Endocrinol Metab.
2020 Dec;35(4):960-964. 10.3803/EnM.2020.732.
Establishment of Reference Intervals for Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor I in Korean Adult Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2511024
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.732
Abstract
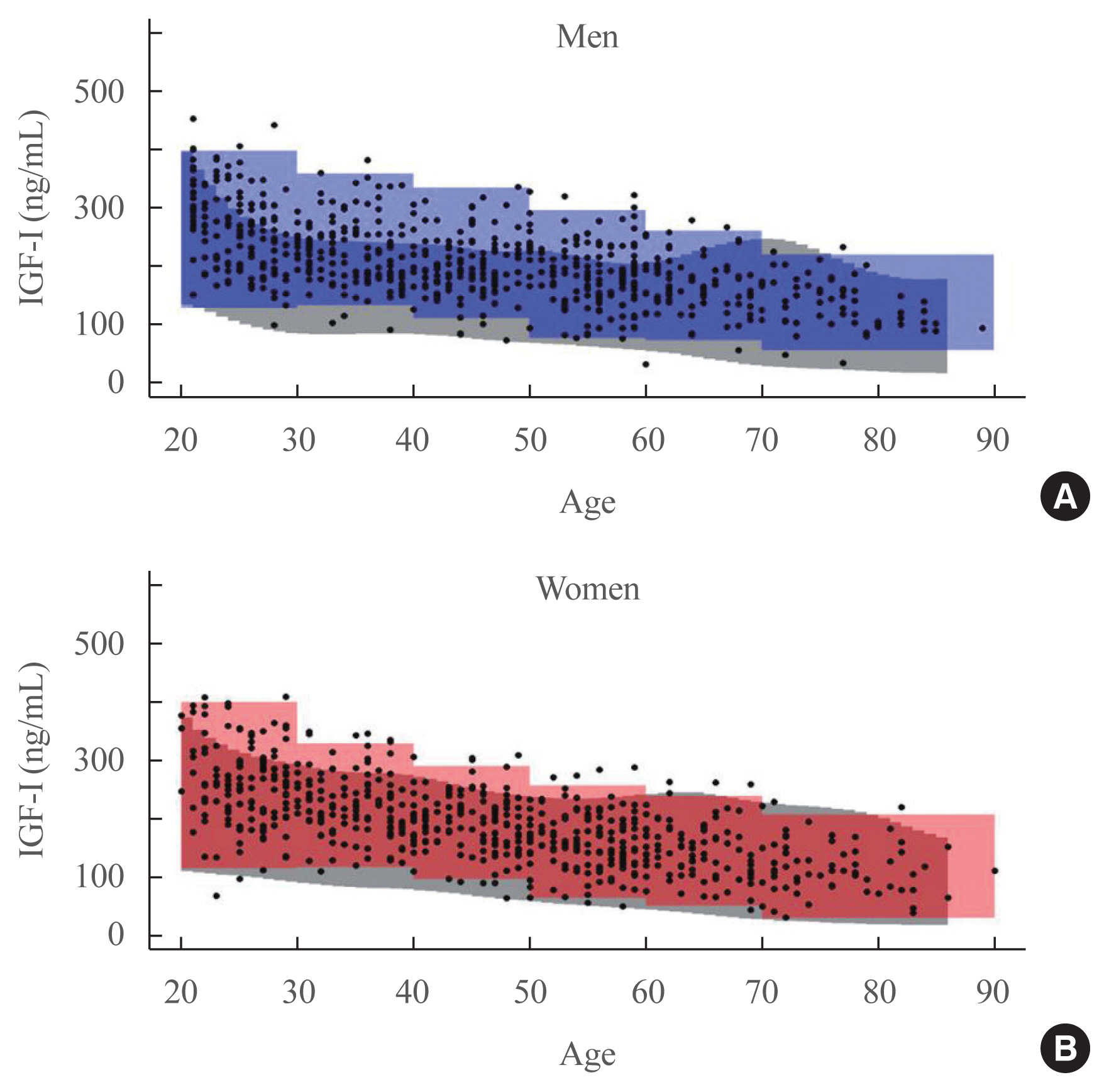
- Appropriate reference intervals of serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is important for diagnosing and monitoring patients with growth hormone-related diseases. To establish reference intervals, adult individuals (n=1,334, 680 men and 654 women) were divided into six age groups (20–29, 30–39, 40–49, 50–59, 60–69, ≥70). Serum IGF-I was measured by chemiluminescence immunoassay (Liaison). Concordance of patient classification based on reference intervals, manufacturer’s intervals, and standard deviation score (SDS) was evaluated. New reference intervals had higher upper and lower limits than those specified by the manufacturer. The agreement between classification using new reference interval and the manufacturer’s reference interval, and that using new reference interval and SDS was 75.0% (weighted kappa, 0.17), 91.9% (weighted kappa, 0.51) in men and 91.0% (weighted kappa, 0.41), 92.5% (weighted kappa, 0.53) in women, respectively. Reference intervals should be established not only based on age and sex, but also on ethnicity and assay method.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mavromati M, Kuhn E, Agostini H, Brailly-Tabard S, Massart C, Piketty ML, et al. Classification of patients with GH disorders may vary according to the IGF-I assay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:2844–52.
Article2. Dogansen SC, Yalin GY, Tanrikulu S, Yarman S. Impact of glucose metabolism disorders on IGF-1 levels in patients with acromegaly. Horm Metab Res. 2018; 50:408–13.
Article3. Hyun SE, Lee BC, Suh BK, Chung SC, Ko CW, Kim HS, et al. Reference values for serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in Korean children and adolescents. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45:16–21.
Article4. Choi HK, Kong MH, Ahn BH, Kim SM, Lee DJ, Kim KM. Insulin-like growth factor 1 level and its relating factor in Korean healthy adults. Korean J Fam Med. 2009; 30:15–22.
Article5. Zhu H, Xu Y, Gong F, Shan G, Yang H, Xu K, et al. Reference ranges for serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in healthy Chinese adults. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0185561.
