Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2022 Jul;10(3):151-157. 10.14791/btrt.2022.0017.
Local Drug Delivery Strategies for Glioblastoma Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Seoul, Korea
- 2School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Materials Science and Engineering, College of Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2532247
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2022.0017
Abstract
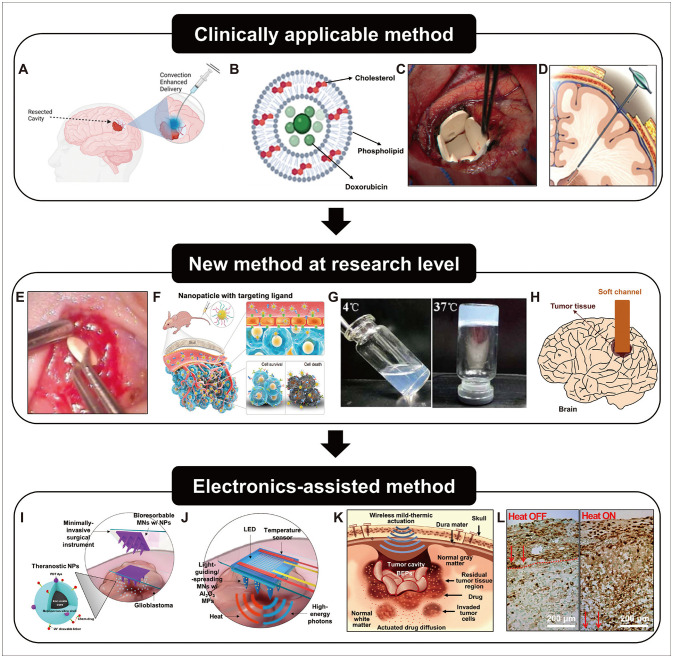
- Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a brain tumor notorious for its malignancy. The key reason for the limited efficacy of standard treatment is the high recurrence rate of GBM, even after surgical resection. Hence, intensive postsurgical chemical therapies, such as the systemic delivery of various drugs and/ or drug combinations, are typically followed after surgery. However, overcoming the blood-brain barrier by systemic administration to efficiently deliver drugs to the brain tumor remains a daunting goal. Therefore, various local drug delivery methods showing potential for improved therapeutic efficacy have been proposed. In particular, the recent application of electronic devices for the controlled delivery of chemotherapy drugs to GBM tissue has attracted attention. We herein review the recent progress of local drug delivery strategies, including electronics-assisted strategies, at the research and commercial level. We also present a brief discussion of the unsolved challenges and future research direction of localized chemotherapy methods for GBM.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Preclinical Study on Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stem Cells after Local Transplantation into the Brain
Narayan Bashyal, Min Gyeong Kim, Jin-Hwa Jung, Rakshya Acharya, Young Jun Lee, Woo Sup Hwang, Jung-Mi Choi, Da-Young Chang, Sung-Soo Kim, Haeyoung Suh-Kim
Int J Stem Cells. 2023;16(4):415-424. doi: 10.15283/ijsc23062.
