J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Sep;31(9):1431-1437. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1431.
Clinical Utility of a New Automated Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen Assay for Prediction of Treatment Response in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gihankhys@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2468276
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1431
Abstract
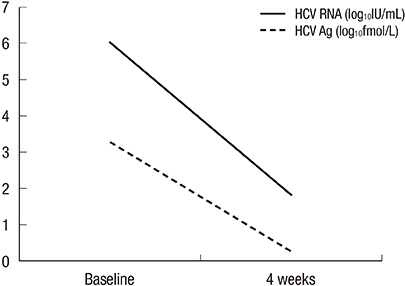
- Hepatitis C virus core antigen (HCV Ag) is a recently developed marker of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. We investigated the clinical utility of the new HCV Ag assay for prediction of treatment response in HCV infection. We analyzed serum from 92 patients with HCV infection who had been treated with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. HCV Ag levels were determined at baseline in all enrolled patients and at week 4 in 15 patients. Baseline HCV Ag levels showed good correlations with HCV RNA (r = 0.79, P < 0.001). Mean HCV Ag levels at baseline were significantly lower in patients with a sustained virologic response (SVR) than in those with a non SVR (relapse plus non responder) based on HCV RNA analysis (2.8 log10fmol/L vs. 3.27 log10fmol/L, P = 0.023). Monitoring of the viral kinetics by determination of HCV RNA and HCV Ag levels resulted in similarly shaped curves. Patients with undetectable HCV Ag levels at week 4 had a 92.3% probability of achieving SVR based on HCV RNA assay results. The HCV Ag assay may be used as a supplement for predicting treatment response in HCV infection, but not as an alternative to the HCV RNA assay.
MeSH Terms
-
Antigens, Viral/*blood
Antiviral Agents/therapeutic use
Automation
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Genotype
Hepacivirus/*genetics/isolation & purification/metabolism
Hepatitis C, Chronic/drug therapy/*virology
Humans
Immunoassay
Interferon-alpha/therapeutic use
Male
Middle Aged
Polyethylene Glycols/therapeutic use
Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Viral/*blood
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Recombinant Proteins/therapeutic use
Recurrence
Ribavirin/therapeutic use
Treatment Outcome
Antigens, Viral
Antiviral Agents
Interferon-alpha
RNA, Viral
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Recombinant Proteins
Polyethylene Glycols
Ribavirin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sagnelli E, Stroffolini T, Mele A, Almasio P, Coppola N, Ferrigno L, Scolastico C, Onofrio M, Imparato M, Filippini P. The importance of HCV on the burden of chronic liver disease in Italy: a multicenter prevalence study of 9,997 cases. J Med Virol. 2005; 75:522–527.2. Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Gonçales FL Jr, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:975–982.3. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2011; 55:245–264.4. Afdhal NH, McHutchison JG, Zeuzem S, Mangia A, Pawlotsky JM, Murray JS, Shianna KV, Tanaka Y, Thomas DL, Booth DR, et al. Hepatitis C pharmacogenetics: state of the art in 2010. Hepatology. 2011; 53:336–345.5. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatitis C. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2014; 20:89–136.6. Berg T, Sarrazin C, Herrmann E, Hinrichsen H, Gerlach T, Zachoval R, Wiedenmann B, Hopf U, Zeuzem S. Prediction of treatment outcome in patients with chronic hepatitis C: significance of baseline parameters and viral dynamics during therapy. Hepatology. 2003; 37:600–609.7. Civeira MP, Prieto J. Early predictors of response to treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1999; 31:Suppl 1. 237–243.8. Zeuzem S, Lee JH, Franke A, Rüster B, Prümmer O, Herrmann G, Roth WK. Quantification of the initial decline of serum hepatitis C virus RNA and response to interferon alfa. Hepatology. 1998; 27:1149–1156.9. Diago M, Shiffman ML, Bronowicki JP, Zeuzem S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Pappas SC, Tietz A, Nelson DR. Identifying hepatitis C virus genotype 2/3 patients who can receive a 16-week abbreviated course of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) plus ribavirin. Hepatology. 