Article6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals in the clinical laboratory; approved guideline. 3rd ed. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.7. Tukey JW. Exploratory data analysis. Reading: Addison-Wesley Pub;1977.8. Solberg HE. Approved recommendation (1987) on the theory of reference values. Part 5. Statistical treatment of collected reference values. Determination of reference limits. Clin Chim Acta. 1987; 170:S13–32.
Article9. Chanson P, Arnoux A, Mavromati M, Brailly-Tabard S, Massart C, Young J, et al. Reference values for IGF-I serum concentrations: comparison of six immunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 101:3450–8.
Article10. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–74.
Article11. Clemmons DR. Consensus statement on the standardization and evaluation of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor assays. Clin Chem. 2011; 57:555–9.
Article12. Gayan-Ramirez G, Vanderhoydonc F, Verhoeven G, Decramer M. Acute treatment with corticosteroids decreases IGF-1 and IGF-2 expression in the rat diaphragm and gastrocnemius. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 159:283–9.
Article13. Prummel MF, Wiersinga WM, Oosting H, Endert E. The effect of long-term prednisone treatment on growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1. J Endocrinol Invest. 1996; 19:620–3.
Article14. Clemmons DR. Value of insulin-like growth factor system markers in the assessment of growth hormone status. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2007; 36:109–29.
Article15. Teppala S, Shankar A. Association between serum IGF-1 and diabetes among U.S. adults. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:2257–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship of Insulin like Growth Factor I with Pharmacologically Stimulated Growth Hormone Secretion in Growth Hormone Deficient Children
- Alteration of Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor(IGF)-I and IGF-Binding Protein-2 in Healthy Population with Aging
- Reference Ranges of Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3: Results from a Multicenter Study in Healthy Korean Adults
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding proteins axis in diabetes mellitus
- Serum Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Children with Idiopathic Short Stature