Reference
-
1. Das M. Iniparib for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Lancet Oncol. 2018; 19:e514. PMID: 30177496.2. Tran B, Rosenthal MA. Survival comparison between glioblastoma multiforme and other incurable cancers. J Clin Neurosci. 2010; 17:417–421. PMID: 20167494.3. Holland EC. Glioblastoma multiforme: the terminator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97:6242–6244. PMID: 10841526.4. Das S, Marsden PA. Angiogenesis in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:1561–1563. PMID: 24131182.5. Komotar RJ, Otten ML, Moise G, Connolly ES Jr. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma—a critical review. Clin Med Oncol. 2008; 2:421–422. PMID: 21892310.6. Ganipineni LP, Danhier F, Préat V. Drug delivery challenges and future of chemotherapeutic nanomedicine for glioblastoma treatment. J Control Release. 2018; 281:42–57. PMID: 29753958.7. Jung E, Osswald M, Ratliff M, Dogan H, Xie R, Weil S, et al. Tumor cell plasticity, heterogeneity, and resistance in crucial microenvironmental niches in glioma. Nat Commun. 2021; 12:1014. PMID: 33579922.8. Dirkse A, Golebiewska A, Buder T, Nazarov PV, Muller A, Poovathingal S, et al. Stem cell-associated heterogeneity in glioblastoma results from intrinsic tumor plasticity shaped by the microenvironment. Nat Commun. 2019; 10:1787. PMID: 30992437.9. Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006; 7:41–53. PMID: 16371949.10. Cha GD, Kang T, Baik S, Kim D, Choi SH, Hyeon T, et al. Advances in drug delivery technology for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. J Control Release. 2020; 328:350–367. PMID: 32896613.11. Xue J, Zhao Z, Zhang L, Xue L, Shen S, Wen Y, et al. Neutrophil-mediated anticancer drug delivery for suppression of postoperative malignant glioma recurrence. Nat Nanotechnol. 2017; 12:692–700. PMID: 28650441.12. Wilhelm S, Tavares A, Dai Q, Ohta S, Audet J, Dvorak HF, et al. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat Rev Mater. 2016; 1:16014.13. Ruan S, Hu C, Tang X, Cun X, Xiao W, Shi K, et al. Increased gold nanoparticle retention in brain tumors by in situ enzyme-induced aggregation. ACS Nano. 2016; 10:10086–10098. PMID: 27934068.14. Shen Z, Liu T, Li Y, Lau J, Yang Z, Fan W, et al. Fenton-reaction-acceleratable magnetic nanoparticles for ferroptosis therapy of orthotopic brain tumors. ACS Nano. 2018; 12:11355–11365. PMID: 30375848.15. Wen L, Wang K, Zhang F, Tan Y, Shang X, Zhu Y, et al. AKT activation by SC79 to transiently re-open pathological blood brain barrier for improved functionalized nanoparticles therapy of glioblastoma. Biomaterials. 2020; 237:119793. PMID: 32044521.16. Alli S, Figueiredo CA, Golbourn B, Sabha N, Wu MY, Bondoc A, et al. Brainstem blood brain barrier disruption using focused ultrasound: a demonstration of feasibility and enhanced doxorubicin delivery. J Control Release. 2018; 281:29–41. PMID: 29753957.17. Nam L, Coll C, Erthal LCS, de la Torre C, Serrano D, Martínez-Máñez R, et al. Drug delivery nanosystems for the localized treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Materials (Basel). 2018; 11:779.18. Jain KK. A critical overview of targeted therapies for glioblastoma. Front Oncol. 2018; 8:419. PMID: 30374421.19. Nance E, Zhang C, Shih TY, Xu Q, Schuster BS, Hanes J. Brain-penetrating nanoparticles improve paclitaxel efficacy in malignant glioma following local administration. ACS Nano. 2014; 8:10655–10664. PMID: 25259648.20. Kim DG, Kim KH, Seo YJ, Yang H, Marcusson EG, Son E, et al. Anti-miR delivery strategies to bypass the blood-brain barrier in glioblastoma therapy. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:29400–29411. PMID: 27102443.21. Zhang C, Nance EA, Mastorakos P, Chisholm J, Berry S, Eberhart C, et al. Convection enhanced delivery of cisplatin-loaded brain penetrating nanoparticles cures malignant glioma in rats. J Control Release. 