Clin Endosc.
2019 Nov;52(6):581-587. 10.5946/ce.2019.017.
Effectiveness of Endoscopic Sclerotherapy with Aluminum Potassium Sulfate and Tannic Acid as a Non-Surgical Treatment for Internal Hemorrhoids
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Coloproctological Surgery, Juntendo University, Faculty of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. tomiki@juntendo.ac.jp
- KMID: 2465801
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.017
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Sclerotherapy with aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid (ALTA) has a potent effect on internal hemorrhoids. In this retrospective study, we compared the effects of endoscopic ALTA therapy and standard ALTA therapy.
METHODS
We investigated patients who underwent treatment for internal hemorrhoids at our institution between 2014 and 2016. They were divided into a standard ALTA group (n=33, treated using proctoscopy) and an endoscopic ALTA group (n=48). We compared the clinical findings between the 2 groups.
RESULTS
There were no intergroup differences in background factors. The mean ALTA dose was 21.9±7.2 mL and 17.8±3.4 mL in the standard and endoscopic ALTA groups, respectively (p<0.01). Adverse events occurred in 4 patients (12.1%) from the standard ALTA group and 6 patients (12.5%) from the endoscopic ALTA group. In both groups, the patients reported good satisfaction with the therapeutic effect at 1 month after the procedure. Hemorrhoids recurred in 2 patients (6.3%) from the standard ALTA group and 4 patients (8.3%) from the endoscopic ALTA group.
