J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Jan;38(3):e21. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e21.
Pediatric Deaths Associated With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Data Analysis Team, Epidemiological Investigation and Analysis Task Force, Central Disease Control Headquarters, Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, Cheongju, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2538373
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e21
Abstract
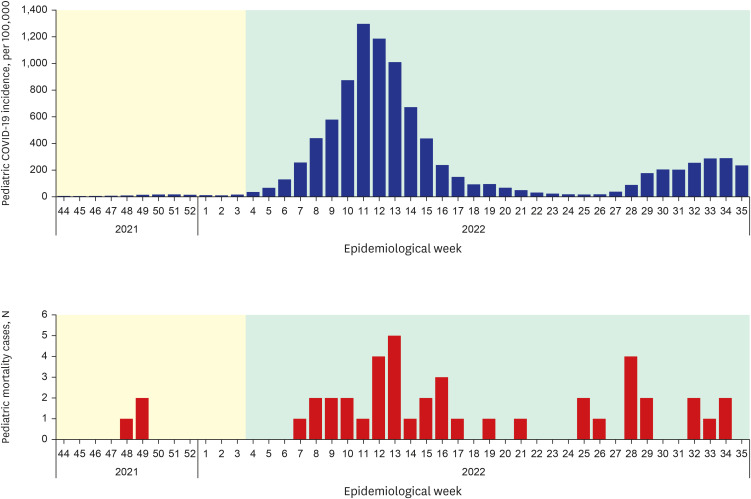
- As of September 3, 2022, 5,388,338 coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases and 46 deaths (3 in 2021 and 43 in 2022) were reported in children ≤ 18 years in Korea. Cumulative confirmed cases accounted for 67.3% of the population aged ≤ 18 years and case fatality rate was 0.85/100,000. Among 46 fatal cases, 58.7% were male and median age was 7 years. Underlying diseases were present in 47.8%; neurologic diseases (63.6%) and malignancy (13.6%) most common. Only four had history of COVID-19 immunization. COVID-19 associated deaths occurred at median 2 days from diagnosis (range: −1 to 21). Among COVID-19 deaths, 41.3% occurred before admission; 2 before hospital arrival and 17 in the emergency department. Among children whose cause was documented, myocarditis, respiratory and multiorgan failure were most common. COVID-19 associated death was seen early after diagnosis in children and public health policies to provide access to medical care for children with COVID-19 are essential during the pandemic.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marks KJ, Whitaker M, Agathis NT, Anglin O, Milucky J, Patel K, et al. Hospitalization of infants and children aged 0-4 years with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 - COVID-NET, 14 states, March 2020-February 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022; 71(11):429–436. PMID: 35298458.2. Shi DS, Whitaker M, Marks KJ, Anglin O, Milucky J, Patel K, et al. Hospitalizations of children aged 5-11 years with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 - COVID-NET, 14 states, March 2020-February 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022; 71(16):574–581. PMID: 35446827.3. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Coronavirus disease 2019. Updated 2022. Accessed September 3, 2022. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en/ .4. Araf Y, Akter F, Tang YD, Fatemi R, Parvez MS, Zheng C, et al. Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines. J Med Virol. 2022; 94(5):1825–1832. PMID: 35023191.5. Gonzalez-Dambrauskas S, Vasquez-Hoyos P, Camporesi A, Cantillano EM, Dallefeld S, Dominguez-Rojas J, et al. Paediatric critical COVID-19 and mortality in a multinational prospective cohort. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022; 12:100272. PMID: 35599855.6. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. COVID-19 vaccination. Revision of COVID-19 vaccination practice standards and related FAQ information (as of Sep. 27, 2022). Updated 2022. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://ncv.kdca.go.kr/ .7. Sigal A, Milo R, Jassat W. Estimating disease severity of omicron and delta SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022; 22(5):267–269. PMID: 35414124.8. Pathak EB, Garcia RB, Menard JM, Salemi JL. Out-of-hospital COVID-19 deaths: consequences for quality of medical care and accuracy of cause of death coding. Am J Public Health. 2021; 111(S2):S101–S106. PMID: 34314208.9. Cho EY, Kim DH, Choi SH, Yun KW, Ahn JG, Cho HK, et al. Statement on healthcare system preparedness in response to COVID-19 omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5 surge in Korea from the Korean Pediatric Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022; 65(11):510–511. PMID: 36229026.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical implications of coronavirus disease 2019 in neonates
- The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and chronic diseases
- Epidemiology, Virology, and Clinical Features of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2; Coronavirus Disease-19)
- Post–Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pulmonary Fibrosis: Wait or Needs Intervention
- Treatment for Immune Thrombocytopenia in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection after COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report