2017; 263:112–119. PMID: 28279797.22. Stephen ZR, Kievit FM, Veiseh O, Chiarelli PA, Fang C, Wang K, et al. Redox-responsive magnetic nanoparticle for targeted convection-enhanced delivery of O6-benzylguanine to brain tumors. ACS Nano. 2014; 8:10383–10395. PMID: 25247850.23. Han D, Serra R, Gorelick N, Fatima U, Eberhart CG, Brem H, et al. Multi-layered core-sheath fiber membranes for controlled drug release in the local treatment of brain tumor. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:17936. PMID: 31784666.24. Colen RR, Zinn PO, Hazany S, Do-Dai D, Wu JK, Yao K, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging appearance and changes on intracavitary Gliadel wafer placement: a pilot study. World J Radiol. 2011; 3:266–272. PMID: 22132297.25. van Solinge TS, Nieland L, Chiocca EA, Broekman MLD. Advances in local therapy for glioblastoma - taking the fight to the tumour. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022; 18:221–236. PMID: 35277681.26. Lee WH, Cha GD, Kim DH. Flexible and biodegradable electronic implants for diagnosis and treatment of brain diseases. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021; 72:13–21. PMID: 34425329.27. Sunwoo SH, Han SI, Joo H, Cha GD, Kim D, Choi SH, et al. Advances in soft bioelectronics for brain research and clinical neuroengineering. Matter. 2020; 3:1923–1947.28. Joo H, Lee Y, Kim J, Yoo JS, Yoo S, Kim S, et al. Soft implantable drug delivery device integrated wirelessly with wearable devices to treat fatal seizures. Sci Adv. 2021; 7:eabd4639. PMID: 33523849.29. Koo JH, Song JK, Kim DH, Son D. Soft implantable bioelectronics. ACS Mater Lett. 2021; 3:1528–1540.30. Cho KW, Sunwoo SH, Hong YJ, Koo JH, Kim JH, Baik S, et al. Soft bioelectronics based on nanomaterials. Chem Rev. 2022; 122:5068–5143. PMID: 34962131.31. Koo JH, Song JK, Yoo S, Sunwoo SH, Son D, Kim DH. Unconventional device and material approaches for monolithic biointegration of implantable sensors and wearable electronics. Adv Mater Technol. 2020; 5:202000407.32. Yoo S, Lee J, Joo H, Sunwoo SH, Kim S, Kim DH. Wireless power transfer and telemetry for implantable bioelectronics. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021; 10:2100614.33. Sunwoo SH, Ha KH, Lee S, Lu N, Kim DH. Wearable and implantable soft bioelectronics: device designs and material strategies. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2021; 12:359–391. PMID: 34097846.34. Lesniak MS, Brem H. Targeted therapy for brain tumours. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004; 3:499–508. PMID: 15173839.35. Mathios D, Kim JE, Mangraviti A, Phallen J, Park CK, Jackson CM, et al. Anti-PD-1 antitumor immunity is enhanced by local and abrogated by systemic chemotherapy in GBM. Sci Transl Med. 2016; 8:370ra180.36. Allard E, Passirani C, Benoit JP. Convection-enhanced delivery of nanocarriers for the treatment of brain tumors. Biomaterials. 2009; 30:2302–2318. PMID: 19168213.37. Wang Y, Jiang Y, Wei D, Singh P, Yu Y, Lee T, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated convection-enhanced delivery of a DNA intercalator to gliomas circumvents temozolomide resistance. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021; 5:1048–1058. PMID: 34045730.38. Pena ES, Graham-Gurysh EG, Bachelder EM, Ainslie KM. Design of biopolymer-based interstitial therapies for the treatment of glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22:13160. PMID: 34884965.39. Engelberth SA, Hempel N, Bergkvist M. Development of nanoscale approaches for ovarian cancer therapeutics and diagnostics. Crit Rev Oncog. 2014; 19:281–315. PMID: 25271436.40. Ibrahim M, Abuwatfa WH, Awad NS, Sabouni R, Husseini GA. Encapsulation, release, and cytotoxicity of doxorubicin loaded in liposomes, micelles, and metal-organic frameworks: a review. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14:254. PMID: 35213987.41. Westphal M, Hilt DC, Bortey E, Delavault P, Olivares R, Warnke PC, et al. A phase 3 trial of local chemotherapy with biodegradable carmustine (BCNU) wafers (Gliadel wafers) in patients with primary malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2003; 5:79–88. PMID: 12672279.42. Kleinberg L. Polifeprosan 20, 3.85% carmustine slow release wafer in malignant glioma: patient selection and perspectives on a low-burden therapy. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016; 10:2397–2406. PMID: 27920506.43. Lau D, Rowland N, Devasagaya S, McDermott MW. Recession of Ommaya Reservoir improves cosmesis in patients undergoing intrathecal chemotherapy for leptomeningeal disease: a technical note. Cureus. 2012; 4:e66.44. Magill ST, Choy W, Nguyen MP, McDermott MW. Ommaya reservoir insertion: a technical note. Cureus. 2020; 12:e7731. PMID: 32432009.45. Szvalb AD, Raad II, Weinberg JS, Suki D, Mayer R, Viola GM. Ommaya reservoir-related infections: clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes. J Infect. 2014; 68:216–224. PMID: 24360921.46. Bastiancich C, Bozzato E, Luyten U, Danhier F, Bastiat G, Préat V. Drug combination using an injectable nanomedicine hydrogel for glioblastoma treatment. Int J Pharm. 2019; 559:220–227. PMID: 30703501.47. Zhang J, Chen C, Li A, Jing W, Sun P, Huang X, et al. Immunostimulant hydrogel for the inhibition of malignant glioma relapse post-resection. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16:538–548. PMID: 33526838.48. Ramachandran R, Junnuthula VR, Gowd GS, Ashokan A, Thomas J, Peethambaran R, et al. Theranostic 3-dimensional nano brain-implant for prolonged and localized treatment of recurrent glioma. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:43271. PMID: 28262735.49. Di Mascolo D, Palange AL, Primavera R, Macchi F, Catelani T, Piccardi F, et al. Conformable hierarchically engineered polymeric micromeshes enabling combinatorial therapies in brain tumours. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16:820–829. PMID: 33795849.50. Meng X, Zhao Y, Han B, Zha C, Zhang Y, Li Z, et al. Dual functionalized brain-targeting nanoinhibitors restrain temozolomide-resistant glioma via attenuating EGFR and MET signaling pathways. Nat Commun. 2020; 11:594. PMID: 32001707.51. Bastiancich C, Bianco J, Vanvarenberg K, Ucakar B, Joudiou N, Gallez B, et al. Injectable nanomedicine hydrogel for local chemotherapy of glioblastoma after surgical resection. J Control Release. 2017; 264:45–54. PMID: 28830791.52. Shi K, Wang YL, Qu Y, Liao JF, Chu BY, Zhang HP, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and application of reversible PDLLA-PEG-PDLLA copolymer thermogels in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:19077. PMID: 26752008.53. Cha GD, Lee WH, Sunwoo SH, Kang D, Kang T, Cho KW, et al. Multifunctional injectable hydrogel for in vivo diagnostic and therapeutic applications. ACS Nano. 2022; 16:554–567.54. Cha GD, Lee WH, Lim C, Choi MK, Kim DH. Materials engineering, processing, and device application of hydrogel nanocomposites. Nanoscale. 2020; 12:10456–10473. PMID: 32388540.55. Jain A, Betancur M, Patel GD, Valmikinathan CM, Mukhatyar VJ, Vakharia A, et al. Guiding intracortical brain tumour cells to an extracortical cytotoxic hydrogel using aligned polymeric nanofibres. Nat Mater. 2014; 13:308–316. PMID: 24531400.56. Cha GD, Kang D, Lee J, Kim DH. Bioresorbable electronic implants: history, materials, fabrication, devices, and clinical applications. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019; 8:1801660.57. Lee Y, Kang T, Cho HR, Lee GJ, Park OK, Kim S, et al. Localized delivery of theranostic nanoparticles and high-energy photons using microneedles-on-bioelectronics. Adv Mater. 2021; 33:2100425.58. Lee J, Cho HR, Cha GD, Seo H, Lee S, Park CK, et al. Flexible, sticky, and biodegradable wireless device for drug delivery to brain tumors. Nat Commun. 2019; 10:5205. PMID: 31729383.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metastatic Glioblastoma in Cervical Lymph Node after Repeated Craniotomies: Report of a Case with Diagnosis by Fine Needle Aspiration
- Glioblastoma in a Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Congenital Cerebral Glioblastoma Multiforme
- Extensive Pachymeningeal Dissemination of Glioblastoma Mimicking Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Case Report
- Implantable Devices for Sustained, Intravesical Drug Delivery