Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2021 May;25(2):230-241. 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.230.
Impact of diabetes mellitus on morbidity and survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy for malignancy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgical Gastroenterology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India
- 2Department of Surgery, B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences, Dharan, Nepal
- 3Department of Surgical Gastroenterology, D Y Patil Medical College, Pune, India
- 4Department of Pharmacology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India
- 5Department of Surgical Gastroenterology, SRM Institutes for Medical Science, Chennai, India
- 6Department of Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery, Gleneagles Global Hospital, Bangalore, India
- 7Department of Gastroenterology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India
- 8Department of Radiotherapy and Oncology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India
- KMID: 2516244
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.230
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a known risk factor for morbidity, length of hospital stay, or mortality after surgery, however, its impact on postoperative course and long-term survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) is not clear.
Methods
This is a retrospective analysis of prospectively maintained database of 141 patients with periampullary and pancreatic head adenocarcinoma operated between January 2001 and March 2019. Clinico-pathological records and follow-up data were retrieved and analyzed. Cumulative hazard was computed for comparing the survival between DM and non-DM.
Results
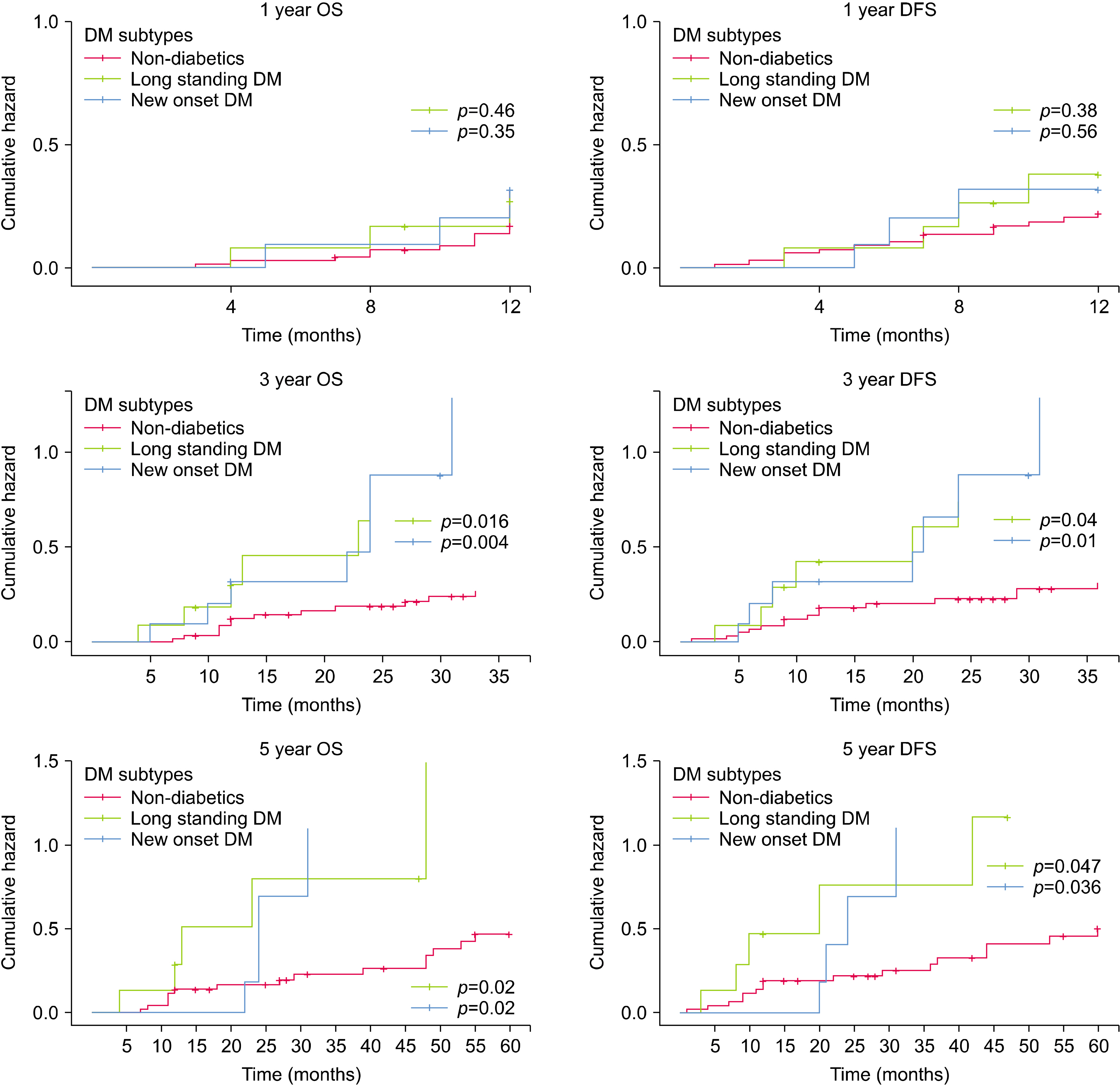
DM was present in 31/141 (21.9%) patients, while 16/31 (51.6%). were new-onset DM (NODM). Tumor size, lymphovascular & perineural invasion, type of surgery, lymph node positivity and R0 resection rate were comparable between diabetic and non-diabetic. There was no significant difference in postoperative pancreatic fistula, delayed gastric emptying, infectious complication, hospital stay and mortality between DM and nondiabetics. Patients with DM had worse survival at 3 years (OS: HR, 3.11 [1.43-6.76] p=0.004, DFS: HR, 2.61 [1.23-5.53] p=0.01) and 5 years (OS: HR, 3.32 [1.46-7.53] p=0.004, DFS: HR, 2.87 [1.29-6.41] p=0.009). On multivariate analysis, DM (3 year OS: HR, 2.61 [1.14-5.98] p=0.022, DFS: HR, 2.19; p=0.058) (5 year OS: HR, 2.55; p=0.04, DFS: HR, 2.25; p=0.068) and pylorus resecting surgery were significantly associated with worse survival at 3 and 5 years.
Conclusions
Preoperative DM has no significant effect on postoperative course but has negative impact on 3-year and 5-year OS and DFS after PD for pancreatic and periampullary adenocarcinoma.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Five-year follow-up after pancreatoduodenectomy performed for malignancy: A single-centre study
