J Korean Diabetes.
2022 Dec;23(4):222-229. 10.4093/jkd.2022.23.4.222.
Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2538091
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2022.23.4.222
Abstract
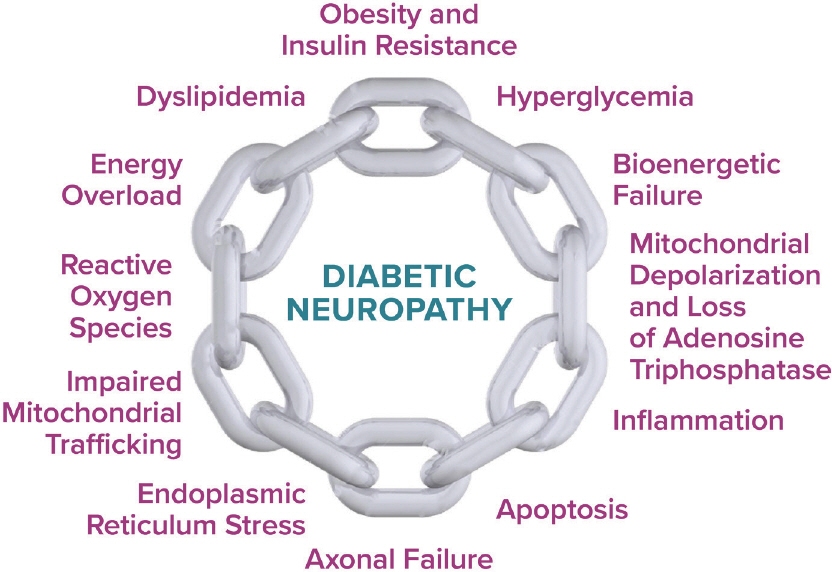
- Diabetic neuropathy is the most common chronic complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), especially, distal symmetric polyneuropathy is the most common form of diabetic neuropathy. Pathogenesis of the DPN is associated with glycemic dysregulation, which results in activation of polyol, aldose reductase, hexosamine, and protein kinase C pathway and leads to downstream inflammation, generation of reactive oxygen species, and decreased blood flow to peripheral nerves. Furthermore, metabolic syndrome components such as obesity, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia result in mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress, eventually contributing to axonal failure and apoptosis of nerve cells. Despite its high prevalence, DPN is still underdiagnosed. Among DPN symptoms, neuropathic pain is challenging to manage, resulting in increased risk of associated problems such as sleep disturbance, reduced quality of life, and socioeconomic consequences. Therefore, early diagnosis and active multidisciplinary treatment of DPN is needed.
Figure
Reference
-
1.Won JC., Kim SS., Ko KS., Cha BY. Current status of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Korea: report of a hospi-tal-based study of type 2 diabetic patients in Korea by the diabetic neuropathy study group of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2014. 38:25–31.2.Moon SS., Kim CH., Kang SM., Kim ES., Oh TJ., Yun JS, et al. Status of diabetic neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort analy-sis (2006 to 2015). Diabetes Metab J. 2021. 45:115–9.
Article3.Dabelea D., Stafford JM., Mayer-Davis EJ., D'Agostino R Jr., Dolan L., Imperatore G, et al. Association of type 1 diabetes vs type 2 diabetes diagnosed during childhood and adolescence with complications during teenage years and young adulthood. JAMA. 2017. 317:825–35.
Article4.Braffett BH., Gubitosi-Klug RA., Albers JW., Feldman EL., Martin CL., White NH, et al. Risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) study. Diabetes. 2020. 69:1000–10.
Article5.Mather KJ., Bebu I., Baker C., Cohen RM., Crandall JP., De-Souza C, et al. Prevalence of microvascular and macrovas-cular disease in the Glycemia Reduction Approaches in Diabetes - A Comparative Effectiveness (GRADE) Study cohort. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020. 165:108235.6.Korean Diabetes Association. Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes. 7th ed.Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2021.7.Pop-Busui R., Ang L., Boulton AJM., Feldman EL., Marcus RL., Mizokami-Stout K, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Arlington: Ameri-can Diabetes Association;2022.8.Vileikyte L., Leventhal H., Gonzalez JS., Peyrot M., Rubin RR., Ulbrecht JS, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and depressive symptoms: the association revisited. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:2378–83.9.Kim SS., Won JC., Kwon HS., Kim CH., Lee JH., Park TS, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: results from a nationwide hospital-based study of diabetic neuropathy in Korea. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014. 103:522–9.
Article10.Kiyani M., Yang Z., Charalambous LT., Adil SM., Lee HJ., Yang S, et al. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Health care costs and complications from 2010 to 2015. Neurol Clin Pract. 2020. 10:47–57.11.Elafros MA., Andersen H., Bennett DL., Savelieff MG., Viswanathan V., Callaghan BC, et al. Towards prevention of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and new treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2022. 21:922–36.
Article12.Feldman EL., Nave KA., Jensen TS., Bennett DLH. New horizons in diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms, bioenergetics, and pain. Neuron. 2017. 93:1296–313.
Article13.Feldman EL., Callaghan BC., Pop-Busui R., Zochodne DW., Wright DE., Bennett DL, et al. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019. 5:42.
Article14.Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001. 414:813–20.15.Tavakoli M., Mojaddidi M., Fadavi H., Malik RA. Patho-physiology and treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2008. 12:192–7.
Article16.Callaghan BC., Little AA., Feldman EL., Hughes RA. En-hanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. 6:CD007543.
