Ann Clin Microbiol.
2020 Sep;23(3):185-194. 10.5145/ACM.2020.23.3.2.
Performance of Modified-EUCAST Rapid Direct Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing on Clinical Urine Samples
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Global Health Security, Yonsei University Graduate school of Public Health, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2506553
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2020.23.3.2
Abstract
- Background
The rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) performed on urine samples would guide the adequate choice of antibiotics for obtaining better treatment outcomes in patients. Our study aimed to evaluate the performance of the modified-EUCAST (European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing) rapid direct AST on urine samples.
Methods
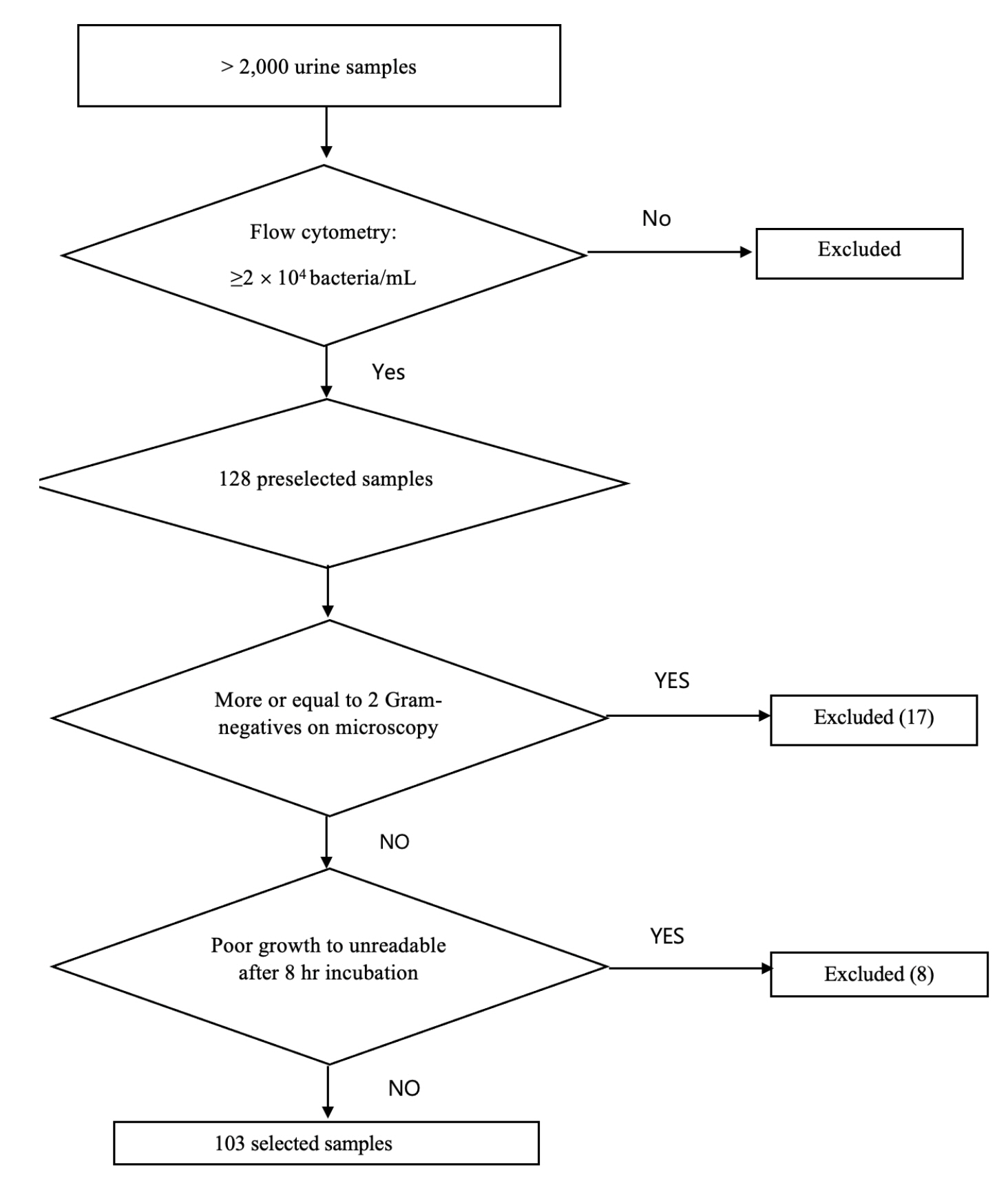
From >2,000 urine samples, a total of 128 urine samples containing bacterial counts of ≥2 × 10 4 CFU/mL with a uniform bacterial shape were initially included based on flow cytometry (Sysmex UF-1000i, Japan) and Gram staining, respectively. A total of 103 samples showing the presence of Enterobacteriaceae were finally selected in this study. The urine samples were directly inoculated on Mueller-Hinton agar, which was used in the current EUCAST rapid direct AST on blood samples. The size of the growth inhibition zones around antimicrobial disks was measured using a digital scanner (BIOMIC vision analyzer, Giles scientific, USA) and further confirmed by visualization with naked eyes after incubation for 4, 6, and 8 hours. The AST interpretations were compared to those of the conventional VITEK 2 AST system (bioMérieux, France) and the discrepancies between both tests were confirmed with the E-test.