Thomas Brendon Russell, Peter Lawrence Zaki Labib, Somaiah Aroori
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2023;27(1):76-86. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.22-039.
Reference
-
1. Buchleitner AM, Martínez-Alonso M, Hernández M, Solà I, Mauricio D. 2012; Perioperative glycaemic control for diabetic patients undergoing surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (9):CD007315. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007315.pub2. PMID: 22972106.
Article2. Yeh CC, Liao CC, Chang YC, Jeng LB, Yang HR, Shih CC, et al. 2013; Adverse outcomes after noncardiac surgery in patients with diabetes: a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Care. 36:3216–3221. DOI: 10.2337/dc13-0770. PMID: 23990518. PMCID: PMC3781492.
Article3. Jehan F, Khan M, Sakran JV, Khreiss M, O'Keeffe T, Chi A, et al. 2018; Perioperative glycemic control and postoperative complications in patients undergoing emergency general surgery: what is the role of Plasma hemoglobin A1c? J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 84:112–117. DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001724. PMID: 29040204.
Article4. Cameron JL, He J. 2015; Two thousand consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies. J Am Coll Surg. 220:530–536. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.12.031. PMID: 25724606.
Article5. Shinde RS, Pandrowala S, Navalgund S, Pai E, Bhandare MS, Chaudhari VA, et al. 2020; Centralisation of pancreatoduodenectomy in India: where do we stand? World J Surg. 44:2367–2376. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-020-05466-6. PMID: 32161986.
Article6. Srivastava S, Sikora SS, Pandey CM, Kumar A, Saxena R, Kapoor VK. 2001; Determinants of pancreaticoenteric anastomotic leak following pancreaticoduodenectomy. ANZ J Surg. 71:511–515. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1622.2001.02184.x. PMID: 11527259.
Article7. Chu CK, Mazo AE, Sarmiento JM, Staley CA, Adsay NV, Umpierrez GE, et al. 2010; Impact of diabetes mellitus on perioperative outcomes after resection for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 210:463–473. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2009.12.029. PMID: 20347739.
Article8. Kunstman JW, Healy JM, Araya DA, Salem RR. 2015; Effects of preoperative long-term glycemic control on operative outcomes following pancreaticoduodenectomy. Am J Surg. 209:1053–1062. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2014.06.029. PMID: 25242683.
Article9. Nakata B, Ishikawa T, Amano R, Kimura K, Hirakawa K. 2013; Impact of preoperative diabetes mellitus on clinical outcome after pancreatectomy. Int J Surg. 11:757–761. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.07.008. PMID: 23891775.
