J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2022 Jun;26(2):84-87. 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.2.84.
The Efficacy of Three-Dimensional Sweeping Mode Extracorporeal Shockwave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Medical Device Engineering and Management, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2530488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.2.84
Abstract
- Purpose
This was a pilot study to examine the clinical usefulness of the newly developed three-dimensional sweep mode extracorporeal shockwave treatment (ESWT) in patients with plantar fasciitis.
Materials and Methods
Three-dimensional sweep mode ESWT was performed once a week for 5 weeks in patients with plantar fasciitis who showed no improvement with the conventional conservative treatment. A 100-mm visual analogue scale (VAS) reading for pain from walking and at rest after walking were collected before the treatment and 8 and 16 weeks after the initial treatment. In addition, the Foot and Ankle Outcome Score (FAOS) and EuroQol-5-dimension (EQ-5D) scores before and 16 weeks after the treatment were evaluated.
Results
VAS for pain for walking improved from 50.60±8.38 to 19.80±15.61 at 8 weeks after the initial treatment (p=0.008) and 9.80±9.62 at 16 weeks after the treatment (p<0.001). VAS for pain at rest after walking improved from 36.60±19.55 to 11.80±12.95 at 8 weeks after the initial treatment (p=0.052) and 8.80±8.87 at 16 weeks after the treatment (p=0.024). Preoperative FAOS increased from an average of 74.80±9.73 before the treatment to an average of 81.00±8.86 at week 16 after the procedure (p=0.49) and compared to pre-treatment levels, there was a decrease of one level in the anxiety/depression domain of the EQ-5D, post-treatment.
Conclusion
The results of this preliminary study confirmed that the newly developed EWST with the smart forging sweep mode was effective in improving pain and function in plantar fasciitis.
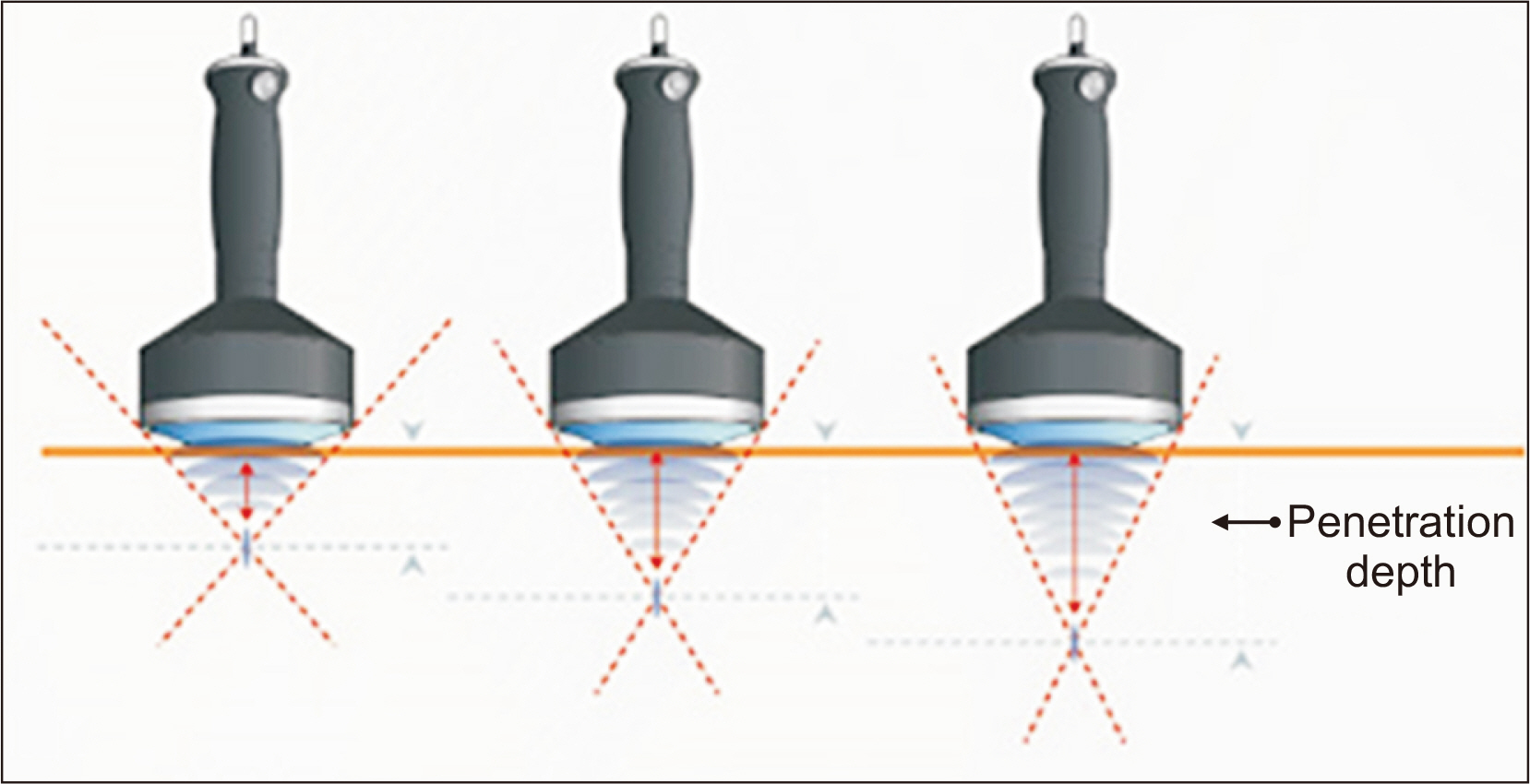
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim BS, Lee KB, Choi J, Park YB, Baik LB. 2006; Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) in patients with chronic proximal plantar fasciitis. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 10:163–7. DOI: 10.1177/107110070302401103. PMID: 11991475.2. Eun IS. 2016; The diagnosis and treatment of plantar fasciitis. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 20:93–9. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2016.20.3.93. DOI: 10.14193/jkfas.2016.20.3.93.