Results
The antibiotics, namely ampicillin, cefazolin, aztreonam, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, cefepime, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, and cotrimoxazole showed excellent correlations with modified-EUCAST rapid direct test and conventional ASTs with >0.75 weighted kappa values. The categorical agreement of the rapid direct AST was 1,442 (93.3%), with 76 (4.9%) minor error, 9 (0.6%) major error and 18 (1.2%) very major error, implicating the reliability of this method for clinical application.
Conclusion
Performing the modified-EUCAST rapid direct AST on urine samples can predict reliable AST results within 8 hours. The rapid direct AST can help the physicians to initiate adequate antimicrobial treatment for urinary tract infections.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mohammad RN and Omer SA. Direct disk testing versus isolation and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of urine from urinary tract infection. Iran J Microbiol 2018;10:37-44.2. Al-Naqshbandi AA, Chawsheen MA, Abdulqader HH. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial pathogens isolated from urine specimens received in rizgary hospital - Erbil. J Infect Public Health 2019;12:330-6.3. Sundqvist M, Olafsson J, Matuschek E. EUCAST breakpoints can be used to interpret direct susceptibility testing of Enterobacteriaceae from urine samples. APMIS 2015;123:152-5.4. Schoepp NG, Schlappi TS, Curtis MS, Butkovich SS, Miller S, Humphries RM, et al. Rapid pathogen-specific phenotypic antibiotic susceptibility testing using digital LAMP quantification in clinical samples. Sci Transl Med 2017;9:eaal3693.5. Mishra P, Mishra K, Singh D, Ganju L, Kumar B, Singh S. Advances in rapid detection and antimicrobial susceptibility tests: a review. Def Life Sci J 2018;4:12-20.6. Paul S, Kannan I, Duraipandian J, Premavathi RK, Shantha S. Evaluation of chromogenic agar and direct antimicrobial susceptibility testing in rapid diagnosis of acute urinary tract infection. Int J Pharm Clin Res 2015;7:333-6.7. Eigner U, Schmid A, Wild U, Bertsch D, Fahr AM. Analysis of the comparative workflow and performance characteristics of the VITEK 2 and Phoenix systems. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:3829-34.8. Perillaud C, Pilmis B, Diep J, Pean de Ponfilly G, Vidal B, Couzigou C, et al. Prospective evaluation of rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing by disk diffusion on Mueller-Hinton rapid-SIR directly on blood cultures. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2019;93:14-21.9. Coorevits L, Boelens J, Claeys G. Direct susceptibility testing by disk diffusion on clinical samples: a rapid and accurate tool for antibiotic stewardship. Eur J Clin Microbiol 2015;34:1207-12.10. EUCAST. EUCAST rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing (RAST) directly from positive blood culture bottles. Version 1.1, 2019.11. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 29th ed. CLSI supplement M100. Wayne; PA: 2019.12. Fleiss JL, Cohen J, Everitt BS. Large sample standard errors of kappa and weighted kappa. Psychol Bull 1969;72:323–7.13. Stokkou S, Geginat G, Schlüter D, Tammer I. Direct disk diffusion test using European clinical antimicrobial susceptibility testing breakpoints provides reliable results compared with the standard method. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 2015;5:103-11.14. Breteler KB, Rentenaar RJ, Verkaart G, Sturm PD. Performance and clinical significance of direct antimicrobial susceptibility testing on urine from hospitalized patients. Scand J Infect Dis 2011;43:771-6.15. Perillaud-Dubois C, Pilmis B, Diep J, de Ponfilly GP, Perreau S, Ruffier d'Epenoux L, et al. Performance of rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing by disk diffusion on MHR-SIR agar directly on urine specimens. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2019;38:185-9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- EUCAST v.12.0 Review Focused on Changes
- Introduction to the Revised International Guidelines on Breakpoints for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing-Recommended Rapid Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus From Positive Blood Culture Bottles
- Strategies for Interpretive Standards of beta-Lactams Susceptibility Testing and Identification of Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamases and Carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae
- Performance Evaluation of Newly Developed Korean Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Panels for MicroScan System Using Clinical Isolates from Teaching Hospitals in Korea