2100 (XE-2100, Sysmex Corporation, Japan) according to the CLSI guideline EP09c. To evaluate the flagging performance for blasts, immature granulocytes (IG), atypical lymphocytes (AL), and nucleated red blood cells (NRBC) of BC-6200, sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency to manual counts were estimated according to the CLSI guideline H20-A2.
Results
Precisions of WBC, red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (Hct), and platelets (PLT) were acceptable. Carryover was less than 1% in WBC, RBC, Hb, Hct, and PLT. In WBC differentials, BC-6200 and XE-2100 showed very high correlations, except for basophils. Flagging performances of BC-6200 showed excellent results in efficiency; 91.4% for blasts, 79.4% for IG, 75.5% for AL, and 98.6% for NRBC.
Conclusions
The analytical performances of BC-6200 were acceptable and comparable with those of XE-2100. The flagging performance was also comparable with that of manual counts. BC-6200 would be a competent instrument in clinical laboratories.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Libby P, Sidlow R, Lin AE, Gupta D, Jones LW, Moslehi J, et al. 2019; Clonal hematopoiesis: crossroads of aging, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 74:567–77. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.06.007. PMID: 31345432. PMCID: PMC6681657.2. Orwoll ES, Orwoll RL. 1987; Hematologic abnormalities in patients with endocrine and metabolic disorders. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1:261–79. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8588(18)30675-0.
Article3. Briggs C, Culp N, Davis B, d'Onofrio G, Zini G, Machin SJ. 2014; ICSH guidelines for the evaluation of blood cell analysers including those used for differential leucocyte and reticulocyte counting. Int J Lab Hematol. 36:613–27. DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.12201. PMID: 24666725.
Article4. Sullivan E. 2006; Hematology analyzer: from workhorse to thoroughbred. LABMEDICINE. 37:273–8. DOI: 10.1309/TMQ6T4CBCG408141.
Article5. Park S, Huh J, Jeong TD. 2020; False-positive flag of WBC and change of mean platelet volume (MPV) caused by K3-EDTA on the DxH 900 hematology analyzer. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 80:644–8. DOI: 10.1080/00365513.2020.1824298. PMID: 32975447.
Article6. Kulik K, Kwiecień I, Chełstowska B, Rutkowska E, Rzepecki P. 2021; Evaluation and comparison of the new Mindray BC-6200 hematology analyzer with ADVIA 2120i. Int J Lab Hematol. 43:395–402. DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.13418. PMID: 33270987.
Article7. Delsol G, Guiu-Godfrin B, Guiu M, Pris J, Corberand J, Fabre J. 1979; Leukoerythroblastosis and cancer frequency, prognosis, and physiopathologic significance. Cancer. 44:1009–13. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(197909)44:3<1009::AID-CNCR2820440331>3.0.CO;2-J.
Article8. Stachon A, Segbers E, Holland-Letz T, Kempf R, Hering S, Krieg M. 2007; Nucleated red blood cells in the blood of medical intensive care patients indicate increased mortality risk: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care. 11:R62. DOI: 10.1186/cc5932. PMID: 17550592. PMCID: PMC2206423.
Article9. Kim H, Hur M, Kim SW, Moon HW, Yun YM. 2020; Reference intervals for clinically reportable platelet parameters on the Mindray BC-6800Plus hematology analyzer. Clin Chem Lab Med. 58:e213–5. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0020. PMID: 32069230.
Article10. Deng J, Chen Y, Zhang S, Li L, Shi Q, Liu M, et al. 2020; Mindray SF-Cube technology: an effective way for correcting platelet count in individuals with EDTA dependent pseudothrombocytopenia. Clin Chim Acta. 502:99–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.12.012. PMID: 31863740.
Article11. Jo YA, Kim M, Kim HS, Kang HJ, Lee YK. 2013; Evaluation of the Mindray BC-6800 complete blood counts analyzer. Lab Med Online. 3:131–7. DOI: 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.3.131.
Article12. Briggs C, Harrison P, Grant D, Staves J, MacHin SJ. 2000; New quantitative parameters on a recently introduced automated blood cell counter - the XE 2100. Clin Lab Hematol. 22:345–50. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2257.2000.00330.x. PMID: 11318800.13. Clinical, Laboratory Standards Institute. 2014. User verification of precision and estimation of bias; Approved guideline-Third edition. CLSI document EP15-A3. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.14. Clinical, Laboratory Standards Institute. 2010. Validation, verification, and quality assurance of automated hematology analyzers; Approved standard-Second edition. CLSI document H26-A2. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.15. Clinical, Laboratory Standards Institute. 2018. Measurement procedure comparison and bias estimation using patient samples, Third edition. CLSI guideline EP09c. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.16. Clinical, Laboratory Standards Institute. 2007. Reference leukocyte (WBC) differential count (proportional) and evaluation of instrumental method; Approved standard-Second edition. CLSI document H20-A2. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.17. Vis JY, Huisman A. 2016; Verification and quality control of routine hematology analyzers. Int J Lab Hematol. 38(S1):100–9. DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.12503. PMID: 27161194.
Article18. Mukaka MM. 2012; Statistics corner: a guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med J. 24:69–71.19. Nakul-Aquaronne D, Sudaka-Sammarcelli I, Ferro-Vacher C, Starck B, Bayle J. 2003; Evaluation of the Sysmex Xe-2100 hematology analyzer in hospital use. J Clin Lab Anal. 17:113–23. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.10083. PMID: 12784259. PMCID: PMC6807756.20. Takemura H, Ai T, Kimura K, Nagasaka K, Takahashi T, Tsuchiya K, et al. 2018; Evaluation of cell count and classification capabilities in body fluids using a fully automated Sysmex XN equipped with high-sensitive Analysis (hsA) mode and DI-60 hematology analyzer system. PLoS One. 13:e0195923. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195923. PMID: 29698492. PMCID: PMC5919509.
Article21. Lesesve JF, Benbih M, Lecompte T. 2005; Accurate basophils counting: not an easy goal! Clin Lab Hematol. 27:143–4. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.2005.00667.x. PMID: 15784131.
Article22. Amundsen EK, Henriksson CE, Holthe MR, Urdal P. 2012; Is the blood basophil count sufficiently precise, accurate, and specific?: three automated hematology instruments and flow cytometry compared. Am J Clin Pathol. 137:86–92. DOI: 10.1309/AJCP19BFTHYTMORO. PMID: 22180481.
Article23. Kim H, Hur M, Choi SG, Moon HW, Yun YM, Hwang HS, et al. 2013; Evaluation of ABX Pentra DX 120 and Sysmex XE-2100 in umbilical cord blood. Int J Lab Hematol. 35:658–65. DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.12110. PMID: 23738834.
Article24. Shen Y, Cao J, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Shen Y, He J. 2019; Clinical performance evaluation of the new hematology analyzer Mindray BC-6000. Int J Lab Hematol. 41:622–34. DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.13075. PMID: 31286670.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the Automated Hematology Analyzer Sysmex XN-2000 and the Accuracy of Differential Leukocyte Counts Using the Low WBC Mode
- Performance Evaluation of the Beckman Coulter DxH 900 Automated Hematology Analyzer
- Evaluation of the Abbott Cell-Dyn Sapphire Hematology Analyzer
- CELL-DYN Sapphire Hematology Analyzer Performance Evaluation on Leukocyte Differential Counts
- Evaluation of a portable hemoglobin photometer for assessment of intra-operative hemoglobin concentrations