Article3. Choi WJ, Lee JW, Kwak YH. 2007; Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of refractory plantar fasciitis. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 11:51–6.4. Yum JK, Ahn SJ. 2018; Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 53:400–6. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.5.400. DOI: 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.5.400. PMID: 22433113. PMCID: PMC3342893.
Article5. Kim SB, Lee KW, Lee JH, Kim YD, Yoon K, Joe YL. 2009; The effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in plantar fasciitis. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 33:333–8.6. Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, Weng LH, Ko JY. 2006; Long-term results of extracorporeal shockwave treatment for plantar fasciitis. Am J Sports Med. 34:592–6. doi: 10.1177/0363546505281811. DOI: 10.1177/0363546505281811. PMID: 16556754.
Article7. Lohrer H, Nauck T, Dorn-Lange NV, Schöll J, Vester JC. 2010; Comparison of radial versus focused extracorporeal shock waves in plantar fasciitis using functional measures. Foot Ankle Int. 31:1–9. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0001. DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0001. PMID: 20067715.
Article8. Kudo P, Dainty K, Clarfield M, Coughlin L, Lavoie P, Lebrun C. 2006; Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial evaluating the treatment of plantar fasciitis with an extracoporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) device: a North American confirmatory study. J Orthop Res. 24:115–23. doi: 10.1002/jor.20008. DOI: 10.1002/jor.20008. PMID: 16435344.
Article9. Roos EM, Brandsson S, Karlsson J. 2001; Validation of the foot and ankle outcome score for ankle ligament reconstruction. Foot Ankle Int. 22:788–94. doi: 10.1177/107110070102201004. DOI: 10.1177/107110070102201004. PMID: 11642530.
Article10. EuroQol Group. 1990; EuroQol--a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy. 16:199–208. doi: 10.1016/0168-8510(90)90421-9. DOI: 10.1016/0168-8510(90)90421-9. PMID: 10109801.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Refractory Plantar Fasciitis
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Musculoskeletal Disorders
- The Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Plantar Fasciitis
- Dose-Related Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis