J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2021 Sep;64(5):827-836. 10.3340/jkns.2020.0333.
Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation in Trigeminal Neuralgia : Analysis of Early and Late Outcomes of 156 Cases and 209 Interventions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Bakirkoy Prof. Dr. Mazhar Osman Training and Research Hospital for Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, Istanbul, Turkey
- KMID: 2519710
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2020.0333
Abstract
Objective
: Trigeminal neuralgia is one of the most common causes of facial pain. Our aim is to investigate the efficacy and borders of percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
Methods
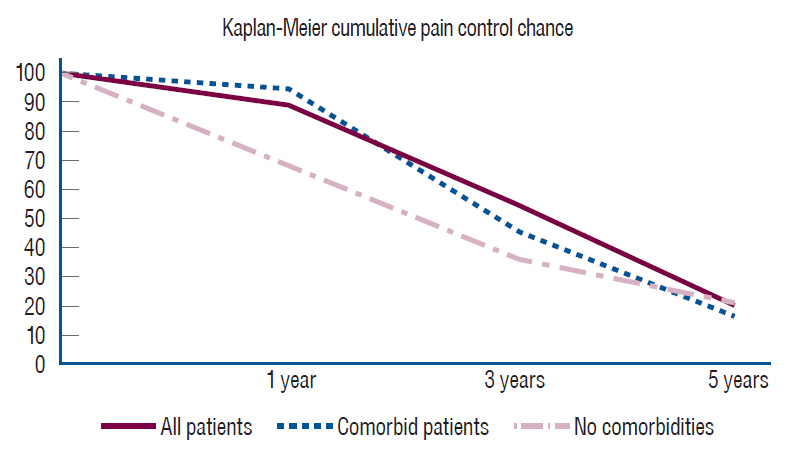
: Between May 2007 and April 2017, 156 patients with trigeminal neuralgia were treated with radiofrequency thermocoagulation. These 156 patients underwent 209 procedures. In our study, we investigated the early and late results of percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation under guiding fluoroscopic imaging in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI) pain scale was used for grading the early results. In addition, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to assess long-term outcomes. Of the 156 patients who underwent radiofrequency thermocoagulation for trigeminal neuralgia, 45 had additional disease. Patients with this condition were evaluated with their comorbidities. Early and late results were compared with those without comorbidity.
Results
: In 193 of 209 interventions BNI pain scale I to III results were obtained. Out of the 193 successful operation 136 patients (65.07%) were discharged as BNI I, 14 (6.70%) as BNI II, 43 (20.58%) as BNI III. Sixteen patients (7.65%) remained uncontrolled (BNI IV and V). While the treatment results of trigeminal neuralgia patients with comorbidity seem more successful in the early period, this difference was not observed in follow-up examinations.
Conclusion
: Finally, we concluded that percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation of the Gasserian ganglion is a safe and effective method in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. However, over time, the effectiveness of the treatment decreases. Neverthless, the reapprability of this intervention gives it a distinct advantage.
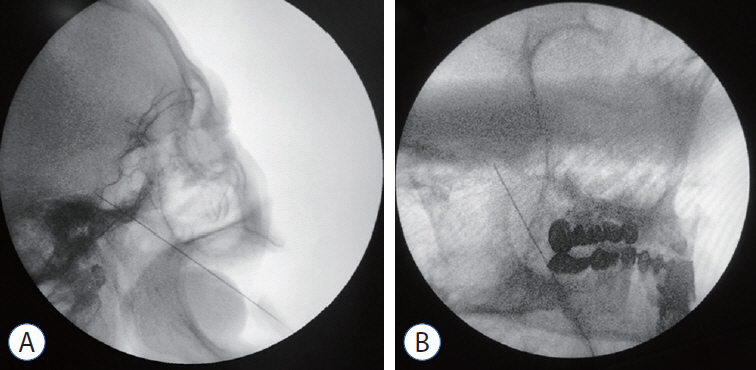
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bharti N, Sujith J, Singla N, Panda NB, Bala I. Radiofrequency thermoablation of the Gasserian ganglion versus the peripheral branches of the trigeminal nerve for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a randomized, control trial. Pain Physician. 22:147–154. 2019.2. Broggi G, Franzini A, Lasio G, Giorgi C, Servello D. Long-term results of percutaneous retrogasserian thermorhizotomy for “essential” trigeminal neuralgia: considerations in 1000 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery. 26:783–786. discussion 786-787. 1990.
Article3. Buono N, Thulesius H, Petrazzuoli F, Castelli E, Cambielli M. Postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and trigeminal neuralgia - chronic peripheral neuropathic pain in 58,480 rural Italian primary care patients. J Family Med Prim Care. 6:110–114. 2017.
Article4. Chen HI, Lee JY. The measurement of pain in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurosurg. 57:129–133. 2010.5. Donnet A, Simon E, Cuny E, Demarquay G, Ducros A, De Gaalon S, et al. French guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of classical trigeminal neuralgia (French Headache Society and French Neurosurgical Society). Rev Neurol (Paris). 173:131–151. 2017.
Article6. Frank F, Fabrizi AP. Percutaneous surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 97:128–130. 1989.
Article7. Goel MK, Khanna P, Kishore J. Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int J Ayurveda Res. 1:274–278. 2010.
Article8. Hart MG, Nowell M, Coakham HB. Radiofrequency thermocoagulation for trigeminal neuralgia without intra-operative patient waking. Br J Neurosurg. 26:392–396. 2012.
Article9. Härtel F. Die Leitungsanästhesie und Injections-Behandlung des Ganglion Gasseri und der Trigeminusstämme, ed 1. Berlin: Springer;1913. p. 1–100.10. Hitchon PW, Holland M, Noeller J, Smith MC, Moritani T, Jerath N, et al. Options in treating trigeminal neuralgia: experience with 195 patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 149:166–170. 2016.
