Ann Lab Med.
2021 Mar;41(2):250-254. 10.3343/alm.2021.41.2.250.
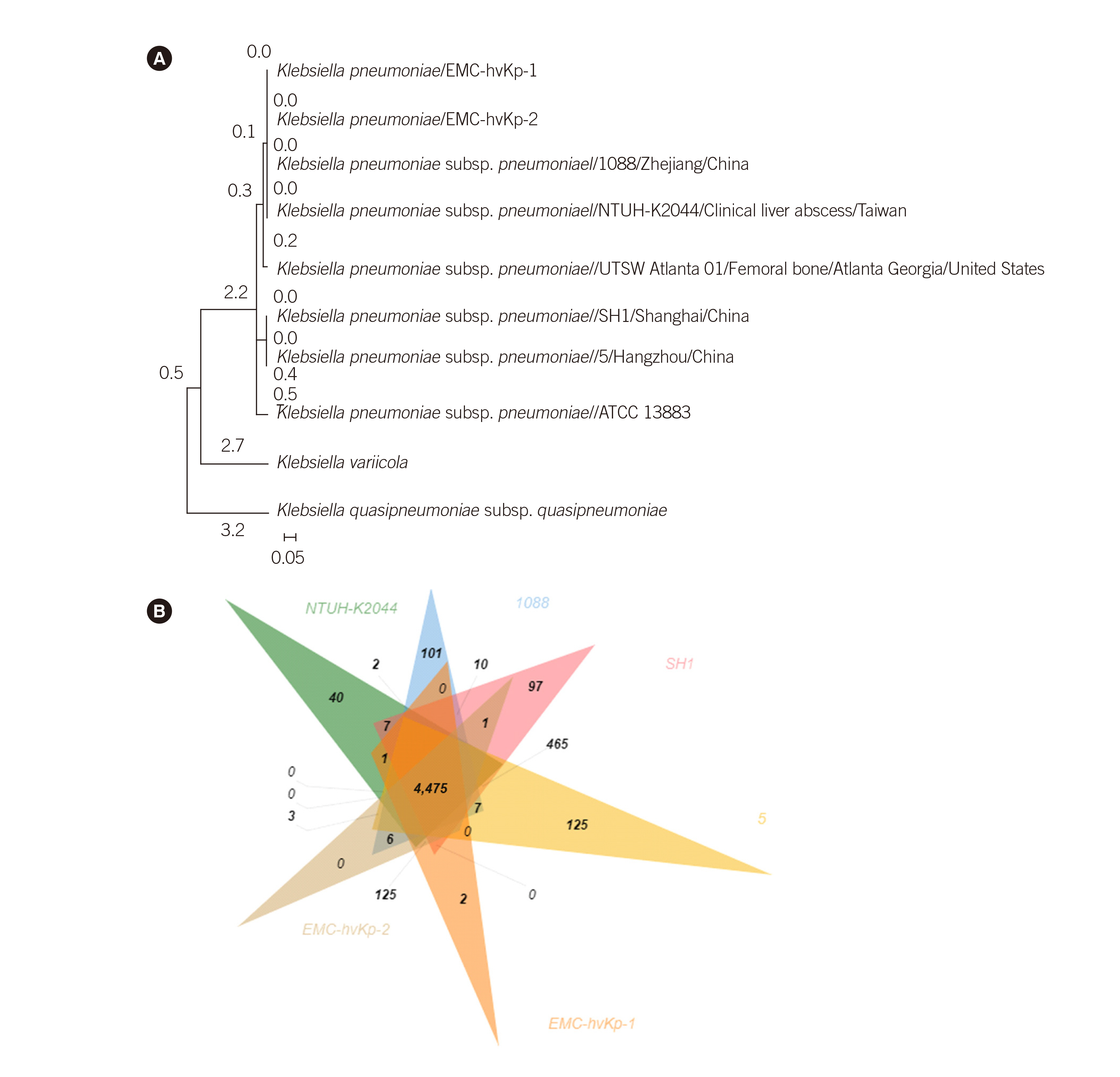
Osteomyelitis Caused by Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: The First Korean Case With Family Spread
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Departments of Laboratory Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea
- 3Departments of Internal Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seegene Medical Foundation, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Daejeon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2512675
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2021.41.2.250
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shon AS, Bajwa RPS, Russo TA. 2013; Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: a new and dangerous breed. Virulence. 4:107–18. DOI: 10.4161/viru.22718. PMID: 23302790. PMCID: PMC3654609.2. Liu Z, Gu Y, Li X, Liu Y, Ye Y, Guan S, et al. 2019; Identification and characterization of NDM-1-producing hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. Ann Lab Med. 39:167–75. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.2.167. PMID: 30430779. PMCID: PMC6240523.3. Prokesch BC, TeKippe M, Kim J, Raj P, TeKippe EM, Greenberg DE. 2016; Primary osteomyelitis caused by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet Infect Dis. 16:e190–5. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30021-4. PMID: 27402393.4. Sturm E, Tai A, Lin B, Kwong J, Athan E, Howden BP, et al. 2018; Bilateral osteomyelitis and liver abscess caused by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniaea rare clinical manifestation (case report). BMC Infect Dis. 18:380. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3277-4. PMID: 30086713. PMCID: PMC6081821.
Article5. Li W, Sun G, Yu Y, Li N, Chen M, Jin R, et al. 2014; Increasing occurrence of antimicrobial-resistant hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in China. Clin Infect Dis. 58:225–32. DOI: 10.1093/cid/cit675. PMID: 24099919.6. Chung DR, Lee H, Park MH, Jung SI, Chang HH, Kim YS, et al. 2012; Fecal carriage of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 strains closely related to liver abscess isolates in Koreans living in Korea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 31:481–6. DOI: 10.1007/s10096-011-1334-7. PMID: 21739348.7. Harada S, Tateda K, Mitsui H, Hattori Y, Okubo M, Kimura S, et al. 2011; Familial spread of a virulent clone of Klebsiella pneumoniae causing primary liver abscess. J Clin Microbiol. 49:2354–6. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00034-11. PMID: 21490191. PMCID: PMC3122714.8. Wu KM, Li LH, Yan JJ, Tsao N, Liao TL, Tsai HC, et al. 2009; Genome sequencing and comparative analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044, a strain causing liver abscess and meningitis. J Bacteriol. 191:4492–501. DOI: 10.1128/JB.00315-09. PMID: 19447910. PMCID: PMC2704730.9. Zhang R, Lin D, Chan EW, Gu D, Chen GX, Chen S. 2016; Emergence of carbapenem-resistant serotype K1 hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 60:709–11. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02173-15. PMID: 26574010. PMCID: PMC4704206.10. Gu D, Dong N, Zheng Z, Lin D, Huang M, Wang L, et al. 2018; A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: a molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 18:37–46. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30489-9. PMID: 28864030.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Osteomyelitis of the Mandible by Extended-Spectrum ββ-Lactamase Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae: A Case Report
- Rapidly Fatal Emphysematous Osteomyelitis with Multiple Septic Emboli and Liver Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Lower Leg Abscess in Klebsiella pneumoniae Invasive Syndrome Caused by Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Case Report
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Cellulitis Associated with Osteomyelitis was Suspected by Highly Elevated Inflammatory Marker Serum Procalcitonin
- Ventriculitis Associated with Invasive
Klebsiella Pneumoniae Syndrome: A Case Report