Neonatal Med.
2021 Feb;28(1):29-35. 10.5385/nm.2021.28.1.29.
Intussusception in Neonates: Clinical Characteristics of Eight Cases in a Single Center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- KMID: 2513356
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2021.28.1.29
Abstract
- Purpose
Intussusception is the most common cause of bowel obstruction in children; however, it is rarely diagnosed in newborn infants. This study aimed to describe the clinical features of intussusception in newborn infants.
Methods
Medical records of eight patients diagnosed with intussusception during the newborn period at Ulsan University Hospital between March 2007 and March 2020 were retrospectively reviewed.
Results
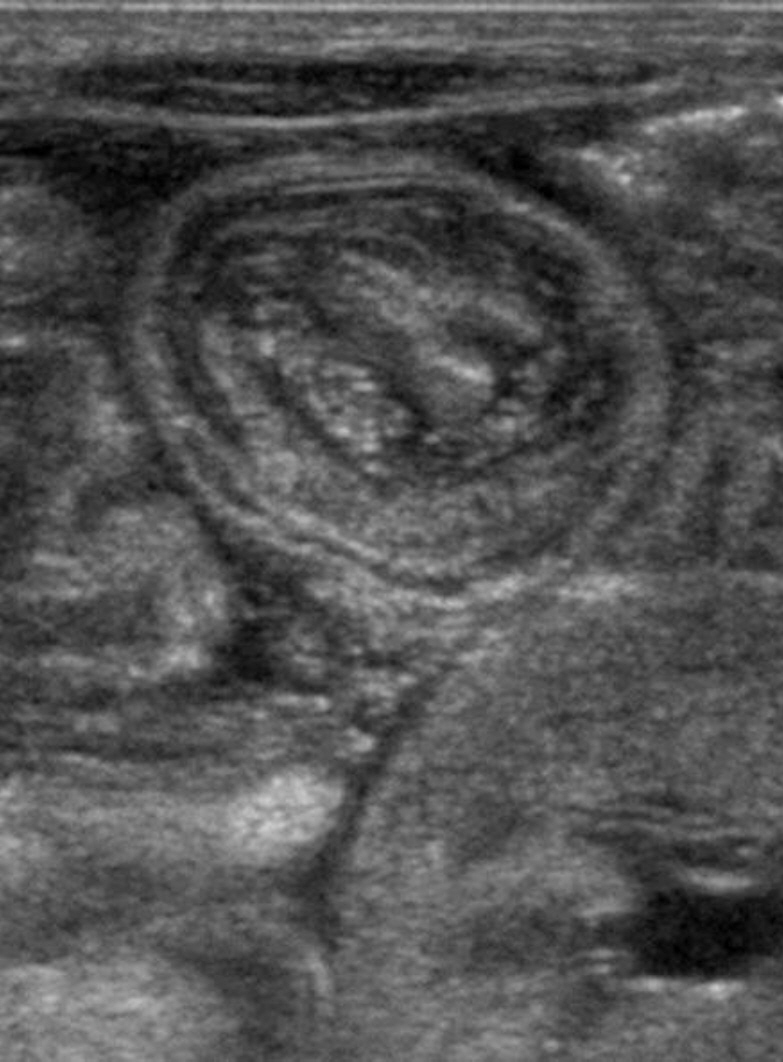
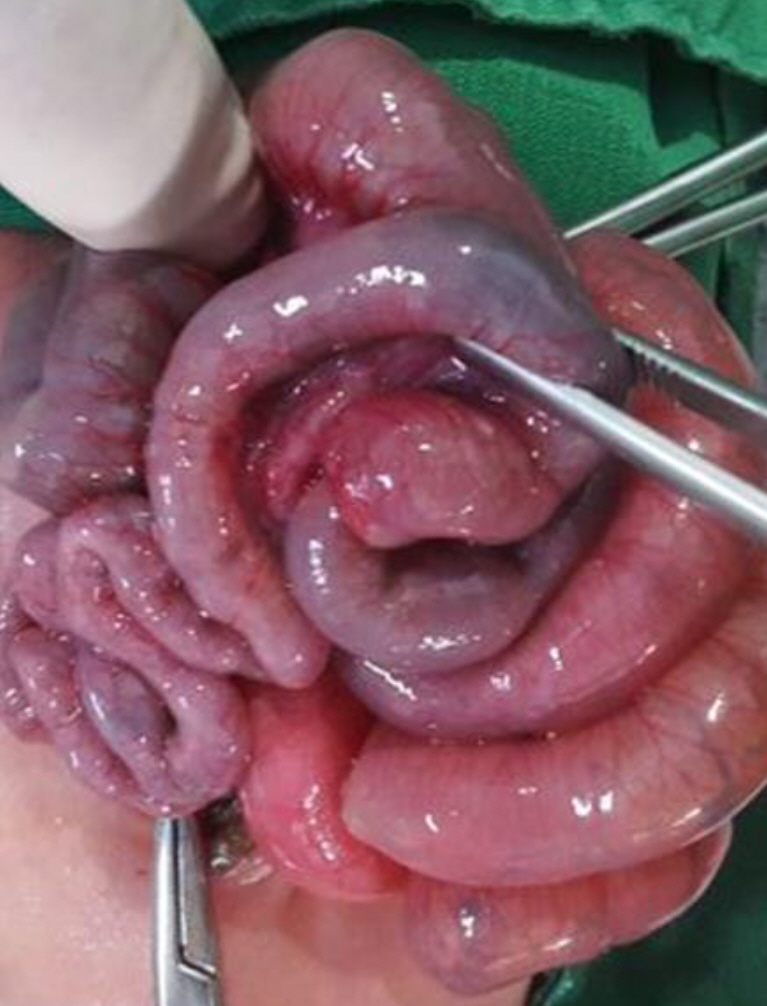
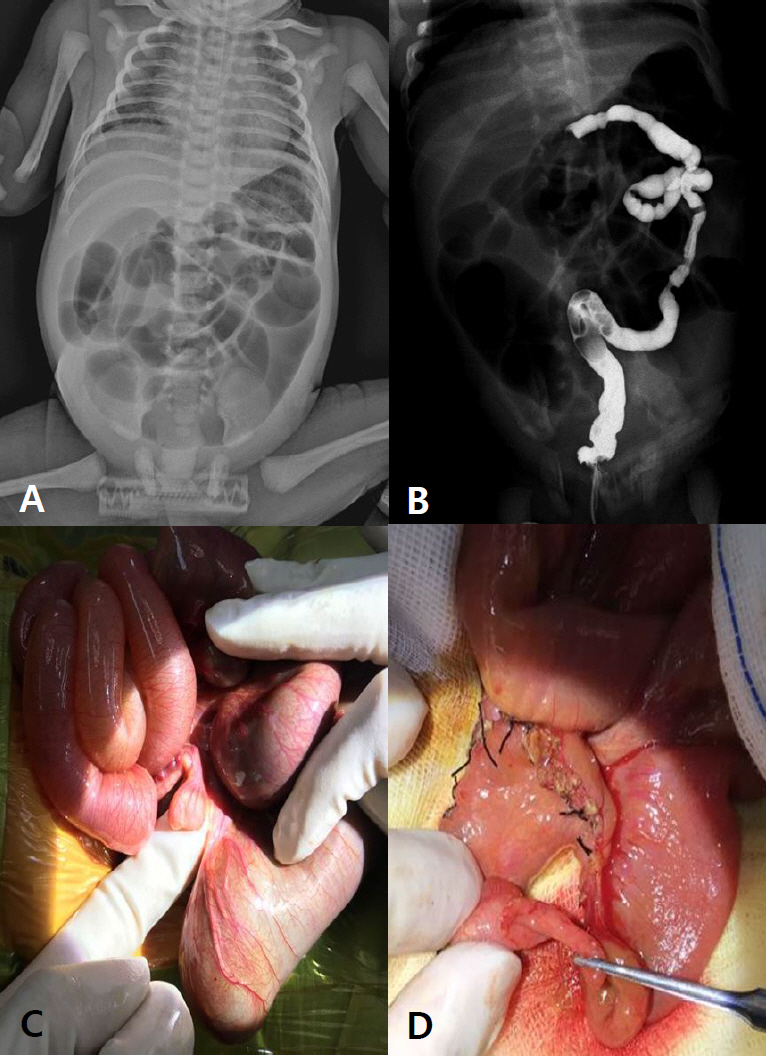
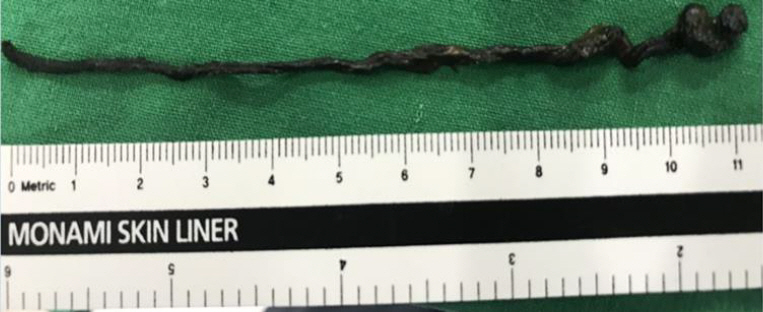
Among the eight cases, two occurred in the intrauterine period and six occurred in the postnatal period. Intrauterine intussusception presented with symptoms of bowel obstruction within 1 to 2 days after birth, and ileal atresia was diagnosed simultaneously through exploratory laparotomy. All the postnatal patients were extremely low birth weight infants (median gestational age and birth weight: 25+6 weeks and 745 g, respectively). Four cases were diagnosed preoperatively using abdominal ultrasonography. One patient was diagnosed by exploratory laparotomy because the clinical symptoms were nonspecific and difficult to differentiate from those of necrotizing enterocolitis, a more prevalent complication in preterm infants. The site of intussusception in all six patients was the small bowel. Meckel’s diverticulum (one case) and meconium obstruction (two cases) were found to be the lead point.
Conclusion
