Arch Hand Microsurg.
2020 Jun;25(2):140-145. 10.12790/ahm.19.0057.
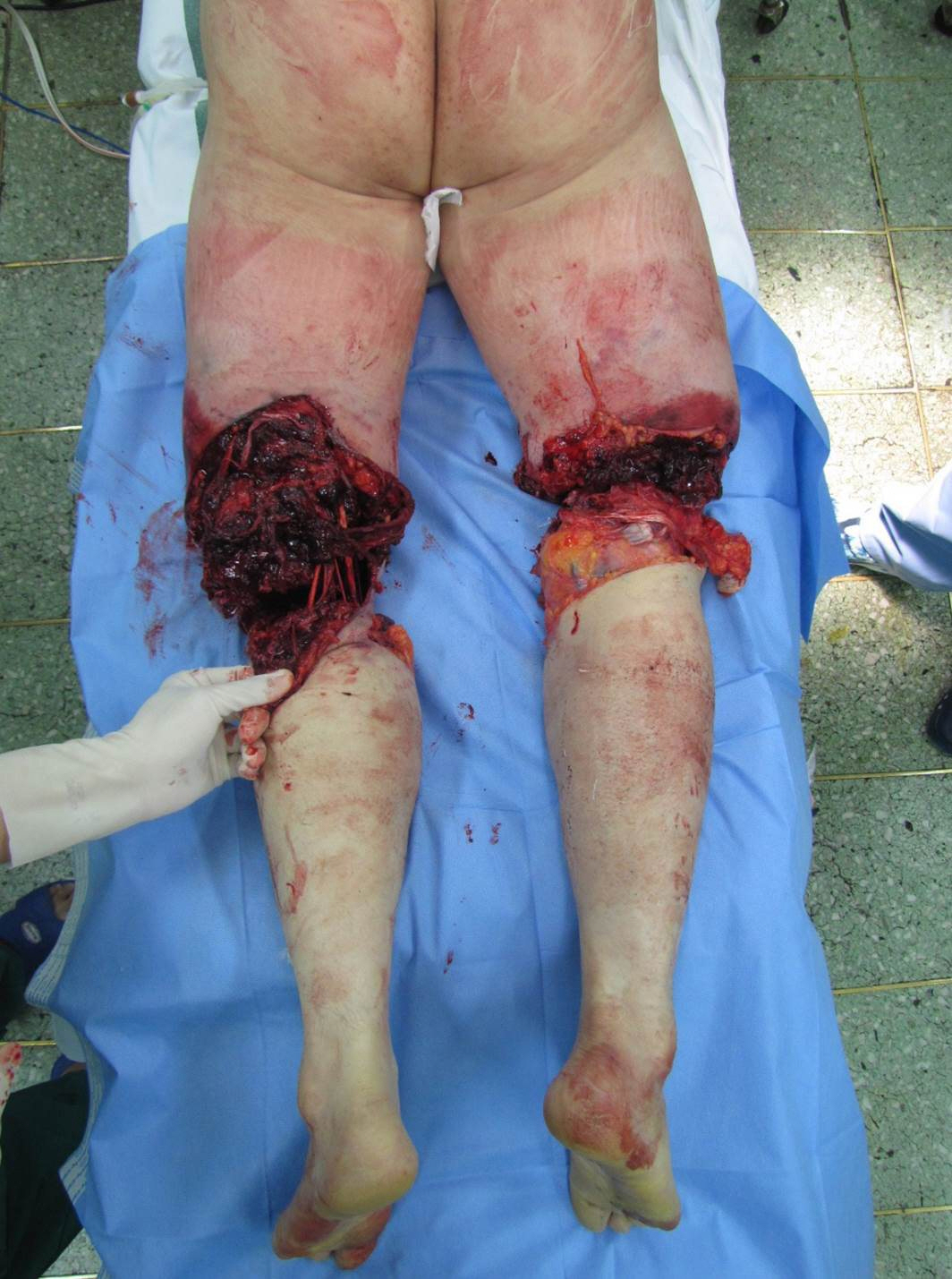
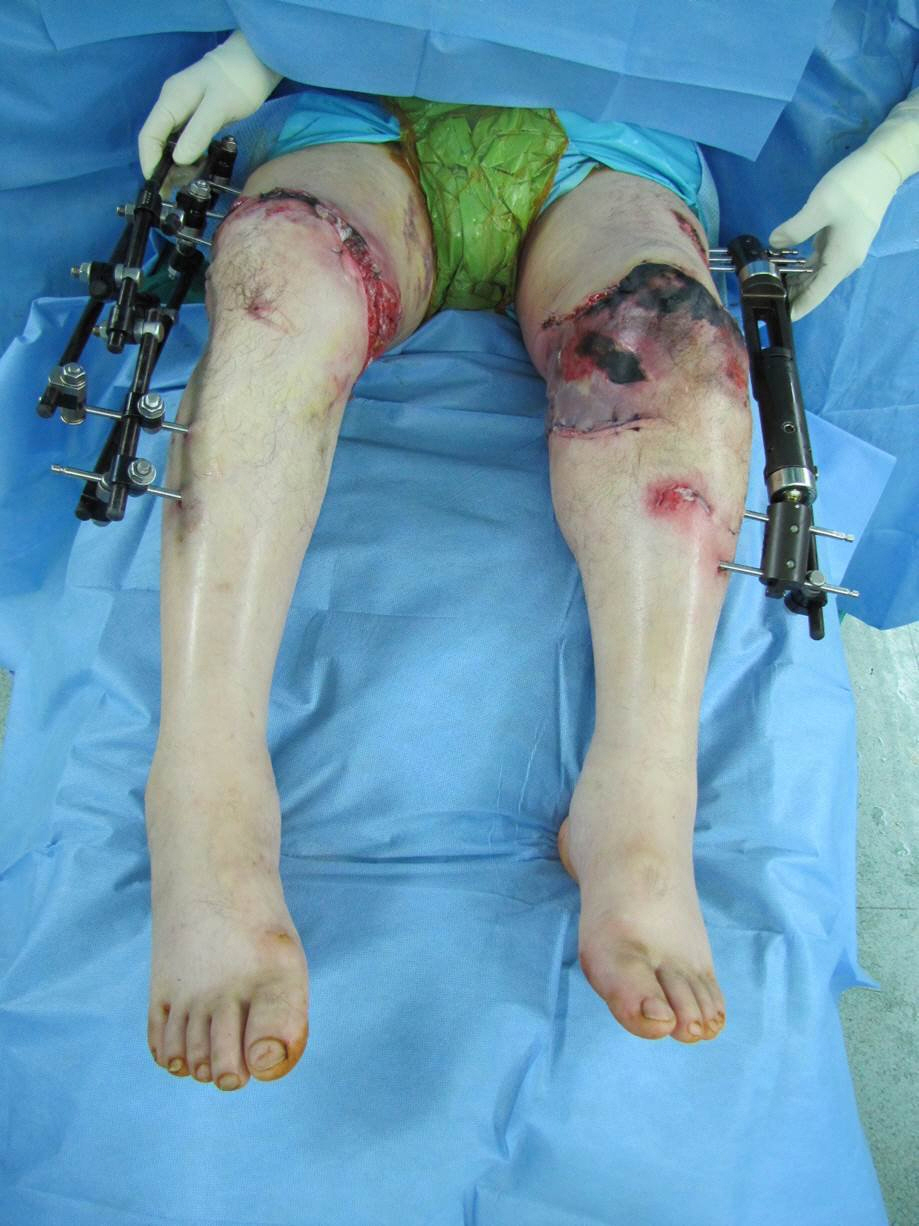
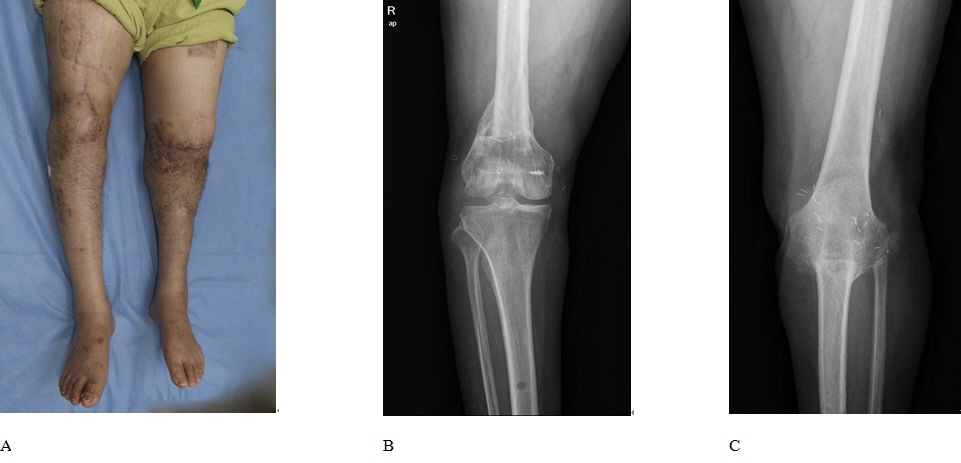
Successful Replantation after Amputation around Both Knee
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
- 4Department of Trauma Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2502711
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.19.0057
Abstract
- Reducing ischemic time is the most important factor associated with good results in major limb replantation. This case describes the surgery and outcome of replantation of both major limbs in a patient with amputation of both lower extremities due to rope entanglement on a ship. Emergency surgery restored circulation in 3 hours and 40 minutes after amputation on the left side, and 4 hours and 50 minutes after amputation on the right side. The left knee of the patient had undergone joint fusion and the right knee could move from 0 degree to 100 degrees. At present, the patient is able to walk using crutches. These results demonstrate that good results can be obtained if bilateral anastomosis is possible in both knees.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hierner R, Betz AM, Comtet JJ, Berger AC. Decision making and results in subtotal and total lower leg amputations: reconstruction versus amputation. Microsurgery. 1995; 16:830–9.
Article2. Tantry TP, Kadam D, Shenoy SP, Bhandary S, Adappa KK. Perioperative evaluation and outcomes of major limb replantations with ischemia periods of more than 6 hours. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2013; 29:165–72.
Article3. Battiston B, Tos P, Pontini I, Ferrero S. Lower limb replantations: indications and a new scoring system. Microsurgery. 2002; 22:187–92.
Article4. Kim HH, Jeong JH, Kim YH, Seul JH, Shon OJ. Rehabilitation after the replantation on a 2-year-old girl with both amputated legs. Br J Plast Surg. 2005; 58:404–8.
Article5. Fang CL, Yang CS, Tang HC, Changchien CH, Lai YY. Successful replantation of amputated bilateral lower limbs. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012; 129:215e–217e.
Article6. Schmidhammer R, Nimmervoll R, Pelinka LE, et al. Bilateral lower leg replantation versus prosthetic replacement: long-term outcome of amputation after an occupational railroad accident. J Trauma. 2004; 57:824–31.
Article7. Fang J, Li H, Dou H, et al. Crossover replantation after bilateral traumatic lower limb amputations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2012; 6:218.
Article8. Mathew S, Smith BP, Cannon JW, Reilly PM, Schwab CW, Seamon MJ. Temporary arterial shunts in damage control: experience and outcomes. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017; 82:512–7.