J Liver Cancer.
2020 Sep;20(2):167-172. 10.17998/jlc.20.2.167.
Huge Hepatocellular Carcinoma Exhibiting a Complete Response after Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2508029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.167
Abstract
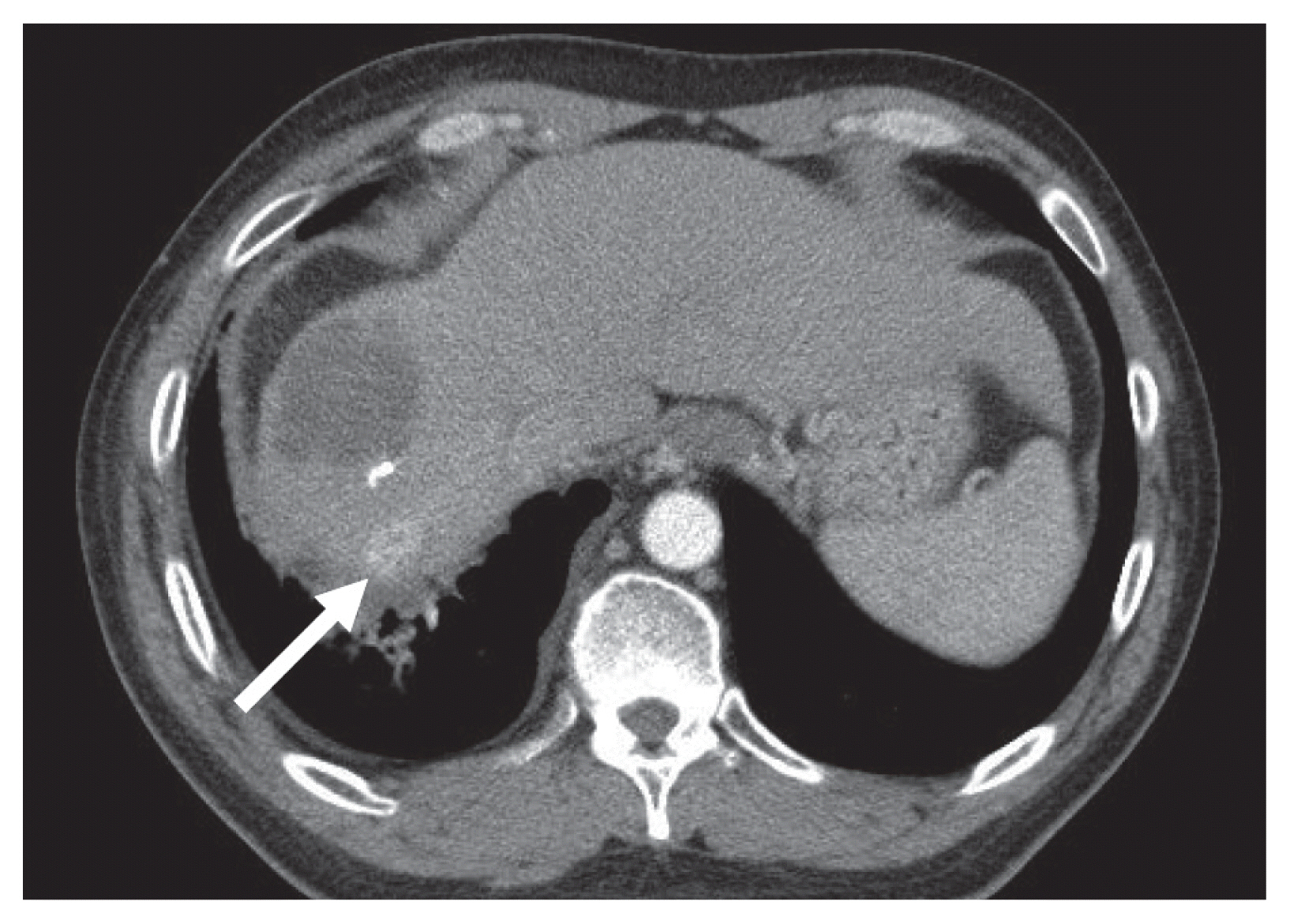
- To date, there are limited data and little consensus on treatment strategies for huge hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Surgical resection provides significantly better survival than other modalities for single large HCC regardless of tumor stage. Recently, with technological advances in radiation therapy, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is considered an alternative treatment option for HCC. Herein, we present a case of huge HCC that was successfully managed by SBRT. Transarterial embolization, previously performed in Russia, was incomplete. It was also not suitable for resection and transarterial chemoembolization. Although the rationale for radiotherapy in huge HCC was insufficient, SBRT was performed because no other treatment options were available. Additional radiofrequency ablation was performed for small HCC in a different segment, and radiological complete response (CR) was achieved. The CR was maintained over 4 years. Therefore, SBRT may be an alternative treatment option for large HCC that is not suitable for curative treatment.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424.2. Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 16:589–604.3. Kudo M, Izumi N, Kubo S, Kokudo N, Sakamoto M, Shiina S, et al. Report of the 20th nationwide follow-up survey of primary liver cancer in Japan. Hepatol Res. 2020; 50:15–46.4. Ohri N, Dawson LA, Krishnan S, Seong J, Cheng JC, Sarin SK, et al. Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: New Indications and Directions for Future Study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016; 108:djw133.5. Rim CH, Seong J. Application of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in current clinical practice guidelines. Radiat Oncol J. 2016; 34:160–167.6. Citrin DE. Recent developments in radiotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:2200–2201.7. Korean Liver Cancer Association, National Cancer Center. 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2019; 20:1042–1113.8. Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010; 30:52–60.9. Xue T, Le F, Chen R, Xie X, Zhang L, Ge N, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for huge hepatocellular carcinoma with diameter over ten centimeters: a large cohort study. Med Oncol. 2015; 32:64.10. Liu PH, Su CW, Hsu CY, Hsia CY, Lee YH, Huang YH, et al. Solitary large hepatocellular carcinoma: staging and treatment strategy. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0155588.11. Sanuki N, Takeda A, Kunieda E. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:3100–3111.12. Cheng SH, Lin YM, Chuang VP, Yang PS, Cheng JC, Huang AT, et al. A pilot study of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999; 14:1025–1033.13. Lawrence TS, Robertson JM, Anscher MS, Jirtle RL, Ensminger WD, Fajardo LF. Hepatic toxicity resulting from cancer treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995; 31:1237–1248.14. Choi SH, Seong J. Strategic application of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2018; 24:114–134.15. Chen CP. Role of radiotherapy in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2019; 7:183–190.16. Su TS, Liang P, Liang J, Lu HZ, Jiang HY, Cheng T, et al. Long-term survival analysis of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus liver resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017; 98:639–646.17. Scorsetti M, Comito T, Cozzi L, Clerici E, Tozzi A, Franzese C, et al. The challenge of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): results of a single-institutional experience on stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015; 141:1301–1309.18. Pan CC, Kavanagh BD, Dawson LA, Li XA, Das SK, Miften M, et al. Radiation-associated liver injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76(3 Suppl):S94–S100.19. Huertas A, Baumann AS, Saunier-Kubs F, Salleron J, Oldrini G, Croisé-Laurent V, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an ablative treatment for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2015; 115:211–216.20. Jun BG, Kim YD, Cheon GJ, Kim ES, Jwa E, Kim SG, et al. Clinical significance of radiation-induced liver disease after stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Intern Med. 2018; 33:1093–1102.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A Case of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Showed Complete Response by Combined Therapy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
- A Case of Complete Response with Biliary Stenosis after Hepatic Arterial Injection and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy to Hepatoecllular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis
- A Case of Achieving Complete Remission with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Macrovascular Invasion after Repeated Transarerial Chemoembolization
- A Case of Achieving Complete Remission with Combination of Stereotac-tic Body Radiation Therapy and Transarterial Chemoemoblization in Pa-tients with 4.8 cm Sized Infiltrative Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Arte-riovenous Shunt