Article10. Mathur A, Pitt HA, Marine M, Saxena R, Schmidt CM, Howard TJ, et al. 2007; Fatty pancreas: a factor in postoperative pancreatic fistula. Ann Surg. 246:1058–1064. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31814a6906. PMID: 18043111.11. Lin JW, Cameron JL, Yeo CJ, Riall TS, Lillemoe KD. 2004; Risk factors and outcomes in postpancreaticoduodenectomy pancreaticocutaneous fistula. J Gastrointest Surg. 8:951–959. DOI: 10.1016/j.gassur.2004.09.044. PMID: 15585382.
Article12. Dandona M, Linehan D, Hawkins W, Strasberg S, Gao F, Wang-Gillam A. 2011; Influence of obesity and other risk factors on survival outcomes in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 40:931–937. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318215a9b1. PMID: 21747317.
Article13. Nakai Y, Isayama H, Sasaki T, Mizuno S, Sasahira N, Kogure H, et al. 2013; Clinical outcomes of chemotherapy for diabetic and nondiabetic patients with pancreatic cancer: better prognosis with statin use in diabetic patients. Pancreas. 42:202–208. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31825de678. PMID: 23000889.14. Karlin NJ, Dueck AC, Cook CB. 2012; Cancer with diabetes: prevalence, metabolic control, and survival in an academic oncology practice. Endocr Pract. 18:898–905. DOI: 10.4158/EP12128.OR. PMID: 22982797.
Article15. Mao Y, Tao M, Jia X, Xu H, Chen K, Tang H, et al. 2015; Effect of diabetes mellitus on survival in patients with pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5:17102. DOI: 10.1038/srep17102. PMID: 26598798. PMCID: PMC4656995.
Article16. Raghavan SR, Ballehaninna UK, Chamberlain RS. 2013; The impact of perioperative blood glucose levels on pancreatic cancer prognosis and surgical outcomes: an evidence-based review. Pancreas. 42:1210–1217. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182a6db8e. PMID: 24152946.17. Toriola AT, Stolzenberg-Solomon R, Dalidowitz L, Linehan D, Colditz G. 2014; Diabetes and pancreatic cancer survival: a prospective cohort-based study. Br J Cancer. 111:181–185. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.224. PMID: 24786605. PMCID: PMC4090724.
Article18. Anjana RM, Deepa M, Pradeepa R, Mahanta J, Narain K, Das HK, et al. 2017; Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes in 15 states of India: results from the ICMR-INDIAB population-based cross-sectional study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5:585–596. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30174-2.
Article19. Ravikumar P, Bhansali A, Ravikiran M, Bhansali S, Walia R, Shanmugasundar G, et al. 2011; Prevalence and risk factors of diabetes in a community-based study in North India: the Chandigarh Urban Diabetes Study (CUDS). Diabetes Metab. 37:216–221. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabet.2010.10.004. PMID: 21195002.
Article20. American Diabetes Association. 2009; Standards of medical care in diabetes-2009. Diabetes Care. 32 Suppl 1:S13–S61. DOI: 10.2337/dc09-S013. PMID: 19118286. PMCID: PMC2613589.21. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. 2004; Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 240:205–213. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. PMID: 15273542. PMCID: PMC1360123.22. Bassi C, Marchegiani G, Dervenis C, Sarr M, Abu Hilal M, Adham M, et al. 2017; The 2016 update of the International Study Group (ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula: 11 years after. Surgery. 161:584–591. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.11.014. PMID: 28040257.23. Wente MN, Veit JA, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fingerhut A, Gouma DJ, et al. 2007; Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (PPH): an International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) definition. Surgery. 142:20–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.02.001. PMID: 17629996.24. Wente MN, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fingerhut A, Gouma DJ, Izbicki JR, et al. 2007; Delayed gastric emptying (DGE) after pancreatic surgery: a suggested definition by the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS). Surgery. 142:761–768. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.05.005. PMID: 17981197.
Article25. Wickham H. 2016. Ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. 2nd ed. Springer;Cham: DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-24277-4.26. Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez JC, et al. 2011; pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:77. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-77. PMID: 21414208. PMCID: PMC3068975.
Article27. R Development Core Team. 2021. Import and Export 'SPSS', 'Stata' and 'SAS' Files (R Package Version 2.4.1). R Foundation for Statistical Computing;Vienna, Austria:28. Therneau TM, Grambsch PM. Therneau TM, Grambsch PM, editors. 2000. Multiple events per subject. Modeling survival data: extending the cox model. Springer;New York: p. 169–229. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4757-3294-8_8.
