Korean J Radiol.
2016 Dec;17(6):864-873. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.6.864.
Short-Term Outcomes and Safety of Computed Tomography-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of Solitary Adrenal Metastasis from Lung Cancer: A Multi-Center Retrospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated with Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong Province 250021, China. yexintaian2014@163.com
- 2Imaging and Interventional Center, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province 510060, China.
- 3Department of Oncology, Teng Zhou Central People's Hospital Affiliated with Jining Medical College, Tengzhou, Shandong Province 277500, China.
- 4Department of Oncology, Jinan Military General Hospital of Chinese People's Liberation Army, Jinan, Shandong Province 250021, China.
- KMID: 2466283
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.6.864
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To retrospectively evaluate the short-term outcomes and safety of computed tomography (CT)-guided percutaneous microwave ablation (MWA) of solitary adrenal metastasis from lung cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2010 to April 2014, 31 patients with unilateral adrenal metastasis from lung cancer who were treated with CT-guided percutaneous MWA were enrolled. This study was conducted with approval from local Institutional Review Board. Clinical outcomes and complications of MWA were assessed.
RESULTS
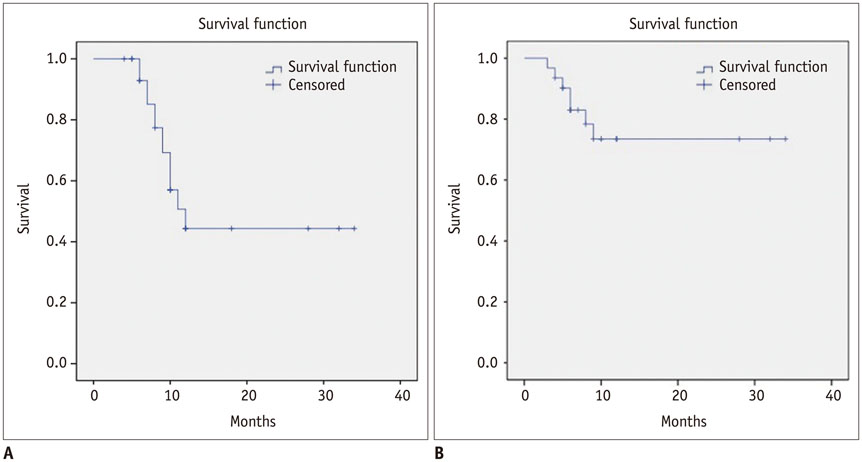
Their tumors ranged from 1.5 to 5.4 cm in diameter. After a median follow-up period of 11.1 months, primary efficacy rate was 90.3% (28/31). Local tumor progression was detected in 7 (22.6%) of 31 cases. Their median overall survival time was 12 months. The 1-year overall survival rate was 44.3%. Median local tumor progression-free survival time was 9 months. Local tumor progression-free survival rate was 77.4%. Of 36 MWA sessions, two (5.6%) had major complications (hypertensive crisis).
