Anesth Pain Med.
2021 Jan;16(1):56-59. 10.17085/apm.20074.
Treatment of rocuronium-induced anaphylaxis using sugammadex - A case report -
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2512282
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.20074
Abstract
- Background
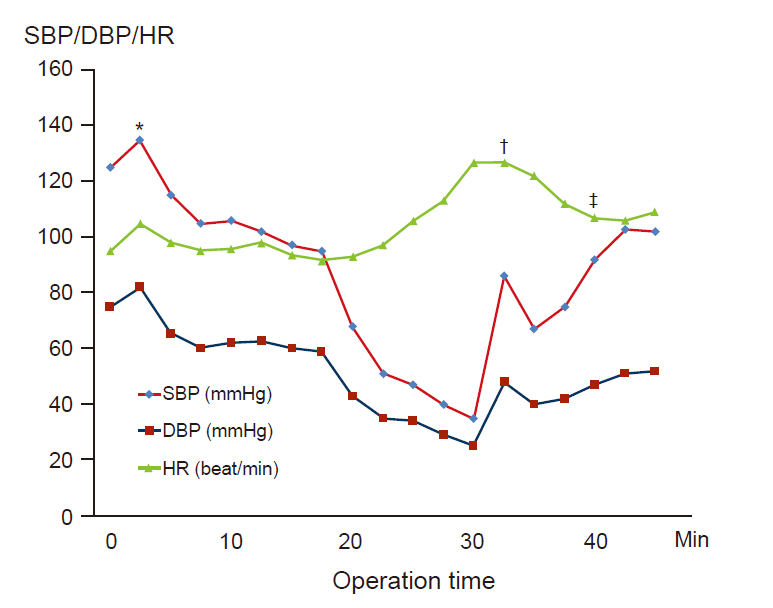
Perioperative anaphylaxis is a life-threatening clinical condition characterized by severe respiratory and cardiovascular manifestations. Neuromuscular blocking agents are the most common cause of anaphylaxis during anesthesia. Case: We report a case of rocuronium-induced anaphylaxis treated with sugammadex. A 75–year-old woman was scheduled to undergo spinal surgery. She had no history of allergies. After the injection of rocuronium, she developed hypotension and tachycardia, and skin rashes and urticaria appeared. The patient received sugammadex to delay the operation, and her vital signs were stabilized. On the 76th postoperative day, we performed intradermal tests for rocuronium, propofol, and cefazolin. Diluted rocuronium alone induced 14 mm of flare and 8 mm of wheal within 5 min, both of which disappeared within 15 min after the intradermal injection.
Conclusions
Sugammadex is a useful rocuronium antagonist that can be used to treat rocuronium-induced anaphylaxis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilò MB, El-Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, et al. World Allergy Organization. World Allergy Organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:13–37.2. Harper NJ, Dixon T, Dugué P, Edgar DM, Fay A, Gooi HC, et al. Working Party of the Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland. Suspected anaphylactic reactions associated with anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2009; 64:199–211.3. McDonnell NJ, Pavy TJ, Green LK, Platt PR. Sugammadex in the management of rocuronium-induced anaphylaxis. Br J Anaesth. 2011; 106:199–201.4. Mertes PM, Laxenaire MC; GERAP. [Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions occurring during anaesthesia in France. Seventh epidemiologic survey (January 2001-December 2002)]. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2004; 23:1133–43. French.5. Jones PM, Turkstra TP. Mitigation of rocuronium-induced anaphylaxis by sugammadex: the great unknown. Anaesthesia. 2010; 65:89–90; author reply 90.6. Peeters PA, van den Heuvel MW, van Heumen E, Passier PC, Smeets JM, van Iersel T, et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of sugammadex using single high doses (up to 96 mg/kg) in healthy adult subjects: a randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled, single-centre study. Clin Drug Investig. 2010; 30:867–74.7. Kim KS. Clinical use of sugammadex. Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 6:307–13.8. Fisher MM, Baldo BA. The incidence and clinical features of anaphylactic reactions during anesthesia in Australia. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 1993; 12:97–104.9. Hepner DL, Castells MC. Anaphylaxis during the perioperative period. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:1381–95.10. Mertes PM, Laxenaire MC, Alla F; Groupe d'Etudes des Réactions Anaphylactoïdes Peranesthésiques. Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions occurring during anesthesia in France in 1999-2000. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:536–45.11. Axon AD, Hunter JM. Editorial III: anaphylaxis and anaesthesia--all clear now? Br J Anaesth. 2004; 93:501–4.12. Mertes PM, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Leynadier F, Laxenaire MC. Skin reactions to intradermal neuromuscular blocking agent injections: a randomized multicenter trial in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology. 2007; 107:245–52.13. Reitter M, Petitpain N, Latarche C, Cottin J, Massy N, Demoly P, et al. French Network of Regional Pharmacovigilance Centres. Fatal anaphylaxis with neuromuscular blocking agents: a risk factor and management analysis. Allergy. 2014; 69:954–9.14. Gijsenbergh F, Ramael S, Houwing N, van Iersel T. First human exposure of Org 25969, a novel agent to reverse the action of rocuronium bromide. Anesthesiology. 2005; 103:695–703.15. Jones RK, Caldwell JE, Brull SJ, Soto RG. Reversal of profound rocuronium-induced blockade with sugammadex: a randomized comparison with neostigmine. Anesthesiology. 2008; 109:816–24.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anaphylaxis induced by sugammadex and sugammadex-rocuronium complex -a case report-
- Anaphylactic shock after sugammadex administration, induced by formation of a sugammadex-rocuronium complex: a case report
- A suspected sugammadex-induced anaphylactic shock: A case report
- In the hour of Sugammadex
- Consecutive anaphylaxis due to rocuronium and cisatracurium during general anesthesia: A case report