Korean J Transplant.
2021 Mar;35(1):15-23. 10.4285/kjt.20.0049.
Prognosis of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma after living donor liver transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2514404
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.20.0049
Abstract
- Background
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is a rare borderline vascular tumor. Due to its rarity and protean behavior, the optimal treatment of hepatic EHE has not yet been standardized. This single-center study describes outcomes in patients with hepatic EHE who underwent living donor liver transplantation (LDLT).
Methods
The medical records of patients who underwent LDLT for hepatic EHE from 2007 to 2016 were reviewed.
Results
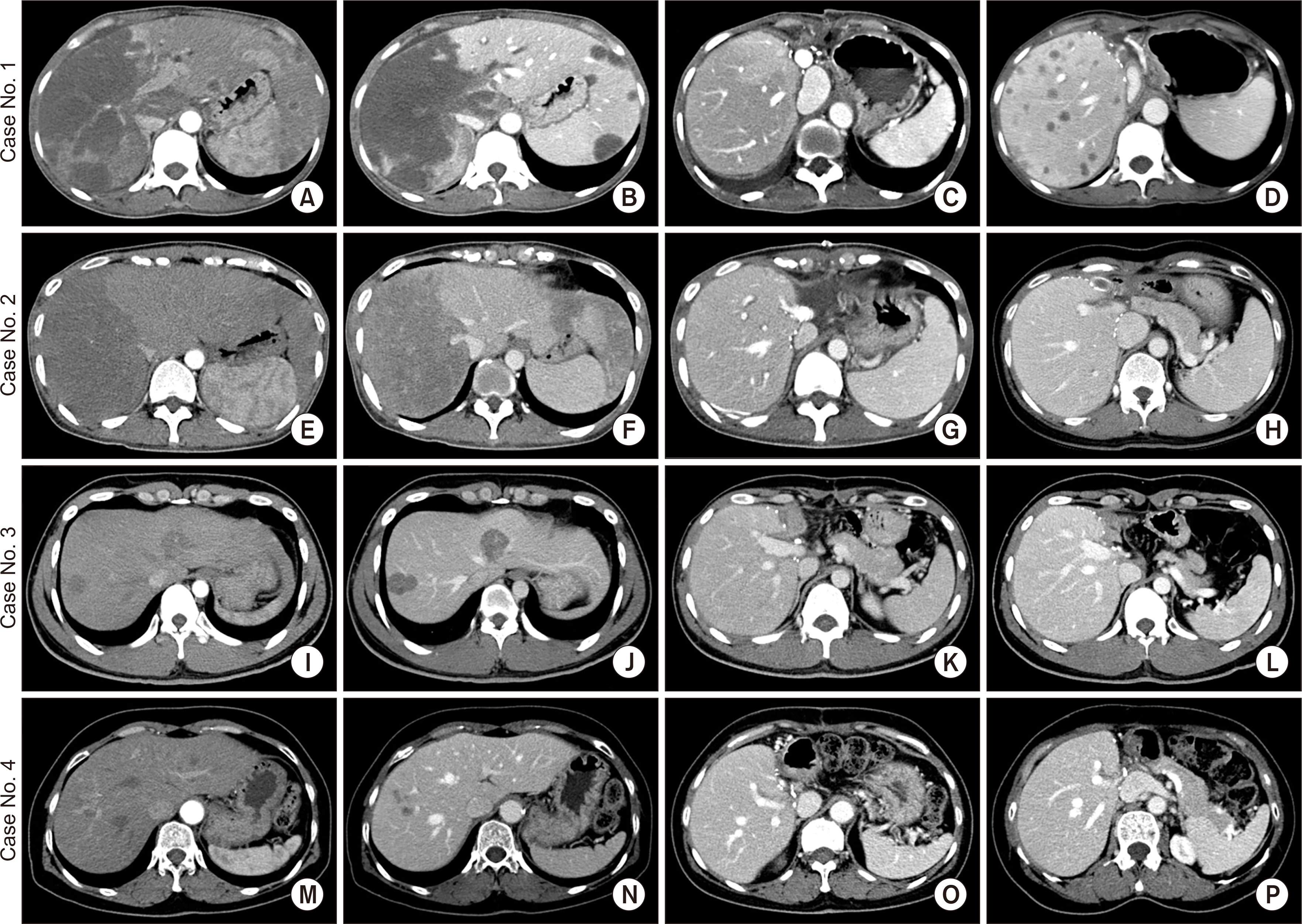
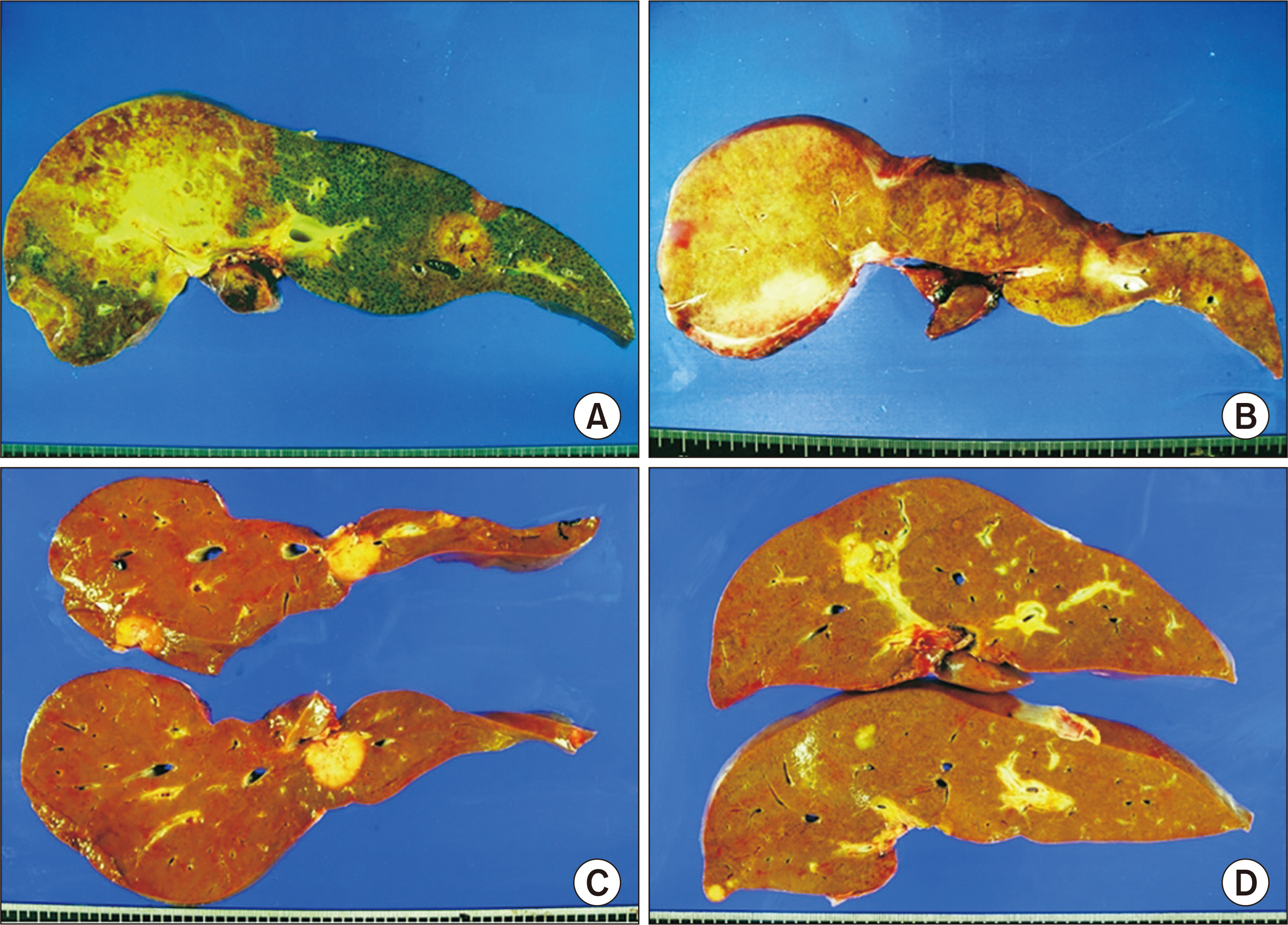
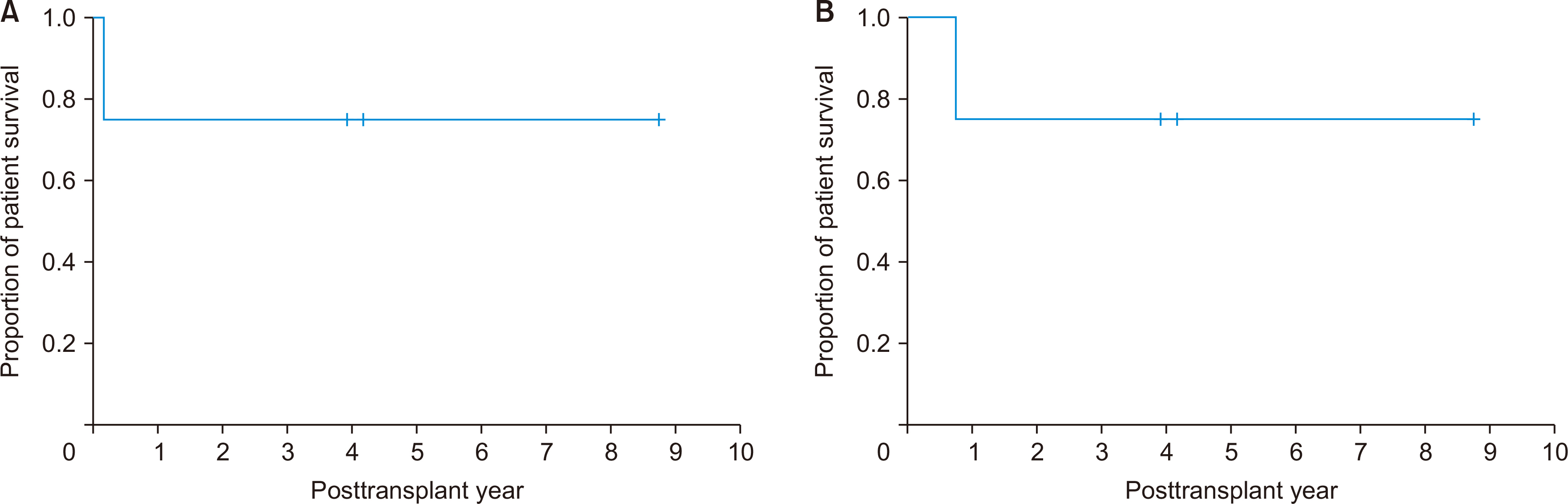
During 10-year period, four patients, one man and three women, of mean age 41.3±11.1 years, underwent LDLT for hepatic EHE. Based on imaging modalities, these patients were preoperatively diagnosed with EHE or hepatocellular carcinoma, with percutaneous liver biopsy confirming that all four had hepatic EHE. The tumors were multiple and scattered over entire liver, precluding liver resection. Blood tumor markers were not elevated, except that CA19-9 and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin was slightly elevated in one patient. Mean model for end-stage liver disease score was 10.8±5.7. All patients underwent LDLT using modified right liver grafts, with graft-recipient weight ratio of 1.11±0.19, and all recovered uneventfully after LDLT. One patient died due to tumor recurrence at 9 months, whereas the other three have done well without tumor recurrence, resulting in 5-year disease-free and overall patient survival rates of 75% each. The patient with tumor recurrence was classified as a high-risk patient based on the original and modified hepatic EHE-LT scoring systems.