CONCLUSION
CT-guided percutaneous MWA may be fairly safe and effective for treating solitary adrenal metastasis from lung cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Gland Neoplasms/diagnostic imaging/secondary
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Blood Pressure/physiology
Catheter Ablation/adverse effects
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Humans
Length of Stay
Lung Neoplasms/diagnostic imaging/mortality/*pathology/surgery
Male
*Microwaves
Middle Aged
Pain/etiology
Retrospective Studies
Survival Rate
*Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Treatment Outcome
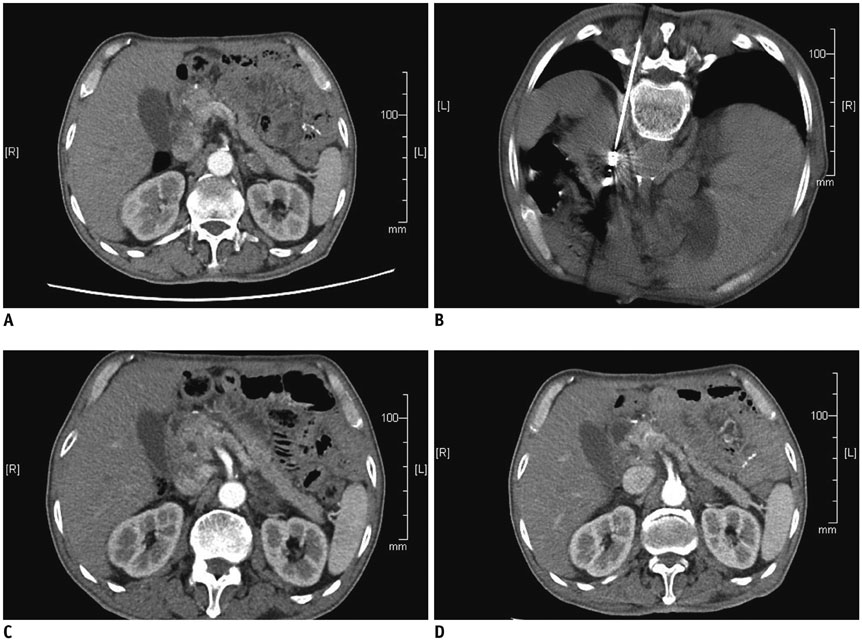
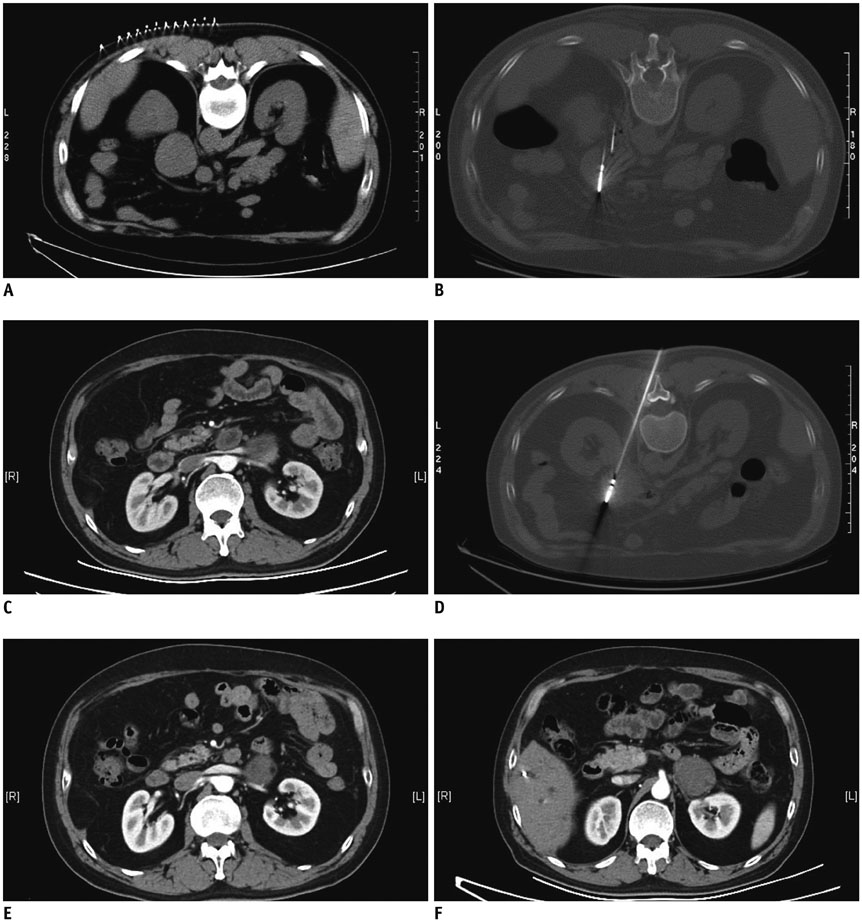
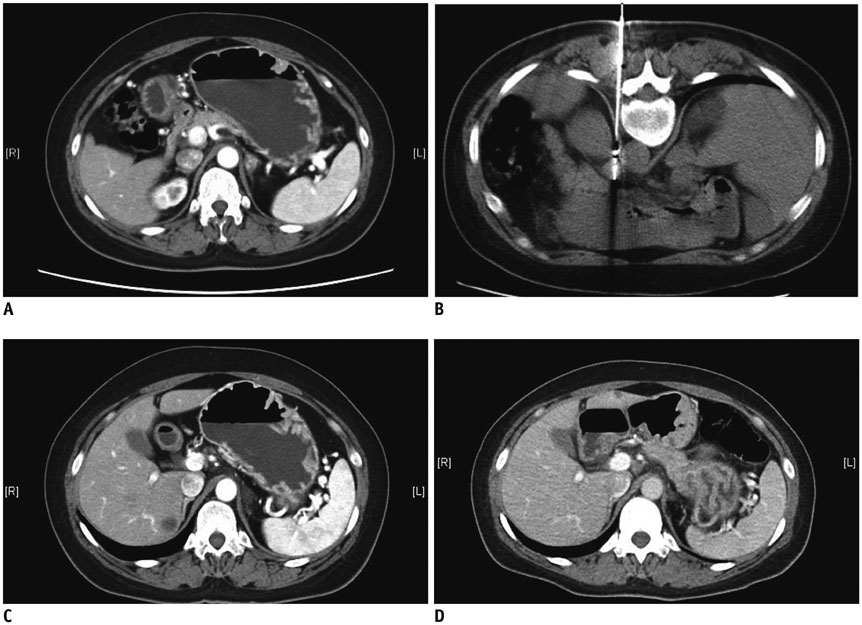
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):553-563. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1008.
Reference
-
1. Yamakado K. Image-guided ablation of adrenal lesions. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2014; 31:149–156.2. Bradley CT, Strong VE. Surgical management of adrenal metastases. J Surg Oncol. 2014; 109:31–35.3. Vazquez BJ, Richards ML, Lohse CM, Thompson GB, Farley DR, Grant CS, et al. Adrenalectomy improves outcomes of selected patients with metastatic carcinoma. World J Surg. 2012; 36:1400–1405.4. Yamakado K, Anai H, Takaki H, Sakaguchi H, Tanaka T, Kichikawa K, et al. Adrenal metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation combined with adrenal arterial chemoembolization in six patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:W300–W305.5. Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE. Adrenal neoplasms: CT-guided radiofrequency ablation--preliminary results. Radiology. 2004; 231:225–230.6. Xiao YY, Tian JL, Li JK, Yang L, Zhang JS. CT-guided percutaneous chemical ablation of adrenal neoplasms. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:105–110.7. Murphy KP, Maher MM, O'Connor OJ. Abdominal ablation techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 204:W495–W502.8. Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL, Breen DJ, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014; 25:1691–1705.e4.9. Ward RC, Healey TT, Dupuy DE. Microwave ablation devices for interventional oncology. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2013; 10:225–238.10. Abbas G. Microwave ablation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; 23:81–83.11. Ye X, Fan W, Chen JH, Feng WJ, Gu SZ, Han Y, et al. Chinese expert consensus workshop report: guidelines for thermal ablation of primary and metastatic lung tumors. Thorac Cancer. 2015; 6:112–121.12. Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, et al. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982; 5:649–655.13. Ong CK, Lirk P, Seymour RA, Jenkins BJ. The efficacy of preemptive analgesia for acute postoperative pain management: a meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 2005; 100:757–773. table of contents.14. Yang X, Ye X, Zheng A, Huang G, Ni X, Wang J, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation of stage I medically inoperable non-small cell lung cancer: clinical evaluation of 47 cases. J Surg Oncol. 2014; 110:758–763.15. Wei Z, Ye X, Yang X, Huang G, Li W, Wang J, et al. Microwave ablation plus chemotherapy improved progression-free survival of advanced non-small cell lung cancer compared to chemotherapy alone. Med Oncol. 2015; 32:464.16. Lubner MG, Brace CL, Hinshaw JL, Lee FT Jr. Microwave tumor ablation: mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010; 21:8 Suppl. S192–S203.17. Crocetti L, Bozzi E, Faviana P, Cioni D, Della Pina C, Sbrana A, et al. Thermal ablation of lung tissue: in vivo experimental comparison of microwave and radiofrequency. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33:818–827.18. Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20:7 Suppl. S377–S390.19. Beland MD, Mayo-Smith WW. Ablation of adrenal neoplasms. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 34:588–592.20. Ethier MD, Beland MD, Mayo-Smith W. Image-guided ablation of adrenal tumors. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013; 16:262–268.21. Pua BB, Solomon SB. Ablative therapies in adrenal tumors: primary and metastatic. J Surg Oncol. 2012; 106:626–631.22. Uppot RN, Gervais DA. Imaging-guided adrenal tumor ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200:1226–1233.23. Brace CL. Radiofrequency and microwave ablation of the liver, lung, kidney, and bone: what are the differences? Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2009; 38:135–143.24. Carrafiello G, Laganà D, Mangini M, Fontana F, Dionigi G, Boni L, et al. Microwave tumors ablation: principles, clinical applications and review of preliminary experiences. Int J Surg. 2008; 6 Suppl 1. S65–S69.25. Fan W, Li X, Zhang L, Jiang H, Zhang J. Comparison of microwave ablation and multipolar radiofrequency ablation in vivo using two internally cooled probes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:W46–W50.26. Poulou LS, Botsa E, Thanou I, Ziakas PD, Thanos L. Percutaneous microwave ablation vs radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2015; 7:1054–1063.27. Spiro SG, Rudd RM, Souhami RL, Brown J, Fairlamb DJ, Gower NH, et al. Chemotherapy versus supportive care in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: improved survival without detriment to quality of life. Thorax. 