J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Sep;37(37):e287. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e287.
Assay Sensitivity Difference Can Induce Anti-Hepatitis A Virus IgM Non-Reactive But Total (IgM and IgG) Reactive Results in Early Acute Hepatitis A
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533560
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e287
Abstract
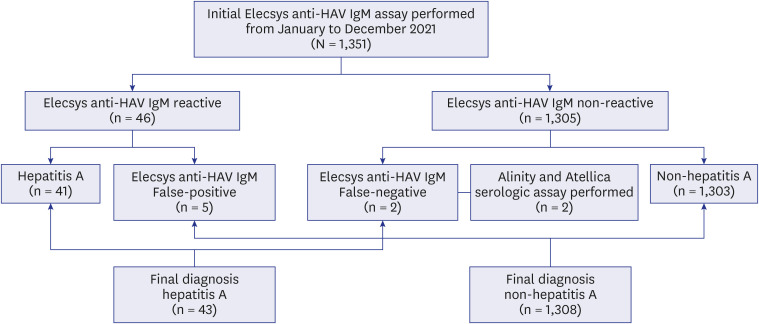
- Although anti-hepatitis A virus (HAV) IgM non-reactive and anti-HAV total (immunoglobulin [Ig] M and IgG) reactive results are generally interpreted as immunity to HAV, some early acute hepatitis A patients show the same results. We compared IgM detection sensitivity between anti-HAV IgM and anti-HAV total assays. Acute hepatitis A patients’ samples were serially diluted and tested with Elecsys anti-HAV IgM and total assay (Roche Diagnostics). This resulted in anti-HAV IgM non-reactive but anti-HAV total reactive results. Samples of two hepatitis A patients showing false-negative anti-HAV IgM at initial presentation were analyzed with Elecsys, Atellica (Siemens Healthineers), and Alinity (Abbott Laboratories) HAV assays. Elecsys, Atellica, and Alinity anti-HAV IgM converted reactive on hospital day 3, whereas Elecsys and Atellica anti-HAV total results were reactive from hospital day 1. The anti-HAV total assay had higher sensitivity in detecting IgM antibodies than the anti-HAV IgM assay.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wang Z, Chen Y, Xie S, Lv H. Changing epidemiological characteristics of hepatitis A in Zhejiang province, China: increased susceptibility in adults. PLoS One. 2016; 11(4):e0153804. PMID: 27093614.
Article2. Martin A, Lemon SM. Hepatitis A virus: from discovery to vaccines. Hepatology. 2006; 43(2):Suppl 1. S164–S172. PMID: 16447259.
Article3. Lee WM, Squires RH Jr, Nyberg SL, Doo E, Hoofnagle JH. Acute liver failure: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008; 47(4):1401–1415. PMID: 18318440.
Article4. Kang SH, Kim MY, Baik SK. Perspectives on acute hepatitis A control in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34(36):e230. PMID: 31538417.
Article5. Kwon SY, Park SH, Yeon JE, Jeong SH, Kwon OS, Lee JW, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of acute hepatitis a in Korea: a nationwide multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29(2):248–253. PMID: 24550653.
Article6. Seo JY, Choi BY, Ki M, Jang HL, Park HS, Son HJ, et al. Risk factors for acute hepatitis A infection in Korea in 2007 and 2009: a case-control study. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28(6):908–914. PMID: 23772157.
Article7. Matheny SC, Kingery JE. Hepatitis A. Am Fam Physician. 2012; 86(11):1027–1034. PMID: 23198670.8. Newsome PN, Cramb R, Davison SM, Dillon JF, Foulerton M, Godfrey EM, et al. Guidelines on the management of abnormal liver blood tests. Gut. 2018; 67(1):6–19. PMID: 29122851.
Article9. Tong MJ, el-Farra NS, Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995; 171(Suppl 1):S15–S18. PMID: 7876641.
Article10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Evaluation of Detection Capability for Clinical Laboratory Measurement Procedures. CLSI Document EP17-A2. Wayne, PA: CLSI;2012.11. 510(k) Substantial equivalence determination decision summary. Accessed February 8, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/k093955.pdf .12. Hyun JJ, Seo YS, An H, Yim SY, Seo MH, Kim HS, et al. Optimal time for repeating the IgM anti-hepatitis A virus antibody test in acute hepatitis A patients with a negative initial test. Korean J Hepatol. 2012; 18(1):56–62. PMID: 22511904.
Article13. Shin HP, Lee JI, Jung SW, Cha JM, Joo KR, Kang SY. Factors for predicting positive results for anti-HAV IgM retesting among initially seronegative patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55(12):3537–3540. PMID: 20108041.
Article14. Lee HK, Kim KA, Lee JS, Kim NH, Bae WK, Song TJ. Window period of anti-hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M antibodies in diagnosing acute hepatitis A. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 25(6):665–668. PMID: 23325281.
Article15. Pondé RA. The serological markers of acute infection with hepatitis A, B, C, D, E and G viruses revisited. Arch Virol. 2017; 162(12):3587–3602. PMID: 28884240.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cross-Reactivity of Disease-Specific Antibody Assays for the Detection of Current Infections: With Potentially Interfering Substances of Other Infections
- Viral Serologic Markers in Patients with Acute and Chronic Liver Diseases
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- The changing patterns of acute hepatitis B infection in Korea in the early 2000's
- The etiology of acute viral hepatitis for the last 3 years at a single institution in Seoul