Infect Chemother.
2020 Mar;52(1):82-92. 10.3947/ic.2020.52.1.82.
Higher Risk for All-cause Mortality of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia in Patients with Non-Dialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2507329
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2020.52.1.82
Abstract
- Background
Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB) is a common and serious infection with a high mortality. Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are vulnerable to SAB, but there have been few studies performed on the clinical characteristics and outcomes of SAB in CKD patients stratified by dialysis. We aimed to estimate the all-cause mortality and identify its predictors in patients with CKD.
Materials and Methods
We conducted a retrospective study on the patients with SAB hospitalized in a tertiary care center in Korea between March 2014 and December 2018. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to compare all-cause mortality following SAB among patients with non-dialysis dependent CKD (ND-CKD), those receiving dialysis, and those without CKD (non-CKD). The predictors of mortality among CKD patients were analyzed by Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results
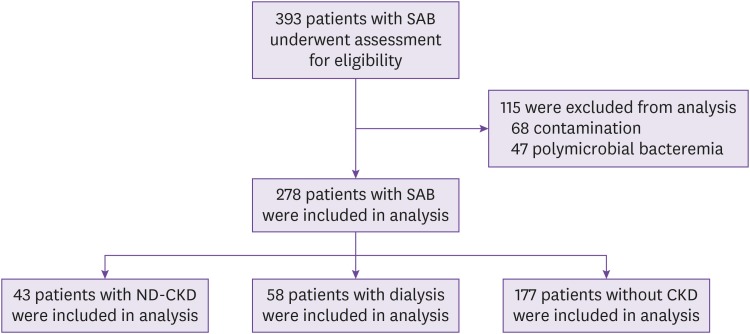
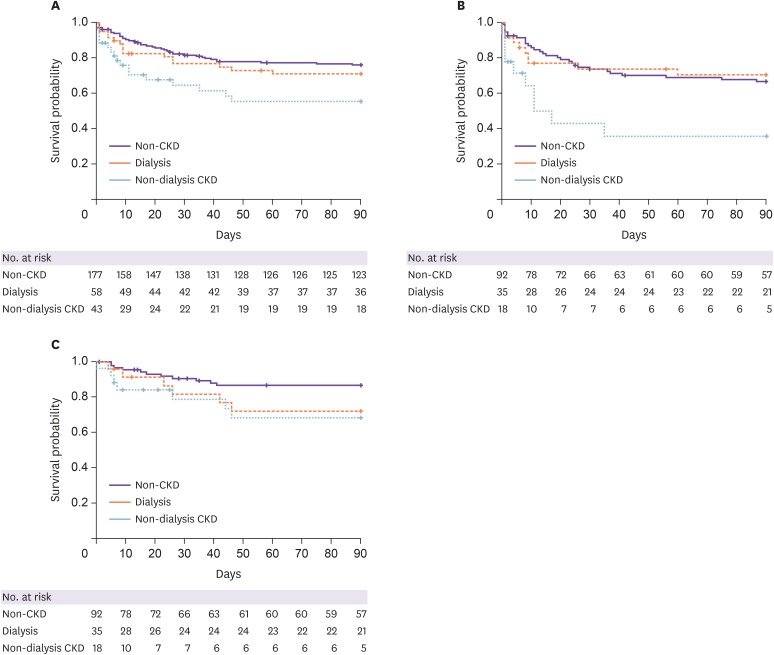
As a total, 278 SAB of 43 ND-CKD (31 males), 58 dialysis (39 males), and 177 nonCKD (112 males) patients were included. The 30-day mortality was 39.5% in ND-CKD, 27.6% in dialysis, and 7.9% in non-CKD patients. The hazard ratio of all-cause mortality following SAB in ND-CKD was 2.335 (95% confidence interval, 1.203 – 4.531; P = 0.003), compared to non-CKD patients. For methicillin-resistant S. aureus bacteremia (MRSAB), the hazard ratio of all-cause mortality in ND-CKD was 2.628 (95% CI, 1.074 – 6.435; P = 0.011), compared to dialysis patients. Appropriate antibiotics <48 h was independently related to improved survival following SAB among ND-CKD (adjusted HR, 0.304; 95% CI, 0,108 – 0.857; P = 0.024) and dialysis (adjusted HR, 0.323; 95% CI, 0,116 – 0.897; P = 0.030) patients.
