J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2021 May;64(3):418-426. 10.3340/jkns.2020.0247.
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis : A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Medical Statistics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- KMID: 2515498
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2020.0247
Abstract
Objective
: A role of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is not wellunderstood. This study evaluates the effectiveness of DWI in the diagnosis of CVT.
Methods
: Literature search was conducted in electronic databases for the identification of studies which reported the outcomes of patients subjected to DWI for CVT diagnosis. Random-effects meta-analyses were performed to achieve overall estimates of important diagnostic efficiency indices including hyperintense signal rate, the sensitivity and specificity of DWI in diagnosing CVT, and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of DWI signal areas and surrounding tissue.
Results
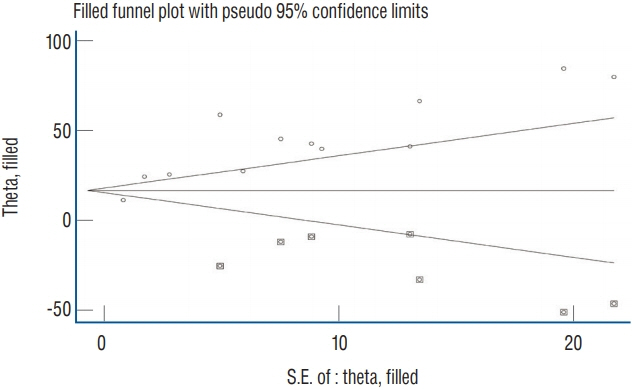
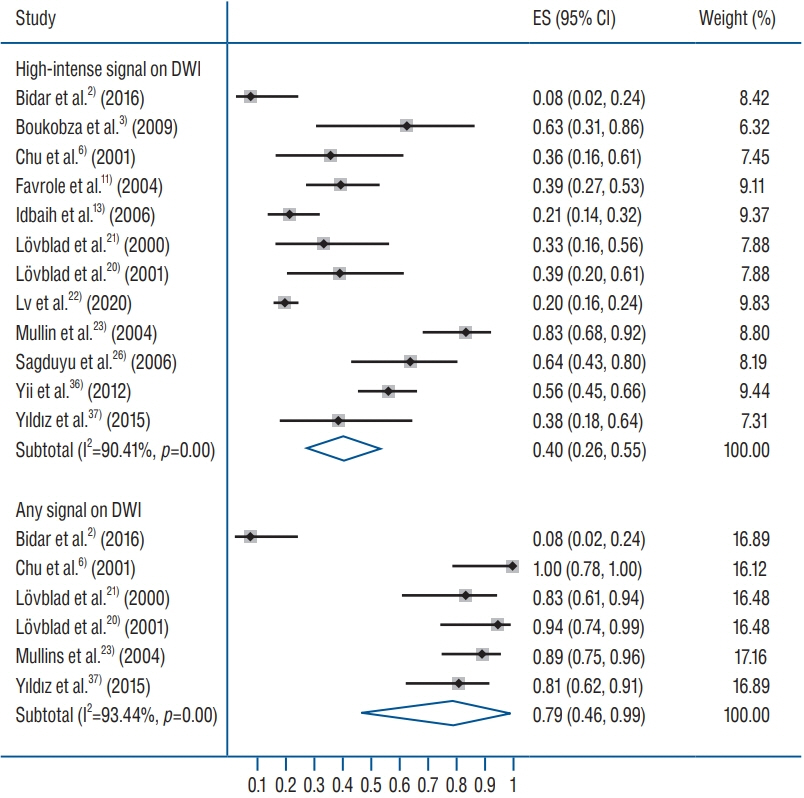
: Nineteen studies (443 patients with 856 CVTs; age 40 years [95% confidence interval (CI), 33 to 43]; 28% males [95% CI, 18 to 38]; symptom onset to DWI time 4.6 days [95% CI, 2.3 to 6.9]) were included. Hyperintense signals on DWI were detected in 40% (95% CI, 26 to 55) of the cases. The sensitivity of DWI for detecting CVT was 22% (95% CI, 11 to 34) but specificity was 98% (95% CI, 95 to 100). ADC values were quite heterogenous in DWI signal areas. However, generally the ADC values were lower in DWI signal areas than in surrounding normal areas (mean difference−0.33×10-3 mm2/s [95% CI, −0.44 to −0.23]; p<0.00001).
