Arch Hand Microsurg.
2020 Sep;25(3):201-206. 10.12790/ahm.20.0028.
Multiple Huge Tendinous Xanthomas with Normal Lipid Profiles in All Extremities
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2505901
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.20.0028
Abstract
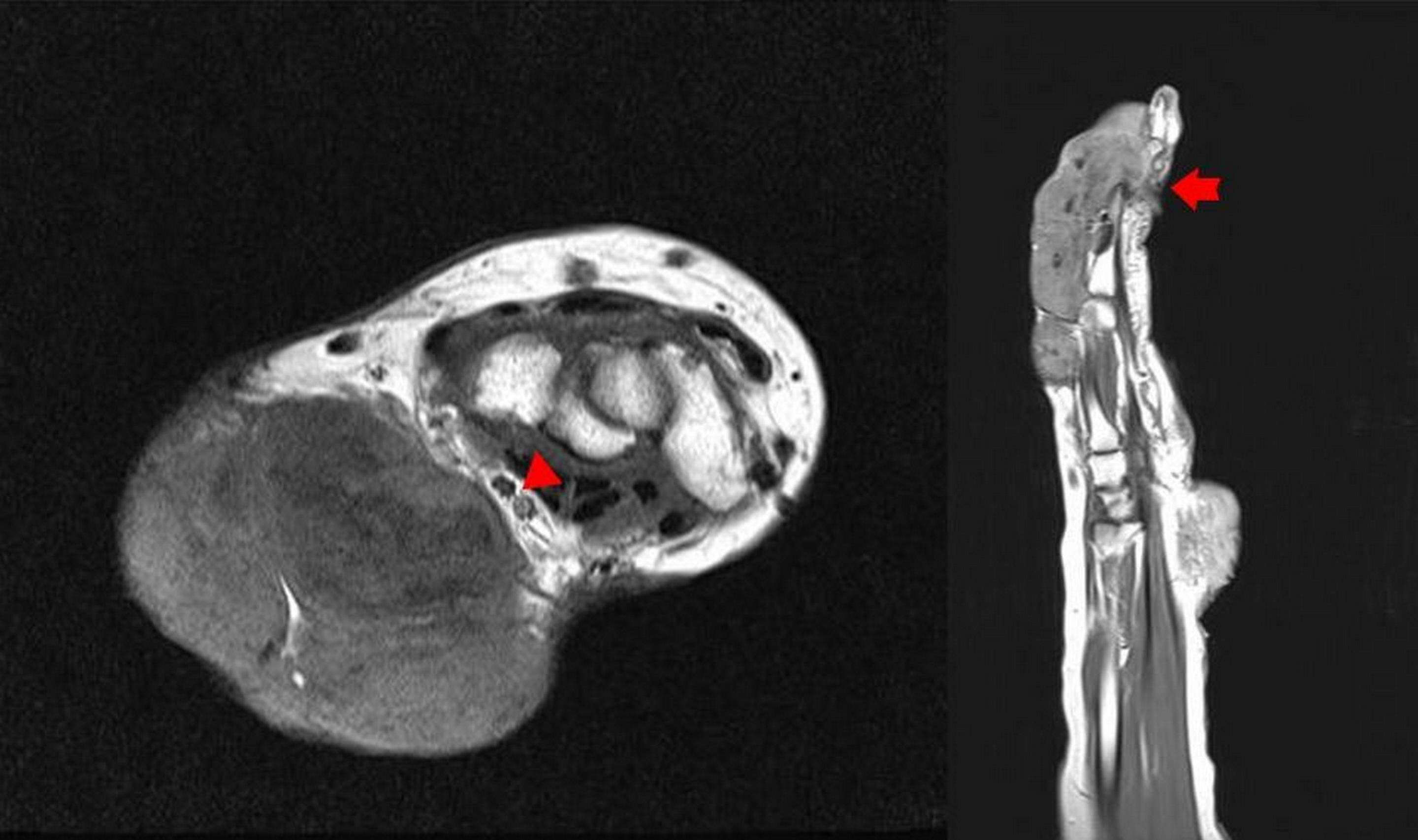
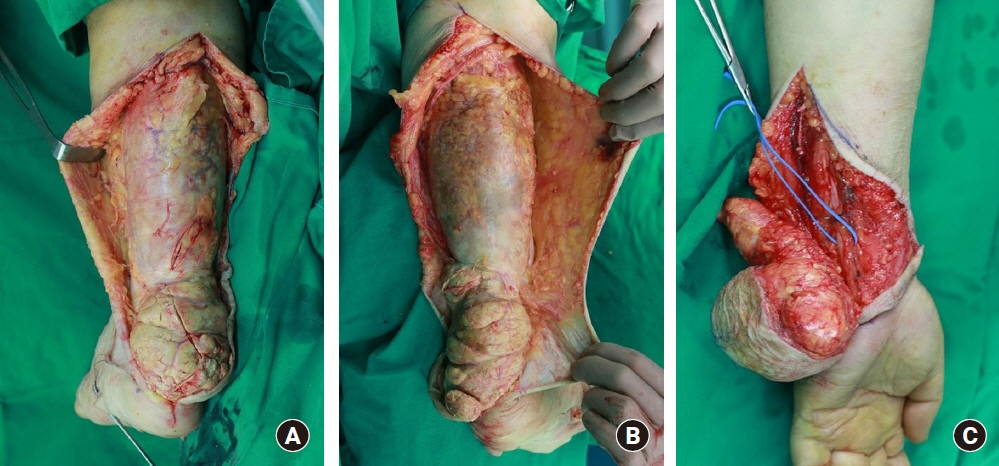
- Xanthomas are grayish-yellow masses composed of lipid-filled foamy histiocytes and are usually accompanied by familial hypercholesterolemia or some other disease associated with dysfunctional lipid metabolism. Here, we report a case of multiple huge tendinous xanthomas with normal lipid profiles involving all extremities. These masses were large enough to cause pain, dysfunction of extremities, and cosmetic compromise and the condition was accompanied by cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Due to the presence of many masses in all extremities, a two-stage operation was planned with a time gap of several months. At 1-month follow-up visits after first and second surgeries, although extension of the left middle finger was poor as a result of sacrificing the 3rd extensor digitorum communis tendon, no problems such as wound dehiscence, hematoma formation, or infection at operative sites were noted.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bude RO, Adler RS, Bassett DR. Diagnosis of Achilles tendon xanthoma in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: MR vs sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 162:913–7.
Article2. Kruth HS. Lipid deposition in human tendon xanthoma. Am J Pathol. 1985; 121:311–5.3. Doyle JR. Tendon xanthoma: a physical manifestation of hyperlipidemia. J Hand Surg Am. 1988; 13:238–41.
Article4. Wang Z, Lin ZW, Huang LL, et al. Primary non-hyperlipidemia xanthoma of bone: a case report with review of the literature. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014; 7:4503–8.5. Lu YT, Chen TJ, Chung WH, Kuo TT, Hong HS. Cutaneous normolipemic plane xanthoma with supraglottic involvement in a patient with hand-Schüller-Christian disease: a case report. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009; 10:189–92.6. Fleischmajer R, Tint GS, Bennett HD. Normolipemic tendon and tuberous xanthomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981; 5:290–6.
Article7. Verrips A, van Engelen BG, Wevers RA, et al. Presence of diarrhea and absence of tendon xanthomas in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Arch Neurol. 2000; 57:520–4.
Article8. Vega GL, Illingworth DR, Grundy SM, Lindgren FT, Connor WE. Normocholesterolemic tendon xanthomatosis with overproduction of apolipoprotein B. Metabolism. 1983; 32:118–25.
Article9. Jones FE, Soule EH, Coventry MB. Fibrous xanthoma of synovium (giant-cell tumor of tendon sheath, pigmented nodular synovitis). A study of one hundred and eighteen cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51:76–86.10. Wilkes LL. Tendon xanthoma in type IV hyperlipoproteinemia. South Med J. 1977; 70:254–5.
Article