J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2022 Oct;39(4):309-313. 10.12701/jyms.2022.00318.
Effects of early clinical and basic laboratory exposure program on premedical students: a questionnaire survey
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Center for Medical Education, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Hematology-Oncology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 5Department of Family Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 7Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2534658
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00318
Abstract
- Background
Because premed students do not take courses related to medicine during their first 2 years, they cannot establish their identity as students at medical schools, making it difficult for them to set goals as future doctors. We conducted an early clinical and basic laboratory exposure program for premed students and studied the effects of the program and student satisfaction levels.
Methods
We performed an early clinical and basic laboratory exposure program for premed students for 2 days and evaluated the effects of the program and student satisfaction with it. The program consisted of two types: type 1, where two to four students formed a group, which was assigned to a particular department to participate and make observations during ward rounds, outpatient clinics, examinations, procedures, and surgeries (in the case of basic laboratory work, the students partook in experimental observations); and type 2, where one student followed a medical school professor to observe the professor’s day. After the program ended, an online survey was conducted to investigate the effects on students, their thoughts, and satisfaction levels.
Results
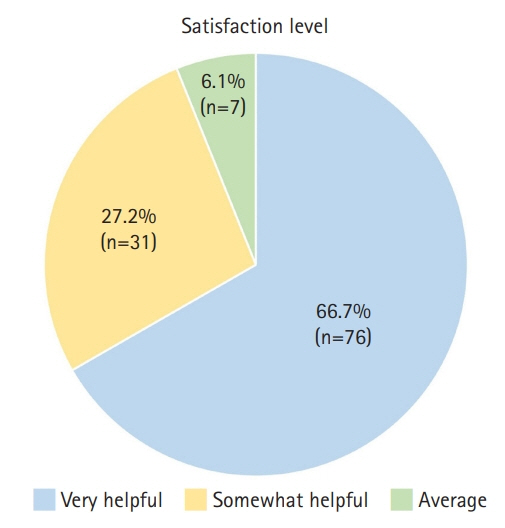
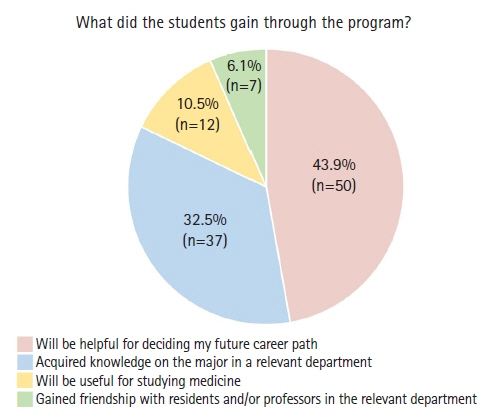
In total, 114 students (91.2%) responded to the survey. Approximately 94% of them were satisfied with the program. They found that the program would be useful for deciding on future career paths, gaining knowledge about a department of interest, studying for a medical program after premedical studies, and befriending residents and professors in certain departments.
Conclusion
Early clinical and basic laboratory exposure programs are recommended for premedical students.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Gross JP, Mommaerts CD, Earl D, De Vries RG. Perspective: after a century of criticizing premedical education, are we missing the point? Acad Med. 2008; 83:516–20.
Article2. Başak O, Yaphe J, Spiegel W, Wilm S, Carelli F, Metsemakers JF. Early clinical exposure in medical curricula across Europe: an overview. Eur J Gen Pract. 2009; 15:4–10.
Article3. Chang CC, Huang HC, Lee WS, Chuang CL, Huang LJ, Lu DY, et al. Early clinical exposure improves medical students' recognition of the need for professionalism and interprofessional collaboration. J Chin Med Assoc. 2021; 84:778–82.
Article4. Davis JM, Anderson MC, Stankevitz KA, Manley AR. Providing premedical students with quality clinical and research experience: the Tobacco Science Scholars Program. WMJ. 2013; 112:195–8.5. Tang KP, Chen CY, Wu MS, Chen TT, Wu BW, Tsai PF. Correlation between early clinical exposure environment, attitudes toward basic medicine, and medical students’ basic science learning performance. BMC Med Educ. 2019; 19:183.
Article6. Franklin G, Martin C, Ruszaj M, Matin M, Kataria A, Hu J, et al. How the COVID-19 pandemic impacted medical education during the last year of medical school: a class survey. Life (Basel). 2021; 11:294.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Computer Skills in Second Year Premedical Students for Medical Informatics Curriculum
- Are Medical Students Satisfied with Their Medical Professionalism Education?
- What We Learned from the Experience of an Introduction to Surgery Class for First Grade Premedical Students
- Premedical Curriculum at Chonnam National University Medical School
- Evaluation of critical thinking course for premedical students using literature and film