Conclusions
LDLT can be an effective treatment for patients with unresectable hepatic EHEs that are confined within the liver and absence of macrovascular invasion and lymph node metastasis.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Living donor liver transplantation in an infant patient with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis along with hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Jung-Man Namgoong, Shin Hwang, Dae-Yeon Kim, Chul-Soo Ahn, Hyunhee Kwon, Suhyeon Ha, Kyung Mo Kim, Seak Hee Oh
Korean J Transplant. 2022;36(1):73-78. doi: 10.4285/kjt.21.0007.
Reference
-
1. Sardaro A, Bardoscia L, Petruzzelli MF, Portaluri M. 2014; Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: an overview and update on a rare vascular tumor. Oncol Rev. 8:259. DOI: 10.4081/oncol.2014.259. PMID: 25992243. PMCID: PMC4419652.
Article2. Fletcher CD, Unni KK, Mertens F. 2002. World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. IRAC Press;Lyon, Fr:3. Ishak KG, Sesterhenn IA, Goodman ZD, Rabin L, Stromeyer FW. 1984; Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 32 cases. Hum Pathol. 15:839–52. DOI: 10.1016/S0046-8177(84)80145-8. PMID: 6088383.
Article4. Lau K, Massad M, Pollak C, Rubin C, Yeh J, Wang J, et al. 2011; Clinical patterns and outcome in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma with or without pulmonary involvement: insights from an internet registry in the study of a rare cancer. Chest. 140:1312–8. DOI: 10.1378/chest.11-0039. PMID: 21546438.5. Mehrabi A, Kashfi A, Fonouni H, Schemmer P, Schmied BM, Hallscheidt P, et al. 2006; Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy. Cancer. 107:2108–21. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.22225. PMID: 17019735.6. Wang LR, Zhou JM, Zhao YM, He HW, Chai ZT, Wang M, et al. 2012; Clinical experience with primary hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: retrospective study of 33 patients. World J Surg. 36:2677–83. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-012-1714-x. PMID: 22890877.
Article7. Lin J, Ji Y. 2010; CT and MRI diagnosis of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 9:154–8. PMID: 20382586.8. Makhlouf HR, Ishak KG, Goodman ZD. 1999; Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: a clinicopathologic study of 137 cases. Cancer. 85:562–82. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990201)85:3<562::AID-CNCR7>3.0.CO;2-T. PMID: 10091730.9. Ben-Haim M, Roayaie S, Ye MQ, Thung SN, Emre S, Fishbein TA, et al. 1999; Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: resection or transplantation, which and when? Liver Transpl Surg. 5:526–31. DOI: 10.1002/lt.500050612. PMID: 10545542.
Article10. Imanishi H, Kawata M, Yanagihara M, Nakayama N, Sato T, Furukawa Y, et al. 2002; Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver associated with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy. Hepatogastroenterology. 49:1673–5. PMID: 12397762.11. Lerut JP, Orlando G, Adam R, Schiavo M, Klempnauer J, Mirza D, et al. 2007; The place of liver transplantation in the treatment of hepatic epitheloid hemangioendothelioma: report of the European liver transplant registry. Ann Surg. 246:949–57. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815c2a70. PMID: 18043096.12. Rodriguez JA, Becker NS, O'Mahony CA, Goss JA, Aloia TA. 2008; Long-term outcomes following liver transplantation for hepatic hemangioendothelioma: the UNOS experience from 1987 to 2005. J Gastrointest Surg. 12:110–6. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-007-0247-3. PMID: 17710508.
Article13. Marino IR, Todo S, Tzakis AG, Klintmalm G, Kelleher M, Iwatsuki S, et al. 1988; Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma with liver transplantation. Cancer. 62:2079–84. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(19881115)62:10<2079::AID-CNCR2820621002>3.0.CO;2-J.
Article14. Seo HI, Park SJ, Kim SH, Suh KS, Yi NJ, Lee WJ, et al. 2006; A hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma treated by living donor liver transplantation. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 10:47–50.15. Jung DH, Hwang S, Hong SM, Kim KH, Lee YJ, Ahn CS, et al. 2016; Clinicopathological features and prognosis of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma after liver resection and transplantation. Ann Transplant. 21:784–90. DOI: 10.12659/AOT.901172. PMID: 28031549.