Article29. R Development Core Team. 2017. Drawing Survival Curves using 'ggplot2' (R Package Version 0.3.1). R Foundation for Statistical Computing;Vienna, Austria:30. R Development Core Team. 2016. Easy analysis and visualization of factorial experiments (R Package Version 4.4-0). R Foundation for Statistical Computing;Vienna, Austria:31. Wickham H. 2011; The split-apply-combine strategy for data analysis. J Stat Softw. 40:1–29. DOI: 10.18637/jss.v040.i01.
Article32. Cheng Q, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Zhang B, Yi B, et al. 2007; Predictive factors for complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Surg Res. 139:22–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.07.028. PMID: 17292419.
Article33. Hank T, Sandini M, Qadan M, Weniger M, Ciprani D, Li A, et al. 2020; Diabetes mellitus is associated with unfavorable pathologic features, increased postoperative mortality, and worse long-term survival in resected pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 20:125–131. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2019.10.007. PMID: 31706821.
Article34. DeOliveira ML, Winter JM, Schafer M, Cunningham SC, Cameron JL, Yeo CJ, et al. 2006; Assessment of complications after pancreatic surgery: a novel grading system applied to 633 patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 244:931–937. discussion 937–939. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000246856.03918.9a. PMID: 17122618. PMCID: PMC1856636.35. Karlin NJ, Amin SB, Kosiorek HE, Buras MR, Verona PM, Cook CB. 2018; Survival and glycemic control outcomes among patients with coexisting pancreatic cancer and diabetes mellitus. Future Sci OA. 4:FSO291. DOI: 10.4155/fsoa-2017-0144. PMID: 29682326. PMCID: PMC5905610.
Article36. Hwang A, Narayan V, Yang YX. 2013; Type 2 diabetes mellitus and survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Cancer. 119:404–410. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.27731. PMID: 23292900.37. McWilliams RR, Matsumoto ME, Burch PA, Kim GP, Halfdanarson TR, de Andrade M, et al. 2010; Obesity adversely affects survival in pancreatic cancer patients. Cancer. 116:5054–5062. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.25465. PMID: 20665496. PMCID: PMC2963722.
Article38. Olson SH, Chou JF, Ludwig E, O'Reilly E, Allen PJ, Jarnagin WR, et al. 2010; Allergies, obesity, other risk factors and survival from pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:2412–2419. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25240. PMID: 20143395.
Article39. Regel I, Kong B, Raulefs S, Erkan M, Michalski CW, Hartel M, et al. 2012; Energy metabolism and proliferation in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 397:507–512. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-012-0933-9. PMID: 22430298.
Article40. Sah RP, Nagpal SJ, Mukhopadhyay D, Chari ST. 2013; New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:423–433. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.49. PMID: 23528347. PMCID: PMC3932322.
Article41. Hart PA, Law RJ, Frank RD, Bamlet WR, Burch PA, Petersen GM, et al. 2014; Impact of diabetes mellitus on clinical outcomes in patients undergoing surgical resection for pancreatic cancer: a retrospective, cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. 109:1484–1492. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2014.193. PMID: 25070053. PMCID: PMC4477801.
Article42. Hatzaras I, George N, Muscarella P, Melvin WS, Ellison EC, Bloomston M. 2010; Predictors of survival in periampullary cancers following pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:991–997. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-009-0883-9. PMID: 20108122. PMCID: PMC2861840.
Article43. Plichta JK, Godambe AS, Fridirici Z, Yong S, Sinacore JM, Abood GJ, et al. 2014; The association between survival and the pathologic features of periampullary tumors varies over time. HPB Surg. 2014:890530. DOI: 10.1155/2014/890530. PMID: 25104878. PMCID: PMC4102018.
Article44. Diener MK, Fitzmaurice C, Schwarzer G, Seiler CM, Hüttner FJ, Antes G, et al. 2014; Pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy (pp Whipple) versus pancreaticoduodenectomy (classic Whipple) for surgical treatment of periampullary and pancreatic carcinoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 11:CD006053. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006053.pub5.
Article45. Tran KT, Smeenk HG, van Eijck CH, Kazemier G, Hop WC, Greve JW, et al. 2004; Pylorus preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy versus standard Whipple procedure: a prospective, randomized, multicenter analysis of 170 patients with pancreatic and periampullary tumors. Ann Surg. 240:738–745. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000143248.71964.29. PMID: 15492552. PMCID: PMC1356476.