Conclusion
ND-CKD patients demonstrated poor outcome following SAB and administration of appropriate antibiotics within 48 h could reduce the risk for mortality.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Keynan Y, Rubinstein E. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia, risk factors, complications, and management. Crit Care Clin. 2013; 29:547–562. PMID: 23830653.2. Jensen AG, Wachmann CH, Espersen F, Scheibel J, Skinhøj P, Frimodt-Møller N. Treatment and outcome of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a prospective study of 278 cases. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162:25–32. PMID: 11784216.3. Benfield T, Espersen F, Frimodt-Møller N, Jensen AG, Larsen AR, Pallesen LV, Skov R, Westh H, Skinhøj P. Increasing incidence but decreasing in-hospital mortality of adult Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia between 1981 and 2000. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007; 13:257–263. PMID: 17391379.4. Sarnak MJ, Jaber BL. Pulmonary infectious mortality among patients with end-stage renal disease. Chest. 2001; 120:1883–1887. PMID: 11742917.
Article5. Prezant DJ. Effect of uremia and its treatment on pulmonary function. Lung. 1990; 168:1–14.
Article6. Nielsen LH, Jensen-Fangel S, Benfield T, Skov R, Jespersen B, Larsen AR, Østergaard L, Støvring H, Schønheyder HC, Søgaard OS. Risk and prognosis of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia among individuals with and without end-stage renal disease: a Danish, population-based cohort study. BMC Infect Dis. 2015; 15:6. PMID: 25566857.
Article7. Chaudry MS, Gislason GH, Kamper AL, Rix M, Larsen AR, Petersen A, Andersen PS, Skov RL, Fosbøl EL, Westh H, Schønheyder HC, Benfield TL, Fowler VG Jr, Torp-Pedersen C, Bruun NE. Increased risk of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in hemodialysis-A nationwide study. Hemodial Int. 2019; 23:230–238. PMID: 30779302.8. Inrig JK, Reed SD, Szczech LA, Engemann JJ, Friedman JY, Corey GR, Schulman KA, Reller LB, Fowler VG Jr. Relationship between clinical outcomes and vascular access type among hemodialysis patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 1:518–524. PMID: 17699254.9. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care Med. 2008; 34:17–60. PMID: 18058085.
Article10. Kim ES, Kim HB, Kim G, Kim KH, Park KH, Lee S, Choi YH, Yi J, Kim CJ, Song KH, Choe PG, Kim NJ, Lee YS, Oh MD. Clinical and epidemiological factors associated with methicillin resistance in community-onset invasive Staphylococcus aureus infections: prospective multicenter cross-sectional study in Korea. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e114127. PMID: 25485895.
Article11. Buck JM, Como-Sabetti K, Harriman KH, Danila RN, Boxrud DJ, Glennen A, Lynfield R. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Minnesota, 2000-2003. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005; 11:1532–1538. PMID: 16318692.12. Miller LG, Perdreau-Remington F, Bayer AS, Diep B, Tan N, Bharadwa K, Tsui J, Perlroth J, Shay A, Tagudar G, Ibebuogu U, Spellberg B. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics cannot distinguish community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection from methicillin-susceptible S. aureus infection: a prospective investigation. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44:471–482. PMID: 17243048.13. Naimi TS, LeDell KH, Boxrud DJ, Groom AV, Steward CD, Johnson SK, Besser JM, O'Boyle C, Danila RN, Cheek JE, Osterholm MT, Moore KA, Smith KE. Epidemiology and clonality of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Minnesota, 1996-1998. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 33:990–996. PMID: 11528570.14. Anonymous . Chapter 1: Definition and classification of CKD. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2013; 3:19–62. PMID: 25018975.15. Harbarth S, Rutschmann O, Sudre P, Pittet D. Impact of methicillin resistance on the outcome of patients with bacteremia caused by Staphylococcus aureus . Arch Intern Med. 1998; 158:182–189. PMID: 9448557.16. Culver DH, Horan TC, Gaynes RP, Martone WJ, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Banerjee SN, Edwards JR, Tolson JS, Henderson TS, Hughes JM. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Surgical wound infection rates by wound class, operative procedure, and patient risk index: National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Am J Med. 1991; 91(Suppl 3B):152S–157S. PMID: 1656747.17. Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987; 40:373–383. PMID: 3558716.
Article18. Paterson DL, Ko WC, Von Gottberg A, Mohapatra S, Casellas JM, Goossens H, Mulazimoglu L, Trenholme G, Klugman KP, Bonomo RA, Rice LB, Wagener MM, McCormack JG, Yu VL. International prospective study of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia: implications of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase production in nosocomial Infections. Ann Intern Med. 2004; 140:26–32. PMID: 14706969.19. Vincent JL, de Mendonça A, Cantraine F, Moreno R, Takala J, Suter PM, Sprung CL, Colardyn F, Blecher S. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on “sepsis-related problems” of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Crit Care Med. 1998; 26:1793–1800. PMID: 9824069.20. Kang CK, Kwak YG, Park Y, Song KH, Kim ES, Jung SI, Park KH, Park WB, Kim NJ, Kim YK, Jang HC, Lee S, Jeon JH, Kwon KT, Kim CJ, Kim YS, Kim HB. Korea Infectious Diseases (KIND) study group. Gender affects prognosis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia differently depending on the severity of underlying disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018; 37:1119–1123. PMID: 29667110.21. Blot SI, Vandewoude KH, Hoste EA, Colardyn FA. Outcome and attributable mortality in critically Ill patients with bacteremia involving methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162:2229–2235. PMID: 12390067.22. Yaw LK, Robinson JO, Ho KM. A comparison of long-term outcomes after meticillin-resistant and meticillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014; 14:967–975. PMID: 25185461.23. Wang JL, Chen SY, Wang JT, Wu GH, Chiang WC, Hsueh PR, Chen YC, Chang SC. Comparison of both clinical features and mortality risk associated with bacteremia due to community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus . Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46:799–806. PMID: 18266610.24. Cosgrove SE, Sakoulas G, Perencevich EN, Schwaber MJ, Karchmer AW, Carmeli Y. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:53–59. PMID: 12491202.25. Paul M, Kariv G, Goldberg E, Raskin M, Shaked H, Hazzan R, Samra Z, Paghis D, Bishara J, Leibovici L. Importance of appropriate empirical antibiotic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010; 65:2658–2665. PMID: 20947620.26. Ammerlaan H, Seifert H, Harbarth S, Brun-Buisson C, Torres A, Antonelli M, Kluytmans J, Bonten M. European Practices of Infections with Staphylococcus aureus (SEPIA) Study Group. Adequacy of antimicrobial treatment and outcome of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in 9 western European countries. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 49:997–1005. PMID: 19719417.27. Minejima E, Mai N, Bui N, Mert M, She RC, Nieberg P, Spellberg B, Wong-Beringer A. Defining the breakpoint duration of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia predictive of poor outcomes. Clin Infect Dis. 2020; 70:566–573. PMID: 30949675.28. Kim SH, Park WB, Lee KD, Kang CI, Kim HB, Oh MD, Kim EC, Choe KW. Outcome of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in patients with eradicable foci versus noneradicable foci. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 37:794–799. PMID: 12955640.29. Kruzel MC, Lewis CT, Welsh KJ, Lewis EM, Dundas NE, Mohr JF, Armitige LY, Wanger A. Determination of vancomycin and daptomycin MICs by different testing methods for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . J Clin Microb. 2011; 49:2272–2273.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Observation on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia of Community Hospital
- Treatment Strategy for Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
- The risk factors and prognosis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: focus on nosocomial acquisition
- Microbiological and genotypic factors affecting mortality in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia
- A study of central venous hemodialysis catheter colonization and peripheral bacteremia in patients undergoing hemodialysis