Conclusion
: DWI has a low sensitivity in detecting CVT and thus has a high risk of missing many CVT cases. However, because of its high specificity, it may have supporting and exploratory roles in CVT diagnosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Atlas SW, DuBois P, Singer MB, Lu D. Diffusion measurements in intracranial hematomas: implications for MR imaging of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 21:1190–1194. 2000.2. Bidar F, Faeghi F, Ghorbani A. Assessment of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis using T2 (*)-weighted gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging sequences. Iran J Neurol. 15:96–99. 2016.3. Boukobza M, Crassard I, Bousser MG, Chabriat H. MR imaging features of isolated cortical vein thrombosis: diagnosis and follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 30:344–348. 2009.
Article4. Chiewvit P, Piyapittayanan S, Poungvarin N. Cerebral venous thrombosis: diagnosis dilemma. Neurol Int. 3:e13. 2011.
Article5. Choi SY, Chang YW, Park HJ, Kim HJ, Hong SS, Seo DY. Correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficiency values on diffusion-weighted imaging with prognostic factors for breast cancer. Br J Radiol. 85:e474–e479. 2012.
Article6. Chu K, Kang DW, Yoon BW, Roh JK. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance in cerebral venous thrombosis. Arch Neurol. 58:1569–1576. 2001.
Article7. Corvol JC, Oppenheim C, Manaï R, Logak M, Dormont D, Samson Y, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in a case of cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke. 29:2649–2652. 1998.
Article8. Doege CA, Tavakolian R, Kerskens CM, Romero BI, Lehmann R, Einhäupl KM, et al. Perfusion and diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in human cerebral venous thrombosis. J Neurol. 248:564–571. 2001.
Article9. Drake-Pérez M, Boto J, Fitsiori A, Lovblad K, Vargas MI. Clinical applications of diffusion weighted imaging in neuroradiology. Insights Imaging. 9:535–547. 2018.
Article10. Ducreux D, Oppenheim C, Vandamme X, Dormont D, Samson Y, Rancurel G, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging patterns of brain damage associated with cerebral venous thrombosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22:261–268. 2001.11. Favrole P, Guichard JP, Crassard I, Bousser MG, Chabriat H. Diffusion-weighted imaging of intravascular clots in cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke. 35:99–103. 2004.
Article12. Guenther G, Arauz A. Cerebral venous thrombosis: a diagnostic and treatment update. Neurologia. 26:488–498. 2011.
Article13. Idbaih A, Boukobza M, Crassard I, Porcher R, Bousser MG, Chabriat H. MRI of clot in cerebral venous thrombosis: high diagnostic value of susceptibility-weighted images. Stroke. 37:991–995. 2006.14. Kang BK, Na DG, Ryoo JW, Byun HS, Roh HG, Pyeun YS. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of intracerebral hemorrhage. Korean J Radiol. 2:183–191. 2001.
Article15. Keller E, Flacke S, Urbach H, Schild HH. Diffusion- and perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in deep cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke. 30:1144–1146. 1999.
Article16. Leach JL, Strub WM, Gaskill-Shipley MF. Cerebral venous thrombus signal intensity and susceptibility effects on gradient recalled-echo MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 28:940–945. 2007.17. Leach JL, Wolujewicz M, Strub WM. Partially recanalized chronic dural sinus thrombosis: findings on MR imaging, time-of-flight MR venography, and contrast-enhanced MR venography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 28:782–789. 2007.18. Linn J, Michl S, Katja B, Pfefferkorn T, Wiesmann M, Hartz S, et al. Cortical vein thrombosis: the diagnostic value of different imaging modalities. Neuroradiology. 52:899–911. 2010.
Article19. Linn J, Pfefferkorn T, Ivanicova K, Müller-Schunk S, Hartz S, Wiesmann M, et al. Noncontrast CT in deep cerebral venous thrombosis and sinus thrombosis: comparison of its diagnostic value for both entities. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 30:728–735. 2009.
