Cancer Res Treat.
2022 Jul;54(3):737-743. 10.4143/crt.2021.773.
Histologic Changes in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer under Various Treatments: A Comparison of Histology and Mutation Status in Serial Samples
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 3Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 5Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea
- 6Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular surgery, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 7Department of Biochemistry, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- KMID: 2531320
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2021.773
Abstract
- Purpose
Histologic change is a resistant mechanism in lung cancer. The most common histological change is the switch from adenocarcinoma (AdenoCa) to small cell carcinoma (SCC) against to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). However, it is not clear whether other treatment modalities are involved in the histologic changes.
Materials and Methods
We investigated histological changes in eight cases, after various treatments, and compared the molecular profiles between primary tumors and changed tumors using exome sequencing where tissue was available.
Results
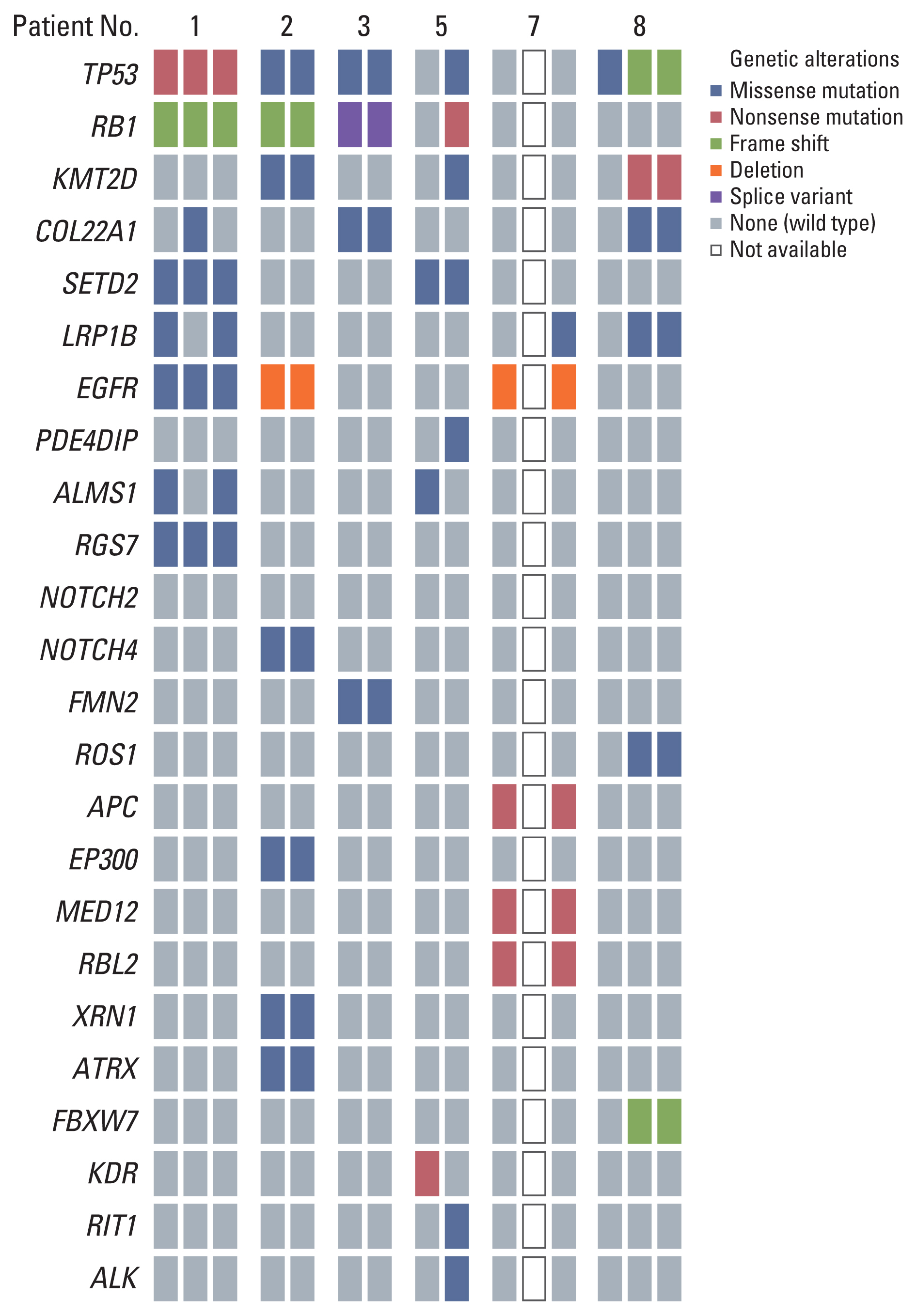
Three cases of AdenoCa that were changed into SCC retained the initial mutations after TKI and/or surgical treatment. After treatment with TKI and immunotherapy, an EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor)-mutant AdenoCa changed to squamous cell carcinoma (SqCa). SqCa in a patient treated with surgery was changed into combined AdenoCa and SqCa. These two cases showed the same genetic variations between the two distinct non–small cell carcinomas (NSCC). Three patients experienced two histologic changes, which the changed tumors returned to its original subtype or changed to a combined tumor after treatments. Four cases showed combined histology in the first or second change.