2010; 51:1897–1903.10. Sarrazin C, Shiffman ML, Hadziyannis SJ, Lin A, Colucci G, Ishida H, Zeuzem S. Definition of rapid virologic response with a highly sensitive real-time PCR-based HCV RNA assay in peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin response-guided therapy. J Hepatol. 2010; 52:832–838.11. Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K, Matsumoto A, Kashiwakuma T, Hasegawa A, Mori H, Yanagihara O, Ohta Y. Serum levels of hepatitis C virus core protein in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with interferon alfa. Hepatology. 1996; 23:1330–1333.12. Enomoto M, Nishiguchi S, Tamori A, Kohmoto M, Habu D, Sakaguchi H, Takeda T, Kawada N, Seki S, Shiomi S. Chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for monitoring hepatitis C virus core protein during interferon-alpha2b and ribavirin therapy in patients with genotype 1 and high viral loads. J Med Virol. 2005; 77:77–82.13. Hayashi K, Hasuike S, Kusumoto K, Ido A, Uto H, Kenji N, Kohara M, Stuver SO, Tsubouchi H. Usefulness of a new immuno-radiometric assay to detect hepatitis C core antigen in a community-based population. J Viral Hepat. 2005; 12:106–110.14. Park Y, Lee JH, Kim BS, Kim DY, Han KH, Kim HS. New automated hepatitis C virus (HCV) core antigen assay as an alternative to real-time PCR for HCV RNA quantification. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:2253–2256.15. Aoyagi K, Ohue C, Iida K, Kimura T, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K, Yagi S. Development of a simple and highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay for hepatitis C virus core antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:1802–1808.16. Laperche S, Le Marrec N, Girault A, Bouchardeau F, Servant-Delmas A, Maniez-Montreuil M, Gallian P, Levayer T, Morel P, Simon N. Simultaneous detection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) core antigen and anti-HCV antibodies improves the early detection of HCV infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:3877–3883.17. Soffredini R, Rumi MG, Parravicini ML, Ronchi G, Del Ninno E, Russo A, Colombo M. Serum levels of hepatitis C virus core antigen as a marker of infection and response to therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:1738–1743.18. Yokosuka O, Kawai S, Suzuki Y, Fukai K, Imazeki F, Kanda T, Tada M, Mikata R, Hata A, Saisho H. Evaluation of clinical usefulness of second-generation HCV core antigen assay: comparison with COBAS AMPLICOR HCV MONITOR assay version 2.0. Liver Int. 2005; 25:1136–1141.19. Morota K, Fujinami R, Kinukawa H, Machida T, Ohno K, Saegusa H, Takeda K. A new sensitive and automated chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay for quantitative determination of hepatitis C virus core antigen. J Virol Methods. 2009; 157:8–14.20. Ross RS, Viazov S, Salloum S, Hilgard P, Gerken G, Roggendorf M. Analytical performance characteristics and clinical utility of a novel assay for total hepatitis C virus core antigen quantification. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:1161–1168.21. Moscato GA, Giannelli G, Grandi B, Pieri D, Marsi O, Guarducci I, Batini I, Altomare E, Antonaci S, Capria A, et al. Quantitative determination of hepatitis C core antigen in therapy monitoring for chronic hepatitis C. Intervirology. 2011; 54:61–65.22. Medici MC, Furlini G, Rodella A, Fuertes A, Monachetti A, Calderaro A, Galli S, Terlenghi L, Olivares M, Bagnarelli P, et al. Hepatitis C virus core antigen: analytical performances, correlation with viremia and potential applications of a quantitative, automated immunoassay. J Clin Virol. 2011; 51:264–269.23. Vermehren J, Susser S, Berger A, Perner D, Peiffer KH, Allwinn R, Zeuzem S, Sarrazin C. Clinical utility of the ARCHITECT HCV Ag assay for early treatment monitoring in patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infection. J Clin Virol. 