Article20. Lövblad KO, Bassetti C, Schneider J, Guzman R, El-Koussy M, Remonda L, et al. Diffusion-weighted mr in cerebral venous thrombosis. Cerebrovasc Dis. 11:169–176. 2001.
Article21. Lövblad KO, Bassetti C, Schneider J, Ozdoba C, Remonda L, Schroth G. Diffusion-weighted MRI suggests the coexistence of cytotoxic and vasogenic oedema in a case of deep cerebral venous thrombosis. Neuroradiology. 42:728–731. 2000.
Article22. Lv B, Tian CL, Cao XY, Liu XF, Wang J, Yu SY. Role of diffusion-weighted imaging in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis. J Int Med Res. 48:300060520933448. 2020.
Article23. Mullins ME, Grant PE, Wang B, Gonzalez RG, Schaefer PW. Parenchymal abnormalities associated with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: assessment with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 25:1666–1675. 2004.24. Mussi TC, Martins T, Tachibana A, Mousessian PN, Baroni RH. Objective value on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map to categorize the intensity of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) restriction for prostate cancer detection on multiparametric prostate MRI. Int Braz J Urol. 44:882–891. 2018.
Article25. Sadigh G, Mullins ME, Saindane AM. Diagnostic performance of MRI sequences for evaluation of dural venous sinus thrombosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 206:1298–1306. 2016.
Article26. Sagduyu A, Sirin H, Mulayim S, Bademkiran F, Yunten N, Kitis O, et al. Cerebral cortical and deep venous thrombosis without sinus thrombosis: clinical MRI correlates. Acta Neurol Scand. 114:254–260. 2006.
Article27. Saposnik G, Barinagarrementeria F, Brown RD Jr, Bushnell CD, Cucchiara B, Cushman M, et al. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 42:1158–1192. 2011.
Article28. Silvera S, Oppenheim C, Touzé E, Ducreux D, Page P, Domigo V, et al. Spontaneous intracerebral hematoma on diffusion-weighted images: Influence of T2-shine-through and T2-blackout effects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 26:236–241. 2005.29. Silvis SM, de Sousa DA, Ferro JM, Coutinho JM. Cerebral venous thrombosis. Nat Rev Neurol. 13:555–565. 2017.
Article30. Stam J. Thrombosis of the cerebral veins and sinuses. N Engl J Med. 352:1791–1798. 2005.
Article31. Wagner MW, Bosemani T, Oshmyansky A, Poretti A, Huisman TA. Neuroimaging findings in pediatric cerebral sinovenous thrombosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 31:705–712. 2015.
Article32. Wasay M, Azeemuddin M. Neuroimaging of cerebral venous thrombosis. J Neuroimaging. 15:118–128. 2005.
Article33. Wasay M, Bakshi R, Bobustuc G, Dubey N, Cheema Z, Dai A. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in superior sagittal sinus thrombosis. J Neuroimaging. 12:267–269. 2002.
Article34. Washida K, Kowa H, Tsuji Y, Sekiguchi K, Kanda F, Toda T. Multiple deep white matter hyperintense lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging: early sign of straight sinus thrombosis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 25:e131–e133. 2016.
Article35. Weimar C, Masuhr F, Hajjar K. Diagnosis and treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 10:1545–1553. 2012.
Article36. Yii IY, Mitchell PJ, Dowling RJ, Yan B. Imaging predictors of clinical deterioration in cerebral venous thrombosis. J Clin Neurosci. 19:1525–1529. 2012.
Article37. Yıldız ME, Ozcan UA, Turk A, Ulus OS, Erzen C, Dinçer A. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings of cortical vein thrombosis at 3 T. Clin Neuroradiol. 25:249–256. 2015.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Susceptibility-Weighted MR Imaging for the Detection of Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Two Cases of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis with High Signal Intensity of Intravascular Clots on Diffusion Weighted Image
- Reversal of a Large Ischemic Lesion with Low Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value by Rapid Spontaneous Recanalization
- A Case of Deep Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Associated with Iron Deficiency Anemia
- A Case of Right Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction Presenting as Thunderclap Headache