Neonatal intussusception tends to show different clinical features according to its period of occurrence. Intussusception, especially in preterm infants, has nonspecific clinical features; therefore, clinicians should always be cautious of this disease for its early diagnosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maqbool A, Liacouras CA. Ileus, adhesions, intussusception, and closed-loop obstructions. In : Kliegman ARM, editor. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 21st ed. Elsevier;2020. p. 1965–7.2. Rachelson MH, Jernigan JP, Jackson WF. Intussusception in the newborn infant with spontaneous expulsion of the intussusceptum; a case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr. 1955; 47:87–94.3. Wang NL, Yeh ML, Chang PY, Sheu JC, Chen CC, Lee HC, et al. Prenatal and neonatal intussusception. Pediatr Surg Int. 1998; 13:232–6.4. Ueki I, Nakashima E, Kumagai M, Tananari Y, Kimura A, Fukuda S, et al. Intussusception in neonates: analysis of 14 Japanese patients. J Paediatr Child Health. 2004; 40:388–91.5. Patriquin HB, Afshani E, Effman E, Griscom T, Johnson F, Kramer SS, et al. Neonatal intussusception. Report of 12 cases. Radiology. 1977; 125:463–6.6. Lee BY, Kim YH, Hwang JB, Kim CS, Lee SL, Kwon TC, et al. A case of ileao-ileal intrauterine intussusception in a preterm neonate. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005; 8:247–51.7. Hong J. Ileal Atresia due to intrauterine intussusception. J Korean Surg Soc. 1997; 52:732–7.8. Huang WC, Wang CH, Yuh YS, Chen YH, Chu CC. A rare type of ileal atresia due to intrauterine intussusception. Eur J Pediatr. 2007; 166:1177–8.9. Imai Y, Nishijima E, Muraji T, Hashimoto K, Hayashi Y, Itoh H. Fusion of intussusceptum and intussuscipiens in intrauterine intussusception: a rare type of intestinal atresia. Pathol Int. 1999; 49:962–7.10. Kim SC, Kim DY, Kim SY, Kim IK, Kim IS, Kim JE, et al. Intestinal atresia: the second national survey. J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2010; 16:1–10.11. Martinez Biarge M, Garcia-Alix A, Luisa del Hoyo M, Alarcon A, Saenz de Pipaon M, Hernandez F, et al. Intussusception in a preterm neonate: a very rare, major intestinal problem. Systematic review of cases. J Perinat Med. 2004; 32:190–4.12. Avansino JR, Bjerke S, Hendrickson M, Stelzner M, Sawin R. Clinical features and treatment outcome of intussusception in premature neonates. J Pediatr Surg. 2003; 38:1818–21.13. Nock ML, Wilson-Costello D. Intussusception in a premature neonate. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2002; 41:721–4.14. Gorgen-Pauly U, Schultz C, Kohl M, Sigge W, Moller J, Gortner L. Intussusception in preterm infants: case report and literature review. Eur J Pediatr. 1999; 158:830–2.15. Mooney DP, Steinthorsson G, Shorter NA. Perinatal intussusception in premature infants. J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 31:695–7.16. Prakash A, Doshi B, Singh S, Vyas T, Jain A. Intussusception in a premature neonate: a rare and often misdiagnosed clinical entity. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2015; 12:82–5.17. Taskinlar H, Gundogdu G, Celik Y, Avlan D, Nayci A. Challenging diagnosis between intussusception and necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants. Pediatr Int. 2014; 56:e1–3.18. Park JY, Kim YG, Lee NM, Cha SJ. Double intussusceptions with necrotizing enterocolitis diagnosed in a premature infant. Neonatal Med. 2015; 22:213–6.19. Yoo RP, Touloukian RJ. Intussusception in the newborn: a unique clinical entity. J Pediatr Surg. 1974; 9:495–8.20. Shad J, Biswas R. Ileo-colic intussusception in premature neonate. BMJ Case Rep. 2011; 2011:bcr1120115109.21. Slam KD, Teitelbaum DH. Multiple sequential intussusceptions causing bowel obstruction in a preterm neonate. J Pediatr Surg. 2007; 42:1279–81.22. Siddiqui MM, Drewett M, Burge DM. Meconium obstruction of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012; 97:F147–50.23. Kim YJ, Kim EK, Kim ES, Kim HS, Choi JH, Cheon JE, et al. Recognition, diagnosis and treatment of meconium obstruction in extremely low birth weight infants. Neonatology. 2012; 101:172–8.24. Starshak RJ, Sty JR, Bruce JS. Meconium plug syndrome associated with neonatal intussusception. Gastrointest Radiol. 1981; 6:75–8.25. Takai A, Hasegawa T, Furukawa T, Tajiri T, Hosoi H. Ultrasonographic findings of multiple intussusception in an extremely preterm infant. Arch Dis Child. 2019; 104:488.26. Aydin E. Intussusception in a preterm newborn. Pediatr Neonatol. 2018; 59:312–4.27. Raza HA, Basamad MS, El Komy MS, Al Maghrabi A, Habbach H, Abokrecha AY. Diagnosing intussusception in preterm neonates: case report and overview. J Clin Neonatol. 2014; 3:103–5.28. Wang Q, Luo M, Xie X, Wu Y, Xiang B. Can intussusceptions of small bowel and colon be transient? A prospective study. Eur J Pediatr. 2019; 178:1537–44.29. Kim JH. US features of transient small bowel intussusception in pediatric patients. Korean J Radiol. 2004; 5:178–84.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Salmonella enteritis: A Rare Cause of Adult Intussusception
- Double Intussusceptions with Necrotizing Enterocolitis Diagnosed in a Premature Infant
- Factors related to the outcome of treatment of the intussusception in children
- Gastrointestinal Emergency in Neonates and Infants: A Pictorial Essay
- Two Cases of Malignant Lymphomas in the Terminal Ileum Causing Intussusception: Diagnosis and Reduction of Intussusception by Colonoscopy