Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2022;24(2):98-100. 10.14253/acn.2022.24.2.98.
A case of idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis presented with seizures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
- KMID: 2535727
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2022.24.2.98
Abstract
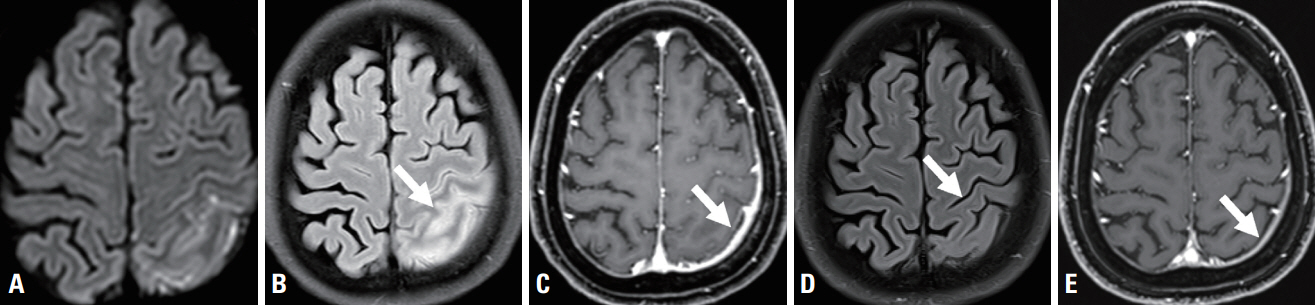
- Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis (IHP) is a rare disease involving localized inflammatory thickening of the intracranial or spinal dura mater without an identified cause. Seizure is a very unusual presentation of IHP. We present a 58-year-old-female patient with seizures caused by IHP. This case indicates that although IHP is rare, it has the potential to cause seizures.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Xiao X, Fu D, Feng L. Hypertrophic pachymeningitis in a southern Chinese population: a retrospective study. Front Neurol. 2020; 11:565088.2. Margoni M, Barbareschi M, Rozzanigo U, Sarubbo S, Chioffi F, Tanel R. Idiopathic hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis as a rare cause of status epilepticus. Neurol Sci. 2019; 40:2193–2195.3. Huang Y, Chen J, Gui L. A case of idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis presenting with chronic headache and multiple cranial nerve palsies: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e7549.4. Choi YJ, Kim SH, Kim JY, Cho YJ, Lee SN, Koo H, et al. A case of idiopathic localized hypertrophic pachymeningitis presented with partial seizures. J Korean Epilepsy Soc. 2004; 8:163–166.5. Jang Y, Lee ST, Jung KH, Chu K, Lee SK. Rituximab treatment for idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. J Clin Neurol. 2017; 13:155–161.6. Kupersmith MJ, Martin V, Heller G, Shah A, Mitnick HJ. Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Neurology. 2004; 62:686–694.7. Scramstad C, Jackson AC. Cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis in critical care patients with seizures. Can J Neurol Sci. 2017; 44:343–349.8. Jia H, Xie X, Qi F, Wang L, Wang L, Che F. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis with simultaneous hypertrophic pachymeningitis in a 68-year-old male: a rare case report. BMC Neurol. 2019; 19:215.9. Navalpotro-Gómez I, Vivanco-Hidalgo RM, Cuadrado-Godia E, Medrano-Martorell S, Alameda-Quitllet F, Villalba-Martínez G, et al. Focal status epilepticus as a manifestation of idiopathic hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis. J Neurol Sci. 2016; 367:232–236.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Hypertrophic Cranial Pachymeningitis: Case Report
- Rapid Recurrence of Spinal Idiopathic Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis: A Case Report
- An Idiopathic Hypertrophic Tentorial Pachymeningitis Presented as an Alternating Recurrent Painful Ophthalmoplegia
- A Case of Idiopathic Localized Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis Presented with Partial Seizures
- IgG4-Related Intracranial Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis : A Case Report and Review of the Literature