Article17.Callaghan BC., Xia R., Banerjee M., de Rekeneire N., Harris TB., Newman AB, et al. Metabolic syndrome components are associated with symptomatic polyneuropathy inde-pendent of glycemic status. Diabetes Care. 2016. 39:801–7.18.Callaghan BC., Xia R., Reynolds E., Banerjee M., Rothberg AE., Burant CF, et al. Association between metabolic syndrome components and polyneuropathy in an obese population. JAMA Neurol. 2016. 73:1468–76.19.Jaiswal M., Fufaa GD., Martin CL., Pop-Busui R., Nelson RG., Feldman EL. Burden of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Pima Indians with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016. 39:e63–4.
Article20.Andersen ST., Witte DR., Dalsgaard EM., Andersen H., Nawroth P., Fleming T, et al. Risk factors for incident diabetic polyneuropathy in a cohort with screen-detected type 2 diabetes followed for 13 years: ADDITION-Den-mark. Diabetes Care. 2018. 41:1068–75.
Article21.Christensen DH., Knudsen ST., Gylfadottir SS., Christensen LB., Nielsen JS., Beck-Nielsen H, et al. Metabolic factors, lifestyle habits, and possible polyneuropathy in early type 2 diabetes: a nationwide study of 5,249 patients in the Danish Centre for Strategic Research in Type 2 Diabetes (DD2) cohort. Diabetes Care. 2020. 43:1266–75.22.Smith S., Normahani P., Lane T., Hohenschurz-Schmidt D., Oliver N., Davies AH. Pathogenesis of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy in diabetes. Life (Basel). 2022. 12:1074.23.Stino AM., Rumora AE., Kim B., Feldman EL. Evolving concepts on the role of dyslipidemia, bioenergetics, and inflammation in the pathogenesis and treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2020. 25:76–84.24.Rumora AE., Savelieff MG., Sakowski SA., Feldman EL. Disorders of mitochondrial dynamics in peripheral neuropathy: clues from hereditary neuropathy and diabetes. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. 145:127–76.25.Callaghan BC., Gallagher G., Fridman V., Feldman EL. diabetic neuropathy: what does the future hold? Diabetolo-gia. 2020. 63:891–7.26.Babetto E., Beirowski B. Stressed axons craving for glial sugar: links to regeneration? Neural Regen Res. 2022. 17:304–6.27.Boulton AJ., Malik RA., Arezzo JC., Sosenko JM. Diabetic somatic neuropathies. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:1458–86.28.Oyibo SO., Prasad YD., Jackson NJ., Jude EB., Boulton AJ. The relationship between blood glucose excursions and painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a pilot study. Diabet Med. 2002. 19:870–3.29.Tesfaye S., Vileikyte L., Rayman G., Sindrup SH., Perkins BA., Baconja M, et al. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: consensus recommendations on diagnosis, assessment and management. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011. 27:629–38.30.Smith S., Normahani P., Lane T., Hohenschurz-Schmidt D., Oliver N., Davies AH. Prevention and management strate-gies for diabetic neuropathy. Life (Basel). 2022. 12:1185.31.Orlando G., Balducci S., Boulton AJM., Degens H., Reeves ND. Neuromuscular dysfunction and exercise training in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a narrative review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022. 183:109183.32.Tatikola SP., Natarajan V., Desai VK., Asirvatham AR., Rajsekhar H. Effect of various exercise protocols on neuropathic pain in individuals with type 2 diabetes with peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-anal-ysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022. 16:102603.33.Lee KA., Jin HY., Lee NY., Kim YJ., Park TS. Effect of em-pagliflozin, a selective sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, on kidney and peripheral nerves in streptozoto-cin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab J. 2018. 42:338–42.34.Iqbal Z., Bashir B., Ferdousi M., Kalteniece A., Alam U., Malik RA, et al. Lipids and peripheral neuropathy. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2021. 32:249–57.35.Ziegler D., Nowak H., Kempler P., Vargha P., Low PA. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2004. 21:114–21.36.Won JC., Kwon HS., Moon SS., Chun SW., Kim CH., Park IB, et al. γ-linolenic acid versus α-lipoic acid for treating painful diabetic neuropathy in adults: a 12-week, dou-ble-placebo, randomized, noninferiority trial. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. 44:542–54.37.Ziegler D., Papanas N., Schnell O., Nguyen BDT., Nguyen KT., Kulkantrakorn K, et al. Current concepts in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. 12:464–75.38.Alam U., Sloan G., Tesfaye S. Treating pain in diabetic neuropathy: current and developmental drugs. Drugs. 2020. 80:363–84.39.Jensen TS., Karlsson P., Gylfadottir SS., Andersen ST., Bennett DL., Tankisi H, et al. Painful and non-painful diabetic neuropathy, diagnostic challenges and implications for future management. Brain. 2021. 144:1632–45.40.Ziegler D., Tesfaye S., Spallone V., Gurieva I., Al Kaabi J., Mankovsky B, et al. Screening, diagnosis and management of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in clinical practice: international expert consensus recommendations. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022. 186:109063.41.D'Souza RS., Barman R., Joseph A., Abd-Elsayed A. Evi-dence-based treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022. 26:583–94.42.Dludla PV., Nkambule BB., Cirilli I., Marcheggiani F., Mabhida SE., Ziqubu K, et al. Capsaicin, its clinical sig-nificance in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. 153:113439.43.Tesfaye S., Sloan G., Petrie J., White D., Bradburn M., Julious S, et al. Comparison of amitriptyline supplemented with pregabalin, pregabalin supplemented with amitriptyline, and duloxetine supplemented with pregabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (OPTION-DM): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2022. 400:680–90. Erratum in: Lancet 2022;400):810.