2012; 55:17–22.24. Alsiö A, Jannesson A, Langeland N, Pedersen C, Färkkilä M, Buhl MR, Mørch K, Westin J, Hellstrand K, Norkrans G, et al. Early quantification of HCV core antigen may help to determine the duration of therapy for chronic genotype 2 or 3 HCV infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31:1631–1635.25. Mederacke I, Wedemeyer H, Ciesek S, Steinmann E, Raupach R, Wursthorn K, Manns MP, Tillmann HL. Performance and clinical utility of a novel fully automated quantitative HCV-core antigen assay. J Clin Virol. 2009; 46:210–215.26. Ferenci P, Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Smith CI, Marinos G, Gonçales FL Jr, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, et al. Predicting sustained virological responses in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a (40 KD)/ribavirin. J Hepatol. 2005; 43:425–433.27. Jensen DM, Morgan TR, Marcellin P, Pockros PJ, Reddy KR, Hadziyannis SJ, Ferenci P, Ackrill AM, Willems B. Early identification of HCV genotype 1 patients responding to 24 weeks peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kd)/ribavirin therapy. Hepatology. 2006; 43:954–960.28. Ferenci P, Laferl H, Scherzer TM, Gschwantler M, Maieron A, Brunner H, Stauber R, Bischof M, Bauer B, Datz C, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin for 24 weeks in hepatitis C type 1 and 4 patients with rapid virological response. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:451–458.29. Jacobson IM, McHutchison JG, Dusheiko G, Di Bisceglie AM, Reddy KR, Bzowej NH, Marcellin P, Muir AJ, Ferenci P, Flisiak R, et al. Telaprevir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:2405–2416.30. Poynard T, Marcellin P, Lee SS, Niederau C, Minuk GS, Ideo G, Bain V, Heathcote J, Zeuzem S, Trepo C, et al. Randomised trial of interferon alpha2b plus ribavirin for 48 weeks or for 24 weeks versus interferon alpha2b plus placebo for 48 weeks for treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group (IHIT). Lancet. 1998; 352:1426–1432.31. Asselah T, Marcellin P. Interferon free therapy with direct acting antivirals for HCV. Liver Int. 2013; 33:Suppl 1. 93–104.32. Schorr GS, Falcone EA, Moretti DJ, Andrews RD. First long-term behavioral records from Cuvier’s beaked whales (Ziphius cavirostris) reveal record-breaking dives. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e92633.33. Aghemo A, Degasperi E, De Nicola S, Bono P, Orlandi A, D’Ambrosio R, Soffredini R, Perbellini R, Lunghi G, Colombo M. Quantification of core antigen monitors efficacy of direct-acting antiviral agents in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. Forthcoming. 2016.34. Pischke S, Polywka S, Proske VM, Lang M, Jordan S, Nashan B, Lohse AW, Sterneck M. Course of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA and HCV core antigen testing are predictors for reaching sustained virologic response in liver transplant recipients undergoing sofosbuvir treatment in a real-life setting. Transpl Infect Dis. 2016; 18:141–145.35. Garbuglia AR, Lionetti R, Lapa D, Taibi C, Visco-Comandini U, Montalbano M, D’Offizi G, Castiglione F, Capobianchi MR, Paci P. The clinical significance of HCV core antigen detection during Telaprevir/Peg-Interferon/Ribavirin therapy in patients with HCV 1 genotype infection. J Clin Virol. 2015; 69:68–73.36. Tillmann HL. Hepatitis C virus core antigen testing: role in diagnosis, disease monitoring and treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:6701–6706.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatitis B Core Antigen Expression in Hepatocytes Reflects Viral Response to Entecavir in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- New biomarkers of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection: HBV RNA and HBV core-related antigen, new kids on the block?
- Effect of the mutation in the carboxyl-terminal processing site of the hepatitis B virus core antigen on the HBeAg secretion
- Mutations in the pre-core region of hepatitis B virus DNA in a patient with severe anti-HBe positive chronic hepatitis B