Conclusion
The histology of NSCC can be changed to a single pattern or combined subtypes after various treatment modalities, and the phenotypic changes seem not fixed. Therefore, additional morphologic changes may occur regardless of their genetic status and types of treatments. To refine the new treatment strategy, consecutive repeated biopsies in progressive disease or recurrent tumor are necessary.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Park S, Ku BM, Jung HA, Sun JM, Ahn JS, Lee SH, et al. EGFR C797S as a resistance mechanism of lazertinib in non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR T790M mutation. Cancer Res Treat. 2020; 52:1288–90.2. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:947–57.
Article3. Norkowski E, Ghigna MR, Lacroix L, Le Chevalier T, Fadel E, Dartevelle P, et al. Small-cell carcinoma in the setting of pulmonary adenocarcinoma: new insights in the era of molecular pathology. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:1265–71.
Article4. Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med. 2011; 3:75ra26.
Article5. Alam N, Gustafson KS, Ladanyi M, Zakowski MF, Kapoor A, Truskinovsky AM, et al. Small-cell carcinoma with an epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in a never-smoker with gefitinib-responsive adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Lung Cancer. 2010; 11:E1–4.
Article6. Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Poirier JT, Mermel CH, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, et al. RB loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:6377.
Article7. Lee JK, Lee J, Kim S, Kim S, Youk J, Park S, et al. Clonal history and genetic rredictors of transformation Into small-cell carcinomas from lung adenocarcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:3065–74.8. Quintanal-Villalonga A, Chan JM, Yu HA, Pe’er D, Sawyers CL, Sen T, et al. Lineage plasticity in cancer: a shared pathway of therapeutic resistance. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020; 17:360–71.
Article9. Offin M, Chan JM, Tenet M, Rizvi HA, Shen R, Riely GJ, et al. Concurrent RB1 and TP53 alterations define a subset of EGFR-mutant lung cancers at risk for histologic transformation and inferior clinical outcomes. J Thorac Oncol. 2019; 14:1784–93.10. Fukui T, Tsuta K, Furuta K, Watanabe S, Asamura H, Ohe Y, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status and clinicopathological features of combined small cell carcinoma with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer Sci. 2007; 98:1714–9.
Article11. Levin PA, Mayer M, Hoskin S, Sailors J, Oliver DH, Gerber DE. Histologic transformation from adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma as a mechanism of resistance to EGFR inhibition. J Thorac Oncol. 2015; 10:e86–8.
Article12. Hsieh MS, Jhuang JY, Hua SF, Chou YH. Histologic evolution from adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma after gefitinib treatment. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015; 99:316–9.
Article13. Hsu CL, Chen KY, Kuo SW, Chang YL. Histologic transformation in a patient with lung cancer treated with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:e75–6.
Article14. Fujita S, Masago K, Katakami N, Yatabe Y. Transformation to SCLC after treatment with the ALK inhibitor alectinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2016; 11:e67–72.
Article15. Shinohara S, Ichiki Y, Fukuichi Y, Honda Y, Kanayama M, Taira A, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma transformation from adenocarcinoma as an acquired resistance after the EGFR TKI therapy in (EGFR-mutated) non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2018; 10:E526–31.
Article16. Yao Y, Zhu Z, Wu Y, Chai Y. Histologic transformation from adenocarcinoma to both small cell lung cancer and squamous cell carcinoma after treatment with gefitinib: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e0650.17. Lu H, Chen B, Qin J, Xie F, Han N, Huang Z. Transformation to small-cell lung cancer following treatment with icotinib in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15:5799–802.
Article18. Lawson DA, Kessenbrock K, Davis RT, Pervolarakis N, Werb Z. Tumour heterogeneity and metastasis at single-cell resolution. Nat Cell Biol. 2018; 20:1349–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Biopsy and Mutation Detection Strategies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Comprison of p53 Mutation in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer between Young patients and Old Patients
- Alterations of the Apoptosis Genes and Their Products in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Tissues
- A Case of Early Gastric Cancer Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Detection of EGFR and KRAS Mutation by Pyrosequencing Analysis in Cytologic Samples of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer