Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor for Renal Function Preservation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea.
- 6Department of Preventive Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 8Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2513009
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0172
Abstract
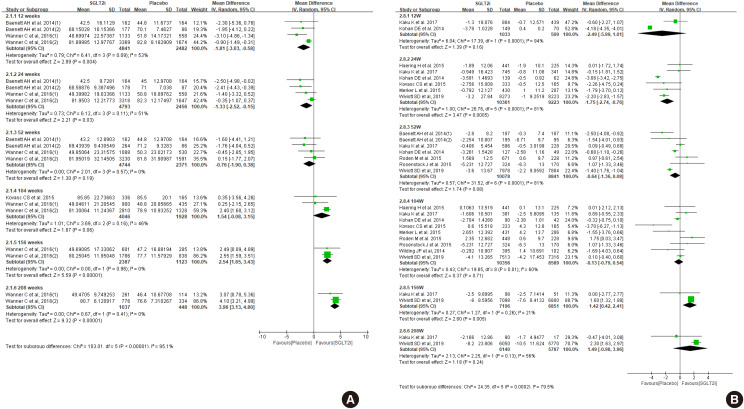
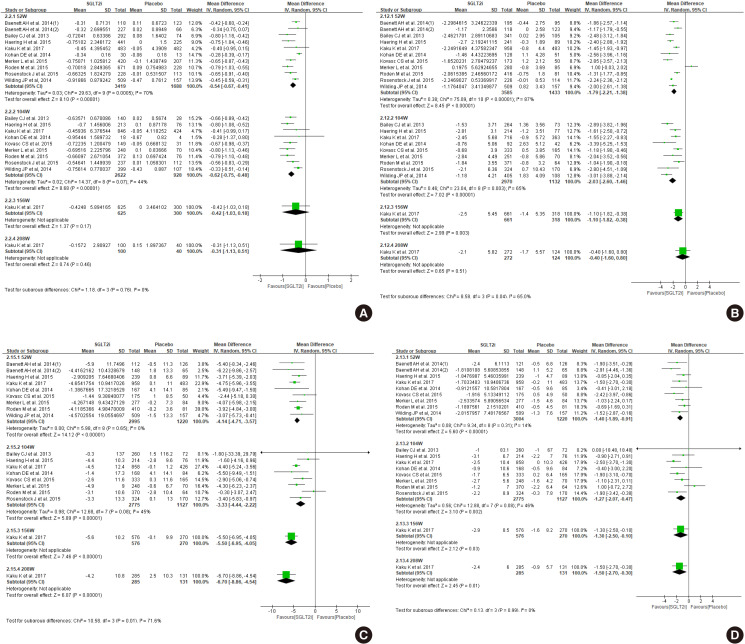
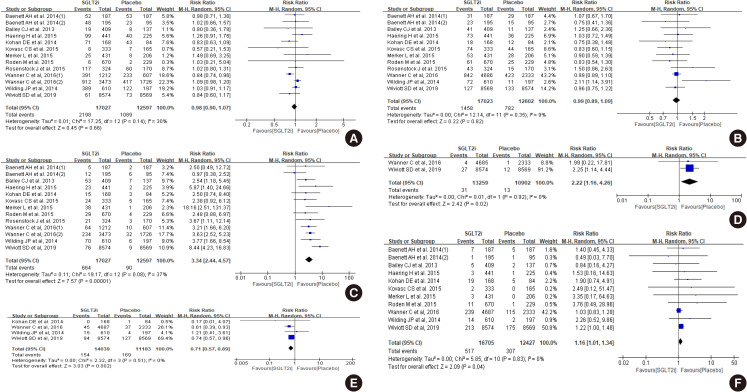
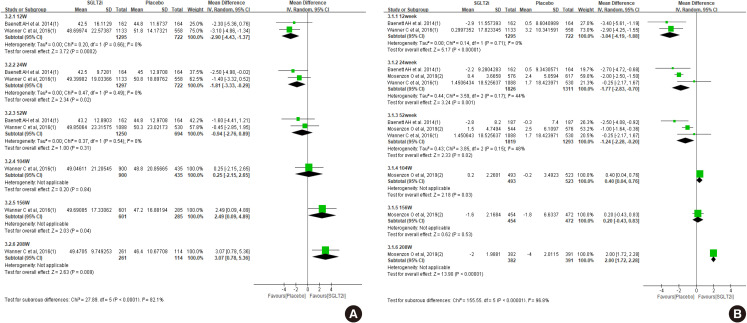
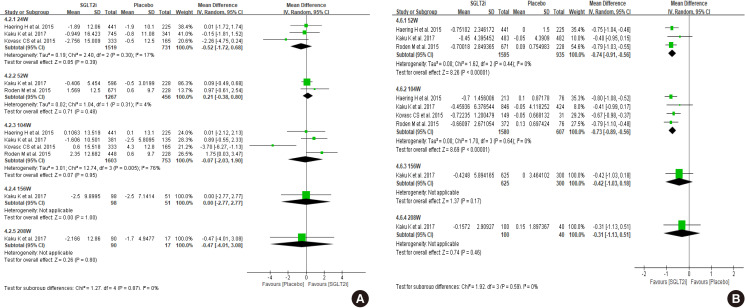
Diabetes is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Therefore, prevention of renal dysfunction is an important treatment goal in the management of diabetes. The data of landmark cardiovascular outcome trials of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed profound reno-protective effects. The Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Nephrology reviewed clinical trials and performed meta-analysis to assess the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the preservation of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). We limited the data of SGLT2 inhibitors which can be prescribed in Korea. Both eGFR value and its change from the baseline were significantly more preserved in the SGLT2 inhibitor treatment group compared to the control group after 156 weeks. However, some known adverse events were increased in SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, such as genital infection, diabetic ketoacidosis, and volume depletion. We recommend the long-term use SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for attenuation of renal function decline. However, we cannot generalize our recommendation due to lack of long-term clinical trials testing reno-protective effects of every SGLT2 inhibitor in a broad range of patients with T2DM. This recommendation can be revised and updated after publication of several large-scale renal outcome trials.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):701-712. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0002.Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):543-551. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0209.Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):279-289. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0225.
Reference
-
1. Jin DC, Yun SR, Lee SW, Han SW, Kim W, Park J. Current characteristics of dialysis therapy in Korea: 2015 registry data focusing on elderly patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2016; 35:204–211. PMID: 27957414.
Article2. Jin DC. Major changes and improvements of dialysis therapy in Korea: review of end-stage renal disease registry. Korean J Intern Med. 2015; 30:17–22. PMID: 25589829.
Article3. Jin DC, Yun SR, Lee SW, Han SW, Kim W, Park J, Kim YK. Lessons from 30 years' data of Korean end-stage renal disease registry, 1985–2015. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2015; 34:132–139. PMID: 26484037.
Article4. Jin DC, Yun SR, Lee SW, Han SW, Kim W, Park J, Kim YK. Current characteristics of dialysis therapy in Korea: 2016 registry data focusing on diabetic patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2018; 37:20–29. PMID: 29629274.
Article5. American Diabetes Association. 10. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:S105–S118. PMID: 29222381.6. Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1296–1305. PMID: 15385656.
Article7. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE. EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2117–2128. PMID: 26378978.
Article8. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Law G, Desai M, Matthews DR. CANVAS Program Collaborative Group. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:644–657. PMID: 28605608.
Article9. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, Silverman MG, Zelniker TA, Kuder JF, Murphy SA, Bhatt DL, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Wilding JPH, Ruff CT, Gause-Nilsson IAM, Fredriksson M, Johansson PA, Langkilde AM, Sabatine MS. DECLARE–TIMI 58 Investigators. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:347–357. PMID: 30415602.
Article10. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Zinman B. EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:323–334. PMID: 27299675.
Article11. Mosenzon O, Wiviott SD, Cahn A, Rozenberg A, Yanuv I, Goodrich EL, Murphy SA, Heerspink HJL, Zelniker TA, Dwyer JP, Bhatt DL, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Wilding JPH, Kato ET, Gause-Nilsson IAM, Fredriksson M, Johansson PA, Langkilde AM, Sabatine MS, Raz I. Effects of dapagliflozin on development and progression of kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:606–617. PMID: 31196815.
Article12. Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, Edwards R, Agarwal R, Bakris G, Bull S, Cannon CP, Capuano G, Chu PL, de Zeeuw D, Greene T, Levin A, Pollock C, Wheeler DC, Yavin Y, Zhang H, Zinman B, Meininger G, Brenner BM, Mahaffey KW. CREDENCE Trial Investigators. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2295–2306. PMID: 30990260.
Article13. Lee JY, Cho Y, Lee M, Kim YJ, Lee YH, Lee BW, Cha BS, Kang ES. Predictors of the therapeutic efficacy and consideration of the best combination therapy of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:158–173. PMID: 30688052.
Article14. Hong AR, Koo BK, Kim SW, Yi KH, Moon MK. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in real-world clinical practice. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:590–606. PMID: 30877709.
Article15. American Diabetes Association. 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42:S124–S138. PMID: 30559237.16. American Diabetes Association. 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:S135–S151. PMID: 31862754.17. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. McFarlane P, Cherney D, Gilbert RE, Senior P. Chronic kidney disease in diabetes. Can J Diabetes. 2018; 42 Suppl 1:S201–S209. PMID: 29650098.
Article18. Kim MK, Ko SH, Kim BY, Kang ES, Noh J, Kim SK, Park SO, Hur KY, Chon S, Moon MK, Kim NH, Kim SY, Rhee SY, Lee KW, Kim JH, Rhee EJ, Chun S, Yu SH, Kim DJ, Kwon HS, Park KS. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2019 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:398–406. PMID: 31441247.
Article19. Neuen BL, Young T, Heerspink HJL, Neal B, Perkovic V, Billot L, Mahaffey KW, Charytan DM, Wheeler DC, Arnott C, Bompoint S, Levin A, Jardine MJ. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:845–854. PMID: 31495651.
Article20. Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, Furtado RHM, Bhatt DL, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Wilding JPH, Sabatine MS. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019; 393:31–39. PMID: 30424892.
Article21. Kaku K, Lee J, Mattheus M, Kaspers S, George J, Woerle HJ. EMPA-REG OUTCOME®. Empagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease: results from EMPA-REG OUTCOME. Circ J. 2017; 81:227–234. PMID: 28025462.22. Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG RENAL trial investigators. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:369–384. PMID: 24795251.
Article23. Bailey CJ, Gross JL, Hennicken D, Iqbal N, Mansfield TA, List JF. Dapagliflozin add-on to metformin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 102-week trial. BMC Med. 2013; 11:43. PMID: 23425012.
Article24. Haering HU, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG EXTEND METSU investigators. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015; 110:82–90. PMID: 26324220.
Article25. Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Tang W, List JF. Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int. 2014; 85:962–971. PMID: 24067431.
Article26. Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G, Stella P, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. on behalf of the EMPA-REG EXTEN PIO investigators.Empagliflozin as add-on therapy to pioglitazone with or without metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther. 2015; 37:1773–1788. PMID: 26138864.
Article27. Merker L, Haring HU, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG EXTEND MET investigators. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2015; 32:1555–1567. PMID: 26031566.
Article28. Roden M, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G, Stella P, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG EXTEND MONO investigators. Safety, tolerability and effects on cardiometabolic risk factors of empagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind extension of a phase III randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015; 14:154. PMID: 26701110.
Article29. Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Zeller C, Kim G, Broedl UC, Woerle HJ. EMPA-REG BASALTM trial investigators. Impact of empagliflozin added on to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin: a 78-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015; 17:936–948. PMID: 26040302.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor for renal function preservation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement
- A Case of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Induced by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor
- The Role of the Kidney in Glucose Metabolism
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Mechanisms of Action and Various Effects
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for People with Type 1 Diabetes