Article16. Hwang S, Ha TY, Song GW, Jung DH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. 2015; Quantified risk assessment for major hepatectomy via the indocyanine green clearance rate and liver volumetry combined with standard liver volume. J Gastrointest Surg. 19:1305–14. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-015-2846-8. PMID: 25947549.
Article17. Song GW, Lee SG, Hwang S, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. 2016; ABO-incompatible adult living donor liver transplantation under the desensitization protocol with rituximab. Am J Transplant. 16:157–70. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.13444. PMID: 26372830.
Article18. Yoon YI, Hwang S, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. 2016; Postresection outcomes of combined hepatocellular carcinoma-cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 20:411–20. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-015-3045-3. PMID: 26628072.
Article19. Miettinen M, Fletcher CD, Kindblom LG, Zimmermann A, Tsui WM. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND, editors. 2010. Mesenchymal tumours of the liver. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. International Agency for Research on Cancer;Lyon, Fr: p. 241–50.20. Lai Q, Feys E, Karam V, Adam R, Klempnauer J, Oliverius M, et al. 2017; Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and adult liver transplantation: proposal for a prognostic score based on the analysis of the ELTR-ELITA Registry. Transplantation. 101:555–64. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001603. PMID: 28212256.21. Kamath PS, Kim WR. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group. 2007; The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology. 45:797–805. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21563. PMID: 17326206.
Article22. Grotz TE, Nagorney D, Donohue J, Que F, Kendrick M, Farnell M, et al. 2010; Hepatic epithelioid haemangioendothelioma: is transplantation the only treatment option? HPB (Oxford). 12:546–53. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00213.x. PMID: 20887322. PMCID: PMC2997660.
Article23. Simpson ND, Ahmed AM, Simpson PW, Parkar JA, Keeffe EB, Ahmed A. 2003; Living donor liver transplantation in a patient with hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 37:349–50. DOI: 10.1097/00004836-200310000-00017. PMID: 14506396.
Article24. Galvão FH, Bakonyi-Neto A, Machado MA, Farias AQ, Mello ES, Diz ME, et al. 2005; Interferon alpha-2B and liver resection to treat multifocal hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a relevant approach to avoid liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 37:4354–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.11.022. PMID: 16387119.
Article25. Cardinal J, de Vera ME, Marsh JW, Steel JL, Geller DA, Fontes P, et al. 2009; Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a single-institution experience with 25 cases. Arch Surg. 144:1035–9. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.2009.121. PMID: 19917940.26. Brahmbhatt M, Prenner S, Bittermann T. 2020; Liver transplantation for hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is facilitated by exception points with acceptable long-term outcomes. Transplantation. 104:1187–92. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002982. PMID: 31577674.
Article27. Kim MS. 2016; Modification of emergency status in deceased donor liver allocation: evidence for Korean model of end-stage liver disease (MELD) system. J Korean Soc Transplant. 30:51–8. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.2.51.
Article28. Lomaglio L, Isaac J, Mirza D, Perera MT, Muiesan P. 2014; Management of synchronous vascular and ductal anomalies in living donor liver transplantation for hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Liver Transpl. 20:247–9. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23781. PMID: 24166881.
Article29. Hasegawa K, Sugawara Y, Ikeda M, Ishizawa T, Ohashi K, Makuuchi M. 2006; Living donor liver transplantation for epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: report of a case. Surg Today. 36:1024–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00595-006-3292-8. PMID: 17072729.
Article30. Ha HS, Hong JJ, Kim IO, Lee SR, Lee AY, Ha TY, et al. 2019; Deceased donor liver transplantation under the Korean model for end-stage liver disease score-based liver allocation system: 2-year allocation results at a high-volume transplantation center. Korean J Transplant. 33:112–7. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2019.33.4.112.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma Treated by Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- Prognosis of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma after living donor liver transplantation
- Hepatic Artery Reconstruction Using the Right Gastroepiploic Artery for Hepatic Artery Inflow in a Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma of the Liver: A Case Report
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver