Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Oct;52(4):1188-1198. 10.4143/crt.2020.402.
Tumor Control and Overall Survival after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Pulmonary Oligometastases from Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology and Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology and Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Neurology and Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- KMID: 2507944
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2020.402
Abstract
- Purpose
In pulmonary oligometastases from colorectal cancer (POM-CRC), the primarily recommended local therapy is metastasectomy. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is another local therapy modality that is considered as an alternative option in patients who cannot undergo surgery. The purpose of this meta-analysis is to demonstrate the effects of SBRT on POM-CRC by integrating the relevant studies.
Materials and Methods
The authors explored MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and SCOPUS, and selected studies including patients treated with SBRT for POM-CRC and availability of local control (LC) or overall survival (OS) rate. In this meta-analysis, the effect of SBRT was presented in the form of the LC and OS rates for 1, 2, 3, and 5 years after SBRT as pooled estimates, and the frequency of pulmonary toxicity of grade 3 or higher after SBRT (PTG3-SBRT).
Results
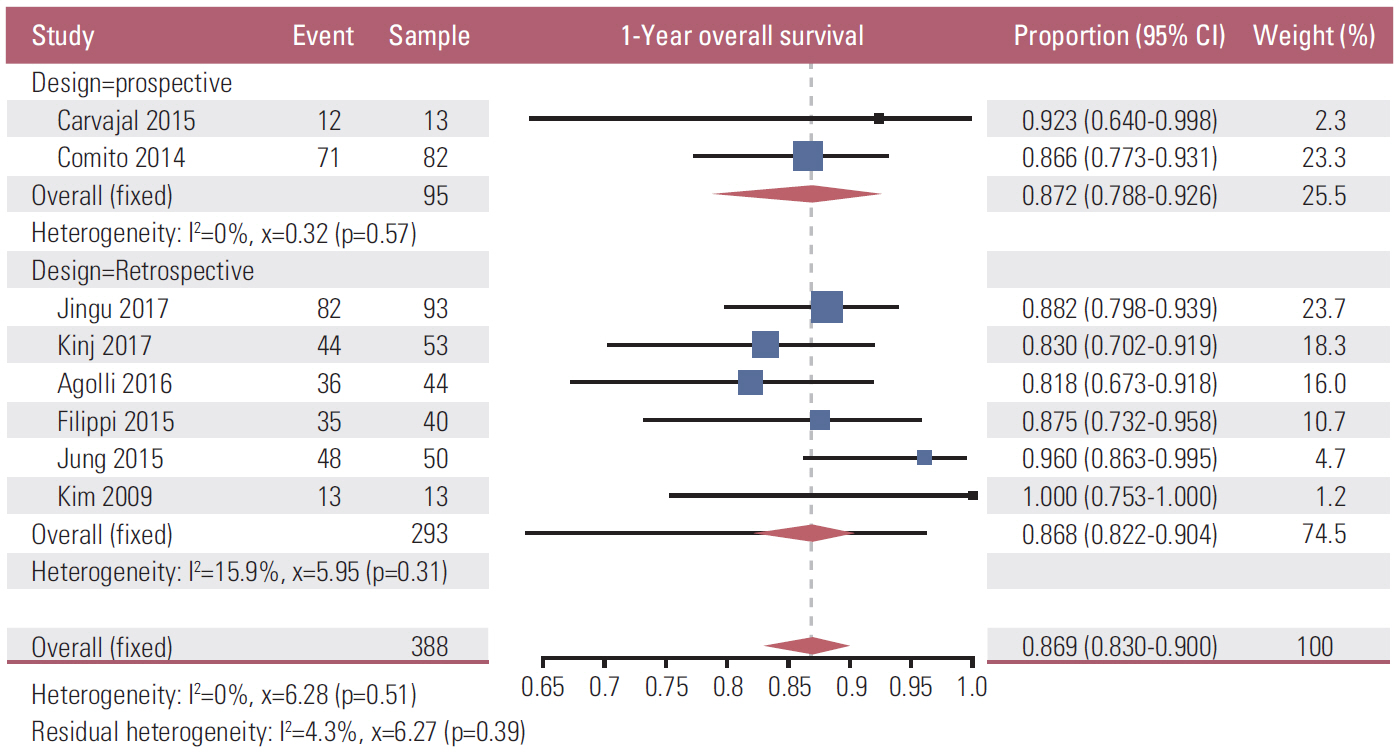
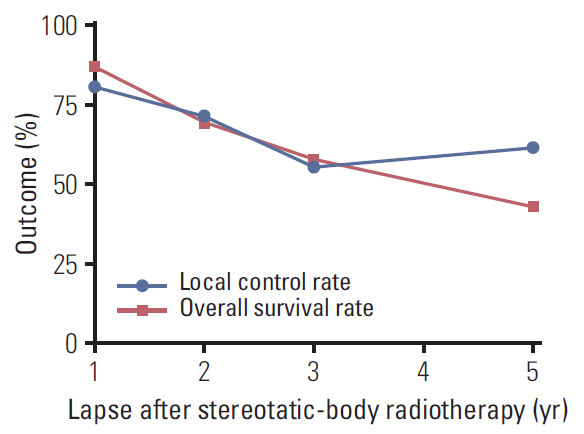
Fourteen full texts among the searched 4,984 studies were the objects of this meta-analysis. The overall number of POM-CRC patients was 495 as per the integration of 14 studies. The pooled estimate LC rate at 1, 2, 3, and 5 years after SBRT was 81.0%, 71.5%, 56.0%, and 61.8%, and the OS rate was 86.9%, 70.1%, 57.9%, and 43.0%, respectively. The LC and OS rates gradually declined until 3 years after SBRT in a similar pattern. Among the 14 studies, only two studies reported PTG3-SBRT as 2.2% and 10.8%, respectively.