Article11. Iwanaga J, Badaloni F, Laws T, Oskouian RJ, Tubbs RS. Anatomic study of extracranial needle trajectory using Hartel technique for percutaneous treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg. 110:e245–e248. 2018.
Article12. Jannetta PJ. Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 26:Suppl:159–162. 1967.
Article13. Jannetta PJ. Vascular compression is the cause of trigeminal neuralgia. APS Journal. 2:217–227. 1993.
Article14. Kanpolat Y, Savas A, Bekar A, Berk C. Percutaneous controlled radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: 25-year experience with 1,600 patients. Neurosurgery. 48:524–532. discussion 532-534. 2001.
Article15. Katusic S, Beard CM, Bergstralh E, Kurland LT. Incidence and clinical features of trigeminal neuralgia, Rochester, Minnesota, 1945-1984. Ann Neurol. 27:89–95. 1990.
Article16. Krishnan S, Bigder M, Kaufmann AM. Long-term follow-up of multimodality treatment for multiple sclerosis-related trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 160:135–144. 2018.
Article17. Linton SJ, Shaw WS. Impact of psychological factors in the experience of pain. Phys Ther. 91:700–711. 2011.
Article18. Liu JK, Apfelbaum RI. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 15:319–334. 2004.
Article19. Maarbjerg S, Di Stefano G, Bendtsen L, Cruccu G. Trigeminal neuralgia - diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia. 37:648–657. 2017.
Article20. Maxwell RE. Clinical diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia and differential diagnosis of facial pain. In : Rovit RL, Murali R, Jannetta PJ, editors. Trigeminal Neuralgia. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;1990. p. 53–77.21. Morris L. Trigeminal neuralgia.: the anatomy of the “Hartel” technique. Lancet. 217:122–126. 1931.22. Nugent GR. Radiofrequency treatment of trigeminal neuralgia using a cordotomy-type electrode. A method. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 8:41–52. 1997.
Article23. Pan SL, Yen MF, Chiu YH, Chen LS, Chen HH. Increased risk of trigeminal neuralgia after hypertension: a population-based study. Neurology. 77:1605–1610. 2011.
Article24. Peris-Celda M, Graziano F, Russo V, Mericle RA, Ulm AJ. Foramen ovale puncture, lesioning accuracy, and avoiding complications: microsurgical anatomy study with clinical implications. J Neurosurg. 119:1176–1193. 2013.
Article25. Sabalys G, Juodzbalys G, Wang HL. Aetiology and pathogenesis of trigeminal neuralgia: a comprehensive review. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 3:e2. 2013.
Article26. Sandell T, Holmen J, Eide PK. Hypertension in patients with cranial nerve vascular compression syndromes and comparison with a population-based cohort. J Neurosurg. 119:1302–1308. 2013.
Article27. Siegfried J. Percutaneous controlled thermocoagulation of gasserian ganglion in trigeminal neuralgia. Experiences with 1000 cases. In : Samii M, Jannetta PJ, editors. The Cranial Nerves, ed 1. Berlin: Springer;1981. p. 322–330.28. Son BC, Kim HS, Kim IS, Yang SH, Lee SW. Percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation under fluoroscopic image-guidance for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 50:446–452. 2011.
Article29. Sweet WH, Wepsic JG. Controlled thermocoagulation of trigeminal ganglion and rootlets for differential destruction of pain fibers. 1. Trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 40:143–156. 1974.
Article30. Taha JM, Tew JM Jr, Buncher CR. A prospective 15-year follow up of 154 consecutive patients with trigeminal neuralgia treated by percutaneous stereotactic radiofrequency thermal rhizotomy. J Neurosurg. 83:989–993. 1995.
Article31. Tatli M, Sindou M. Anatomoradiological landmarks for accuracy of radiofrequency thermorhizotomy in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 63(1 Suppl 1):ONS129–ONS137. discussion ONS137-ONS138. 2008.
Article32. Tew JM Jr, Taha KM. Percutaneous rhizotomy in the treatment of intractable facial pain (trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, and vagal nerves). In : Schmidek HH, Sweet WH, editors. Operative Neurosurgical Techniques: Indications, Methods, and Results, ed 3. Philadelphia: Saunders;1995. p. 1469–1484.33. van Loveren H, Tew JM Jr, Keller JT, Nurre MA. A 10-year experience in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Comparison of percutaneous stereotaxic rhizotomy and posterior fossa exploration. J Neurosurg. 57:757–764. 1982.34. Xu Z, Zhang P, Long L, He H, Zhang J, Sun S. Diabetes mellitus in classical trigeminal neuralgia: a predisposing factor for its development. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 151:70–72. 2016.
Article35. Yoshimasu F, Kurland LT, Elveback LR. Tic douloureux in Rochester, Minnesota 1945-1969. Neurology. 22:952–956. 1972.
Article36. Zakrzewska JM. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia. Clin J Pain. 18:14–21. 2002.
Article37. Zakrzewska JM, Jassim S, Bulman SJ. A prospective, longitudinal study on patients with trigeminal neuralgia who underwent radiofrequency thermocoagulation of the Gasserian ganglion. Pain. 79:51–58. 1999.
Article38. Zakrzewska JM, Wu J, Brathwaite TS. A systematic review of the management of trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis. World Neurosurg. 111:291–306. 2018.
Article39. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) the international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 38:1–211. 2018.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation of the Gasserian Ganglion
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation on Trigeminal Neuralgia: Two cases report
- Stereotactic Radiofrequency Gasserian Ganglionotomy
- Percutaneous radiofrequency Thermal Rhizotomy for Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation for Recurred Trigeminal Neuralgia: A case report