Neonatal Med.
2022 Nov;29(4):130-134. 10.5385/nm.2022.29.4.130.
A Case of Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex (Dowling-Meara 1 Type) in Newborn
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2536658
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2022.29.4.130
Abstract
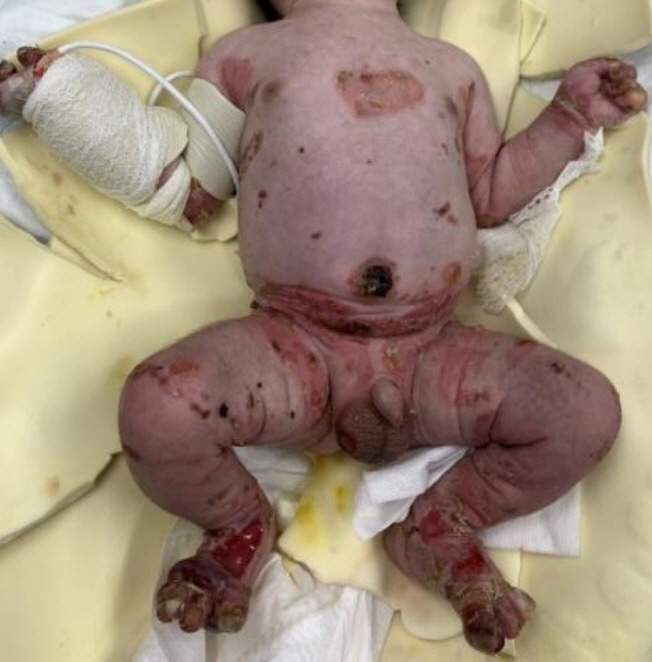
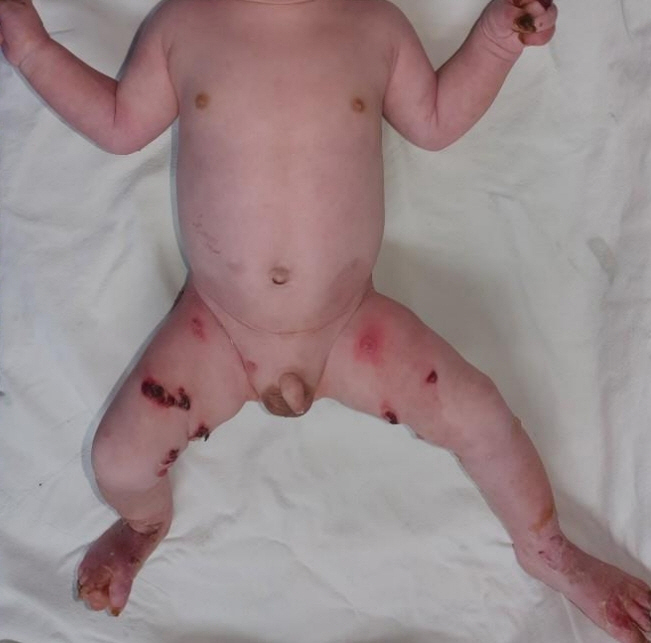
- Epidermolysis bullosa is a rare genetic skin disease in which skin easily peels off and blisters are formed with mild mechanical trauma. It is classified into simple, borderline, dysmorphic, and mixed type. These four subtypes are further classified according to the location of gene mutation and genetic patterns. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS) is characterized by separation in the epidermal or subepidermal layer. And it is mostly caused by mutation of keratin 5 (KRT5) and KRT14 genes. Recently, genetic test has become increasingly important for diagnosis, confirming subtypes and genetic counseling. And there are moderate correlation exists between the EBS phenotype and genotype. Here, we report a case of 2-day-old boy with EBS Dowling-Meara type (EBS-DM) diagnosed by mutation analysis in KRT14.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peterside O, Kunle-Olowu OE, Adeyemi OO, Akinbami FO, Omene J. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: a case report. Niger J Paediatr. 2012; 39:194–6.2. Yasukawa K, Sawamura D, Goto M, Nakamura H, Jung SY, Kim SC, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex in Japanese and Korean patients: genetic studies in 19 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2006; 155:313–7.3. Lim SM, Kim JH, Kim Y, Paik SS, Kim JE, Ko JY, et al. A novel mutation of KRT14 gene in a newborn with epidermolysis bullosa simplex (Dowling-Meara type): case report. Perinatology. 2020; 31:39–43.4. Kang TW, Lee JS, Kim SE, Oh SW, Kim SC. Novel and recurrent mutations in keratin 5 and 14 in Korean patients with epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Dermatol Sci. 2010; 57:90–4.5. Dabas H, Xavier T, Varghese P, Malik S. Management of newborn with epidermolysis bullosa: case report. Ann Clin Case Rep. 2019; 4:1667.6. Sawamura D, Nakano H, Matsuzaki Y. Overview of epidermolysis bullosa. J Dermatol. 2010; 37:214–9.7. Muller FB, Kuster W, Wodecki K, Almeida H Jr, BrucknerTuderman L, Krieg T, et al. Novel and recurrent mutations in keratin KRT5 and KRT14 genes in epidermolysis bullosa simplex: implications for disease phenotype and keratin filament assembly. Hum Mutat. 2006; 27:719–20.8. Gonzalez ME. Evaluation and treatment of the newborn with epidermolysis bullosa. Semin Perinatol. 2013; 37:32–9.9. So JY, Teng J. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex. In : Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, editors. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle: University of Washington, Seattle;1993-2022. [cited 2022 Oct 25]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1369.10. Fallatah BA, Al-shareef OM. Generalized epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Dowling Meara in Saudi family: case report and review of literature, Saudi Arabia 2017-2018. Int J Med Res Prof. 2018; 4:469–71.11. Son MK, Lee TK, Choeh HJ, Choeh KC. A case of pyloric atresia associated with epidermolysis bullosa. Korean J Pediatr. 1996; 39:1015–9.12. Boesen ML, Bygum A, Hertz JM, Zachariassen G. Newborn with severe epidermolysis bullosa: to treat or not to treat? BMJ Case Rep. 2016; 2016:bcr2016214727.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex ( Dowling - Meara Type )
- Two Cases of Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex (Dowling-Meara Type)
- Corrigendum: A Case of Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex (Dowling-Meara 1 Type) in Newborn
- Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (Dowling-Meara type) associated with pyloric atresia and congenital urologic abnormalities
- A Case of Epidermolysis Bullosa Herpetiformis