Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2021 Dec;26(4):237-241. 10.6065/apem.2142242.121.
History of insulin treatment of pediatric patients with diabetes in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 4Korea International Cooperation Agency, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2523829
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2142242.121
Abstract
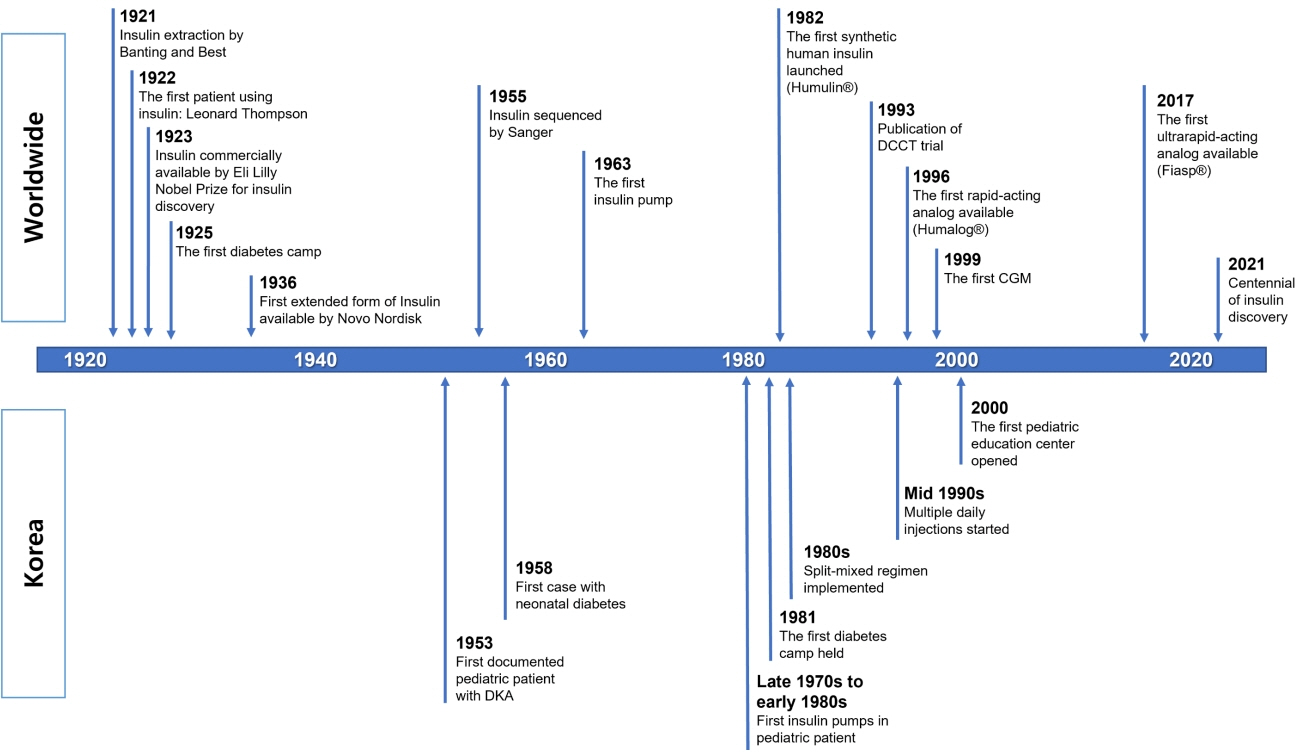
- The year 2021 is the centennial of insulin discovery. The discovery of insulin changes diabetes mellitus from a death sentence to a manageable disease. It became a historical turning point in the lives of people with diabetes. Since the first use of insulin in a patient in 1922, insulin and its analogs have been remarkable in saving the lives of people with diabetes. As insulin began to be used as a drug, it was introduced to, and used in Korea until now. This review briefly summarizes the history of insulin treatment in Korean children and adolescents with diabetes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Banting FG, Best CH. The internal secretion of the pancreas. J Lab Clin Med. 1922; 7:251–66.2. Fralick M, Zinman B. The discovery of insulin in Toronto: beginning a 100 year journey of research and clinical achievement. Diabetologia. 2021; 64:947–53.
Article3. Patterson CC, Karuranga S, Salpea P, Saeedi P, Dahlquist G, Soltesz G, et al. Worldwide estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 157:107842.
Article4. Shin CH. Epidemiologic characteristics of type 1 diabetes in children aged 14 years or under in Korea, 1985-2000. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:569–75.
Article5. Chae HW, Seo GH, Song K, Choi HS, Suh J, Kwon A, et al. Incidence and prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus among Korean children and adolescents between 2007 and 2017: an epidemiologic study based on a national database. Diabetes Metab J. 2020; 44:866–74.
Article6. The Nobel prize in pharmacy. Chosun Ilbo [Internet]. 1923. [cited 2021 Dec 1]. Available from: https://newslibrary.naver.com/viewer/index.naver?publishDate=1923-10-29&officeId=00023&pageNo=3.7. Urination in children. Chosun Ilbo [Internet]. 1924; [cited 2021 Dec 1]. Available from: https://newslibrary.naver.com/viewer/index.naver?publishDate=1924-12-06&officeId=00023&pageNo=1#.8. Chin DS, Lim ES. Diabetes mellitus in infant. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1959; 2:131–5.9. Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Dong-A Ilbo [Internet]. 1962; [cited 2021 Dec 1]. Available from: https://newslibrary.naver.com/viewer/index.naver?publishDate=1962-12-18&officeId=00020&pageNo=1.10. Im NJ, Hong I, Ko KW. A case of juvenile diabetic coma. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1966; 9:185–8.11. Pyun KH, Lee BS, Chung CY. A case of juvenile diabetes mellitus. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1972; 15:229–31.12. Choi JJ, Yun SH. Three cases of juvenile diabetes mellitus occurring in siblings. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1974; 17:154–60.13. Kwon YC, Ahn DH, Ko KW. Remission in juvenile diabetes mellitus. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1971; 14:509–13.14. Suk SB, Ahn HS, Choi Y, Ko KW. Clinical assessment on juvenile diabetes mellitus. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1979; 22:223–33.15. Cheong HI, Kim DG, Choi Y, Ko KW. Clinical observation of juvenile diabetes mellitus. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1983; 26:553–63.16. Moon JS, Won JC, Cho YM. The history of insulin therapy in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:623–8.
Article17. Yoo BS. Recent trends in diabetes treatment. Korean J Med. 1959; 2:35–8.18. Moon HR. Juvenile diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Assoc. 1968; 11:966–71.19. Lee TH, Park SC, Kim CH, Shin SM, Lee SJ. Three cases of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1983; 26:285–9.20. Moon SJ, Jung I, Park CY. Current advances of artificial pancreas systems: a comprehensive review of the clinical evidence. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:813–39.
Article21. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–86.
Article22. Choe J, Won SH, Choe Y, Park SH, Lee YJ, Lee J, et al. Temporal trends for diabetes management and glycemic control between 2010 and 2019 in Korean children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021; Nov. 18. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2021.0274. [Epub].
Article23. Home PD, Mehta R. Insulin therapy development beyond 100 years. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021; 9:695–707.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effective Use of Insulin Pump in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
- Insulin Therapy in Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Role of Diabetes camp in the Management of Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- The Effects of Cyclosporin in Treatment of Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Insulin Secretion and Insulin Sensitivity in Women with a Previous Gestational Diabetes: Understanding of Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes