J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Apr;35(17):e104. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e104.
Influence of Besifovir Dipivoxil Maleate Combined with L-Carnitine on Hepatic Steatosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Yonsei Liver Center, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2500207
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e104
Abstract
- Background
Besifovir dipivoxil maleate (BSV) with L-carnitine is the first-line antiviral agent for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection. We investigated whether BSV combined with L-carnitine improves hepatic steatosis (HS).
Methods
Treatment-naïve patients with CHB who were initiated on antiviral therapy (AVT) were enrolled. The magnitude of HS was assessed using hepatic steatosis index (HSI), and HS improvement was defined as a ≥ 10% reduction in the HSI score from the baseline.
Results
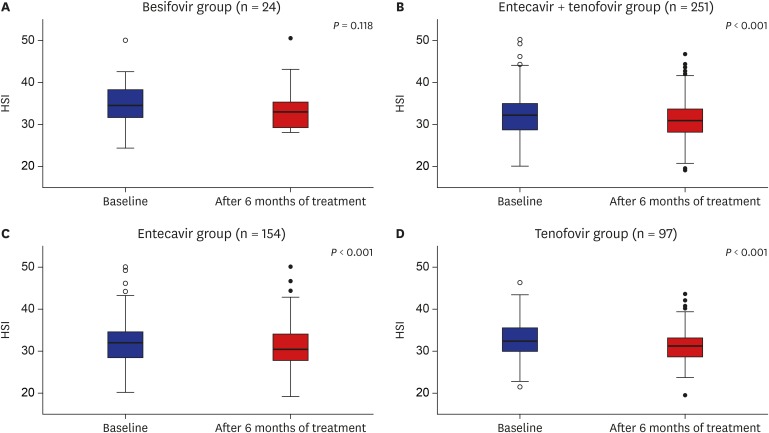
The mean age of the study patients was 56 years with a male predominance (n = 178, 64.7%). The mean body mass index (BMI), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and platelet count were 23.5 kg/m2, 49.6 IU/L, 49.0 IU/L, and 191.3 × 109/L, respectively. The mean HSI and fibrosis (FIB)-4 index were 32.6 and 0.5, respectively. After 6 months of AVT, platelet count (mean, 191.3→167.0 × 109/L), fasting glucose (mean, 113.1→105.9 mg/dL), AST (mean, 49.6→28.0 IU/L), ALT (mean, 49.0→33.9 IU/L), and total cholesterol (mean, 170.0→162.1 mg/dL) levels significantly decreased (all P < 0.05). In the BSV group, AST (mean, 95.2→30.2 IU/L) and ALT (mean, 81.1→31.1 IU/L) levels significantly reduced (all P < 0.05), whereas HSI and FIB-4 index were maintained (all P > 0.05). In the univariate analysis, age, BMI, diabetes, cirrhosis, fasting glucose level, and ALT were significantly associated with HS improvement (all P < 0.05).
Conclusion
BSV with L-carnitine did not show any improvement of HS in patients with CHB. Further prospective randomized controlled studies are needed to validate the potential beneficial effects of BSV with L-carnitine in CHB infection.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lai CL, Yuen MF. Chronic hepatitis B--new goals, new treatment. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359(23):2488–2491. PMID: 19052131.2. Yuen MF, Lai CL. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Lancet Infect Dis. 2001; 1(4):232–241. PMID: 11871510.
Article3. Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127(5):Suppl 1. S35–S50. PMID: 15508101.
Article4. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2019; 25(2):93–159. PMID: 31185710.5. Brown RS Jr, McMahon BJ, Lok AS, Wong JB, Ahmed AT, Mouchli MA, et al. Antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B viral infection during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2016; 63(1):319–333. PMID: 26565396.
Article6. Lampertico P, Agarwal K, Berg T, Buti M, Janssen HL, Papatheodoridis G, et al. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017; 67(2):370–398. PMID: 28427875.
Article7. Lai CL, Ahn SH, Lee KS, Um SH, Cho M, Yoon SK, et al. Phase IIb multicentred randomised trial of besifovir (LB80380) versus entecavir in Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gut. 2014; 63(6):996–1004. PMID: 23979965.
Article8. Yuen MF, Lee SH, Kang HM, Kim CR, Kim J, Ngai V, et al. Pharmacokinetics of LB80331 and LB80317 following oral administration of LB80380, a new antiviral agent for chronic hepatitis B (CHB), in healthy adult subjects, CHB patients, and mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53(5):1779–1785. PMID: 19223649.
Article9. Yuen MF, Kim J, Kim CR, Ngai V, Yuen JC, Min C, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled, dose-finding study of oral LB80380 in HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B. Antivir Ther. 2006; 11(8):977–983. PMID: 17302367.10. Yuen MF, Han KH, Um SH, Yoon SK, Kim HR, Kim J, et al. Antiviral activity and safety of LB80380 in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with lamivudine-resistant disease. Hepatology. 2010; 51(3):767–776. PMID: 20091678.
Article11. Yuen MF, Ahn SH, Lee KS, Um SH, Cho M, Yoon SK, et al. Two-year treatment outcome of chronic hepatitis B infection treated with besifovir vs. entecavir: results from a multicentre study. J Hepatol. 2015; 62(3):526–532. PMID: 25450709.
Article12. Fan JG, Kim SU, Wong VW. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J Hepatol. 2017; 67(4):862–873. PMID: 28642059.
Article13. Kim DS, Jeon MY, Lee HW, et al. Influence of hepatic steatosis on the outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir and tenofovir. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2019; 25(3):283–293. PMID: 30419649.
Article14. Wang B, Li W, Fang H, Zhou H. Hepatitis B virus infection is not associated with fatty liver disease: Evidence from a cohort study and functional analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2019; 19(1):320–326. PMID: 30387826.
Article15. Wang MM, Wang GS, Shen F, Chen GY, Pan Q, Fan JG. Hepatic steatosis is highly prevalent in hepatitis B patients and negatively associated with virological factors. Dig Dis Sci. 2014; 59(10):2571–2579. PMID: 24838496.
Article16. Seto WK, Hui RW, Mak LY, Fung J, Cheung KS, Liu KS, et al. Association between hepatic steatosis, measured by controlled attenuation parameter, and fibrosis burden in chronic hepatitis B. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 16(4):575–583.e2. PMID: 28970146.
Article17. Cheng JY, Wong VW, Tse YK, Chim AM, Chan HL, Wong GL. Metabolic syndrome increases cardiovascular events but not hepatic events and death in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016; 64(5):1507–1517. PMID: 27680510.
Article18. Chon YE, Kim KJ, Jung KS, Kim SU, Park JY, Kim Y, et al. The relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease measured by controlled attenuation parameter. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57(4):885–892. PMID: 27189281.
Article19. Wong GL, Wong VW, Choi PC, Chan AW, Chim AM, Yiu KK, et al. Metabolic syndrome increases the risk of liver cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B. Gut. 2009; 58(1):111–117. PMID: 18832522.
Article20. Ishikawa H, Takaki A, Tsuzaki R, Yasunaka T, Koike K, Shimomura Y, et al. L-carnitine prevents progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in a mouse model with upregulation of mitochondrial pathway. PLoS One. 2014; 9(7):e100627. PMID: 24983359.
Article21. Fujisawa K, Takami T, Matsuzaki A, Matsumoto T, Yamamoto N, Terai S, et al. Evaluation of the effects of L-carnitine on medaka (Oryzias latipes) fatty liver. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):2749. PMID: 28584294.
Article22. Jun DW, Kim BI, Cho YK, Kim HJ, Kwon YO, Park SY, et al. Efficacy and safety of entecavir plus carnitine complex (GODEX®) compared to entecavir monotherapy in patient with ALT elevated chronic hepatitis B: randomized, multicenter open-label trials. The GOAL study. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013; 19(2):165–172. PMID: 23837141.
Article23. Lee JH, Kim D, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Yang JI, Kim W, et al. Hepatic steatosis index: a simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2010; 42(7):503–508. PMID: 19766548.
Article24. Zhang Z, Wang G, Kang K, Wu G, Wang P. Diagnostic accuracy and clinical utility of a new noninvasive index for hepatic steatosis in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Sci Rep. 2016; 6(1):32875. PMID: 27597515.
Article25. Kahl S, Straßburger K, Nowotny B, Livingstone R, Klüppelholz B, Keßel K, et al. Comparison of liver fat indices for the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. PLoS One. 2014; 9(4):e94059. PMID: 24732091.
Article26. Nishikawa H, Nishijima N, Enomoto H, Sakamoto A, Nasu A, Komekado H, et al. Comparison of FIB-4 index and aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index on carcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir. J Cancer. 2017; 8(2):152–161. PMID: 28243319.
Article27. Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346(16):1221–1231. PMID: 11961152.
Article28. Haga Y, Kanda T, Sasaki R, Nakamura M, Nakamoto S, Yokosuka O. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatic cirrhosis: comparison with viral hepatitis-associated steatosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21(46):12989–12995. PMID: 26675364.
Article29. Zhang Z, Wang G, Kang K, Wu G, Wang P. Diagnostic accuracy and clinical utility of a new noninvasive index for hepatic steatosis in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Sci Rep. 2016; 6(1):32875. PMID: 27597515.
Article30. Kahl S, Straßburger K, Nowotny B, Livingstone R, Klüppelholz B, Keßel K, et al. Comparison of liver fat indices for the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. PLoS One. 2014; 9(4):e94059. PMID: 24732091.
Article31. Chang Y, Jung HS, Yun KE, Cho J, Cho YK, Ryu S. Cohort study of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD fibrosis score, and the risk of incident diabetes in a Korean population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(12):1861–1868. PMID: 24100261.
Article32. Ju DY, Choe YG, Cho YK, Shin DS, Yoo SH, Yim SH, et al. The influence of waist circumference on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in apparently healthy Korean adults. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013; 19(2):140–147. PMID: 23837138.
Article33. Huh JH, Lee KJ, Lim JS, Lee MY, Park HJ, Kim MY, et al. High dietary sodium intake assessed by estimated 24-h urinary sodium excretion is associated with NAFLD and hepatic fibrosis. PLoS One. 2015; 10(11):e0143222. PMID: 26571018.
Article34. Machado MV, Oliveira AG, Cortez-Pinto H. Hepatic steatosis in hepatitis B virus infected patients: meta-analysis of risk factors and comparison with hepatitis C infected patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26(9):1361–1367. PMID: 21649726.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Another oral antiviral treatment, but still far away from hepatitis B virus cure
- Noninferiority Outcomes of Besifovir Compared to Tenofovir Alafenamide in Treatment-Naïve Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Application and Efficacy of Adefovir Dipivoxil in Hepatitis B Virus-assoicated Chronic Liver Diseases
- How does hepatic steatosis affect the outcome of patients with chronic hepatitis B?
- Efficacy of New Anti-viral Agent in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B