2004; 59:828–836.28. Plönes T, Osei-Agyemang T, Krohn A, Passlick B. Surgical treatment of extrapulmonary oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Indian J Surg. 2015; 77:Suppl 2. 216–220.29. Luketich JD, Burt ME. Does resection of adrenal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer improve survival? Ann Thorac Surg. 1996; 62:1614–1616.30. Moreno P, de la Quintana Basarrate A, Musholt TJ, Paunovic I, Puccini M, Vidal O, et al. Adrenalectomy for solid tumor metastases: results of a multicenter European study. Surgery. 2013; 154:1215–1222. discussion 1222-1223.31. Porte H, Siat J, Guibert B, Lepimpec-Barthes F, Jancovici R, Bernard A, et al. Resection of adrenal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter study. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001; 71:981–985.32. Desai A, Rai H, Haas J, Witten M, Blacksburg S, Schneider JG. A retrospective review of cyberKnife stereotactic body radiotherapy for adrenal tumors (primary and metastatic): Winthrop University Hospital experience. Front Oncol. 2015; 5:185.33. Soejima T, Hirota S, Hishikawa Y, Hamanaka A, Ozawa Z, Endo M, et al. [Radiation therapy for adrenal metastases]. Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 1997; 57:801–804.34. Li X, Fan W, Zhang L, Zhao M, Huang Z, Li W, et al. CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of adrenal malignant carcinoma: preliminary results. Cancer. 2011; 117:5182–5188.35. Wang Y, Liang P, Yu X, Cheng Z, Yu J, Dong J. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of adrenal metastasis: preliminary results. Int J Hyperthermia. 2009; 25:455–461.36. Tsoumakidou G, Buy X, Zickler P, Zupan M, Douchet MP, Gangi A. Life-threatening complication during percutaneous ablation of adrenal gland metastasis: Takotsubo syndrome. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33:646–649.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Percutaneous Adrenal Radiofrequency Ablation: A Short Review for Endocrinologists
- Adenocarcinoma of Lung Cancer with Solitary Metastasis to the Stomach
- Percutaneous ablation of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: a comparison between the outcomes of ultrasound guidance and CT guidance using propensity score matching
- Ultrasound (US)-Guided Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
- Hematoma-Filled Pneumatocele after CT-Guided Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Lung Biopsy: Two Case Reports