Conclusion
For POM-CRC, SBRT is an ablative therapy with a benefit on LC and OS rates and less adverse effects on the lung.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13:8–10.
Article2. Elias D, Benizri E, Vernerey D, Eldweny H, Dipietrantonio D, Pocard M. Preoperative criteria of incomplete resectability of peritoneal carcinomatosis from non-appendiceal colorectal carcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2005; 29:1010–3.
Article3. Galandiuk S, Wieand HS, Moertel CG, Cha SS, Fitzgibbons RJ Jr, Pemberton JH, et al. Patterns of recurrence after curative resection of carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992; 174:27–32.4. Lee WS, Yun SH, Chun HK, Lee WY, Yun HR, Kim J, et al. Pulmonary resection for metastases from colorectal cancer: prognostic factors and survival. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007; 22:699–704.
Article5. Van Cutsem E, Nordlinger B, Adam R, Kohne CH, Pozzo C, Poston G, et al. Towards a pan-European consensus on the treatment of patients with colorectal liver metastases. Eur J Cancer. 2006; 42:2212–21.
Article6. Gonzalez M, Poncet A, Combescure C, Robert J, Ris HB, Gervaz P. Risk factors for survival after lung metastasectomy in colorectal cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:572–9.
Article7. Pfannschmidt J, Muley T, Hoffmann H, Dienemann H. Prognostic factors and survival after complete resection of pulmonary metastases from colorectal carcinoma: experiences in 167 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003; 126:732–9.
Article8. Saito Y, Omiya H, Kohno K, Kobayashi T, Itoi K, Teramachi M, et al. Pulmonary metastasectomy for 165 patients with colorectal carcinoma: a prognostic assessment. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002; 124:1007–13.
Article9. Yedibela S, Klein P, Feuchter K, Hoffmann M, Meyer T, Papadopoulos T, et al. Surgical management of pulmonary metastases from colorectal cancer in 153 patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006; 13:1538–44.
Article10. Zampino MG, Maisonneuve P, Ravenda PS, Magni E, Casiraghi M, Solli P, et al. Lung metastases from colorectal cancer: analysis of prognostic factors in a single institution study. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014; 98:1238–45.
Article11. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Rectal cancer (version 1. 2020) [Internet]. Plymouth Meeting, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network;2020. [cited 2020 Jul 19]. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/rectal.pdf.12. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Colon cancer (version 1. 2020) [Internet]. Plymouth Meeting, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network;2020. [cited 2020 Jul 19]. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colon.pdf.13. Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, Sobrero A, Van Krieken JH, Aderka D, et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016; 27:1386–422.
Article14. Kobiela J, Spychalski P, Marvaso G, Ciardo D, Dell’Acqua V, Kraja F, et al. Ablative stereotactic radiotherapy for oligometastatic colorectal cancer: systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018; 129:91–101.
Article15. Cao C, Wang D, Tian DH, Wilson-Smith A, Huang J, Rimner A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of stereotactic body radiation therapy for colorectal pulmonary metastases. J Thorac Dis. 2019; 11:5187–98.
Article16. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151:264–9.
Article17. Booth A, Clarke M, Dooley G, Ghersi D, Moher D, Petticrew M, et al. The nuts and bolts of PROSPERO: an international prospective register of systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2012; 1:2.
Article18. Clarivate Analytics. Endnote X9.2. Philadelphia, PA: Clarivate Analytics;2019.19. R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing [Internet]. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing;2019. [cited 2020 Jul 19]. Available from: https://www.R-project.org/.20. Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of norandomized wtudies in meta-analysis [Internet]. Ottawa: Ottawa Hospital Research Institue;2000. [cited 2020 Jul 19]. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.21. Agolli L, Bracci S, Nicosia L, Valeriani M, De Sanctis V, Osti MF. Lung metastases treated with stereotactic ablative radiation therapy in oligometastatic colorectal cancer patients: outcomes and prognostic factors after long-term follow-up. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2017; 16:58–64.
Article22. Aoki M, Hatayama Y, Kawaguchi H, Hirose K, Sato M, Akimoto H, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung metastases as oligo-recurrence: a single institutional study. J Radiat Res. 2016; 57:55–61.
Article23. Bae SH, Kim MS, Cho CK, Kang JK, Kang HJ, Kim YH, et al. High dose stereotactic body radiotherapy using three fractions for colorectal oligometastases. J Surg Oncol. 2012; 106:138–43.
Article24. Binkley MS, Trakul N, Jacobs LR, von Eyben R, Le QT, Maxim PG, et al. Colorectal histology is associated with an increased risk of local failure in lung metastases treated with stereotactic ablative radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015; 92:1044–52.
Article25. Carvajal C, Navarro-Martin A, Cacicedo J, Ramos R, Guedea F. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for colorectal lung oligometastases: preliminary single-institution results. J BUON. 2015; 20:158–65.26. Comito T, Cozzi L, Clerici E, Campisi MC, Liardo RL, Navarria P, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) in inoperable oligometastatic disease from colorectal cancer: a safe and effective approach. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:619.
Article27. Dell’Acqua V, Surgo A, Kraja F, Kobiela J, Zerella MA, Spychalski P, et al. Stereotactic radiation therapy in oligometastatic colorectal cancer: outcome of 102 patients and 150 lesions. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2019; 36:331–42.
Article28. Filippi AR, Badellino S, Ceccarelli M, Guarneri A, Franco P, Monagheddu C, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy as first local therapy for lung oligometastases from colorectal cancer: a single-institution cohort study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015; 91:524–9.
Article29. Jingu K, Matsuo Y, Onishi H, Yamamoto T, Aoki M, Murakami Y, et al. Dose escalation improves outcome in stereotactic body radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases from colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017; 37:2709–13.30. Jung J, Song SY, Kim JH, Yu CS, Kim JC, Kim TW, et al. Clinical efficacy of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for lung metastases arising from colorectal cancer. Radiat Oncol. 2015; 10:238.
Article31. Kinj R, Bondiau PY, Francois E, Gerard JP, Naghavi AO, Leysalle A, et al. Radiosensitivity of colon and rectal lung oligometastasis treated with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2017; 16:e211–20.
Article32. Navarria P, Ascolese AM, Tomatis S, Cozzi L, De Rose F, Mancosu P, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (sbrt) in lung oligometastatic patients: role of local treatments. Radiat Oncol. 2014; 9:91.
Article33. Takeda A, Kunieda E, Ohashi T, Aoki Y, Koike N, Takeda T. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for oligometastatic lung tumors from colorectal cancer and other primary cancers in comparison with primary lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2011; 101:255–9.
Article34. Kim MS, Yoo SY, Cho CK, Yoo HJ, Choi CW, Seo YS, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy using three fractions for isolated lung recurrence from colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2009; 76:212–9.
Article35. Treasure T, Farewell V, Macbeth F, Monson K, Williams NR, Brew-Graves C, et al. Pulmonary Metastasectomy versus Continued Active Monitoring in Colorectal Cancer (PulMiCC): a multicentre randomised clinical trial. Trials. 2019; 20:718.
Article36. van Laarhoven HW, Kaanders JH, Lok J, Peeters WJ, Rijken PF, Wiering B, et al. Hypoxia in relation to vasculature and proliferation in liver metastases in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 64:473–82.
Article37. Franceschini D, Cozzi L, De Rose F, Navarria P, Franzese C, Comito T, et al. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases from radio-resistant primary tumours. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017; 143:1293–9.
Article38. Siva S, MacManus M, Ball D. Stereotactic radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases: a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:1091–9.
Article39. Jingu K, Matsushita H, Yamamoto T, Umezawa R, Ishikawa Y, Takahashi N, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases from colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 17:1533033818794936.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- Bone-only oligometastatic prostate cancer: can SABR improve outcomes? A single-center experience
- Treatment Outcome of Brain Metastasis after the Cranial Radiotherapy Followed by Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy and Its Prognostic Factors
- Stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer
- An 87-year-old patient with repeated oligorecurrences over six years whose disease were treated with radiotherapy alone