CONCLUSIONS
Endoscopic ALTA sclerotherapy is equivalent to standard ALTA therapy in terms of efficacy, adverse events, and recurrence. Therefore, it is a useful non-surgical option for patients with internal hemorrhoids who prefer a less invasive treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
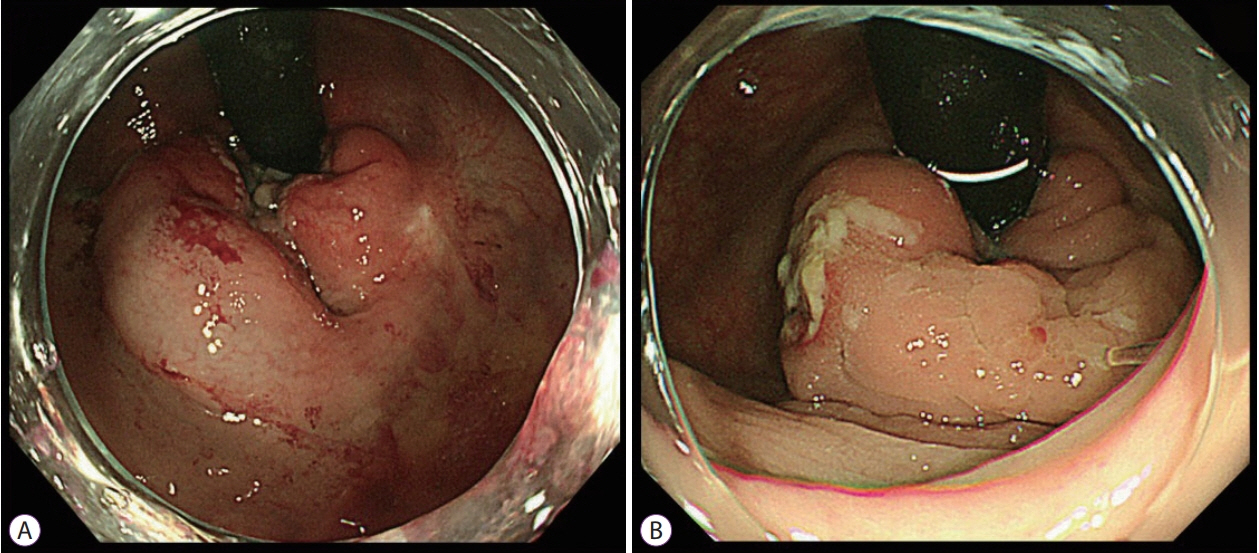
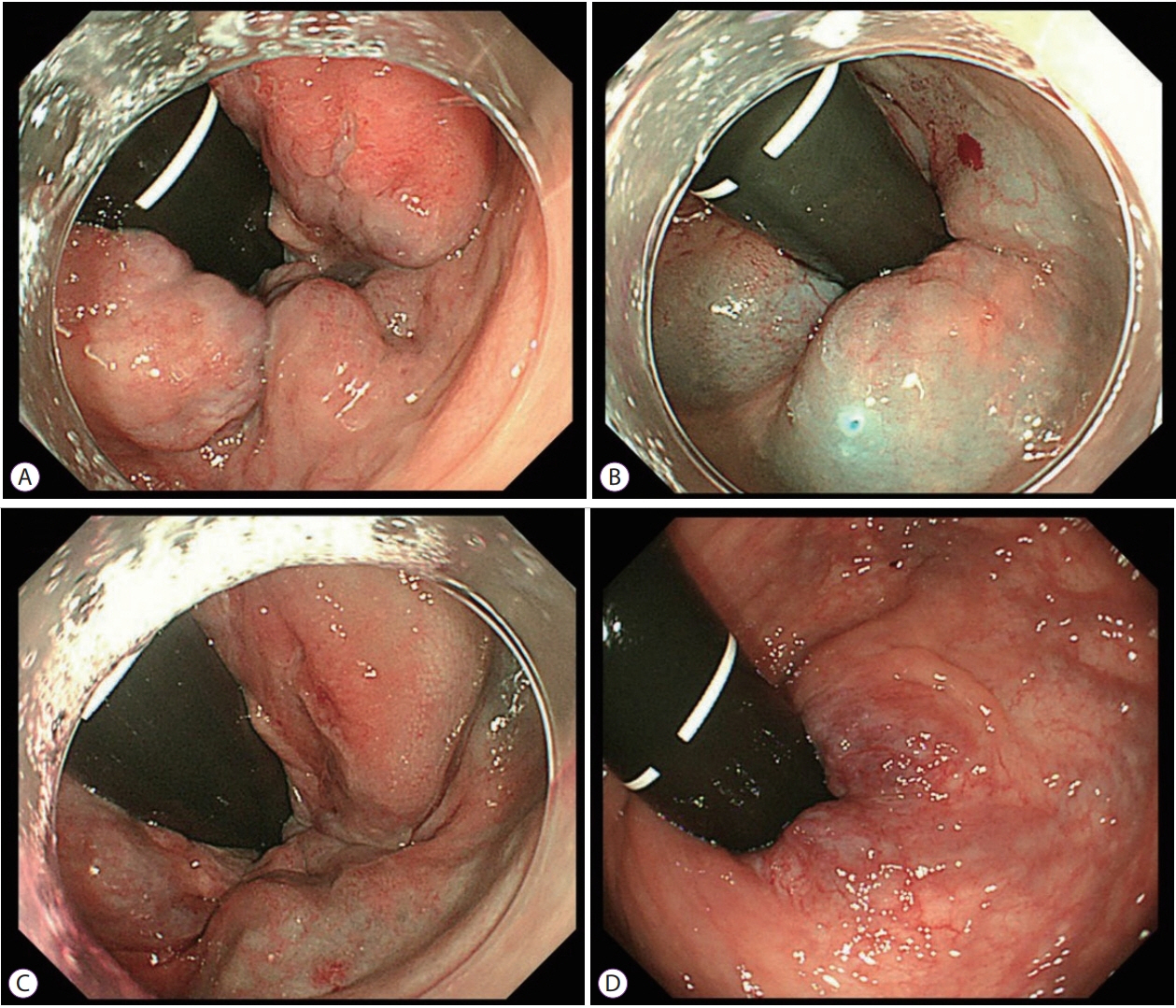
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Endoscopic Sclerotherapy with Aluminum Potassium Sulfate and Tannic Acid: An Effective and Less Invasive Strategy for Internal Hemorrhoids
Naoki Muguruma, Tetsuji Takayama
Clin Endosc. 2019;52(6):521-522. doi: 10.5946/ce.2019.162.
Reference
-
1. Hachiro Y, Kunimoto M, Abe T, Kitada M, Ebisawa Y. Aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid (ALTA) injection as the mainstay of treatment for internal hemorrhoids. Surg Today. 2011; 41:806–809.
Article2. Miyamoto H, Asanoma M, Miyamoto H, Shimada M. ALTA injection sclerosing therapy:non-excisional treatment of internal hemorrhoids. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012; 59:77–80.3. Tokunaga Y, Sasaki H. Impact of less invasive treatments including sclerotherapy with a new agent and hemorrhoidopexy for prolapsing internal hemorrhoids. Int Surg. 2013; 98:210–213.
Article4. Miyamoto H, Hada T, Ishiyama G, Ono Y, Watanabe H. Aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid sclerotherapy for Goligher Grades II and III hemorrhoids: results from a multicenter study. World J Hepatol. 2016; 8:844–849.
Article5. Davis BR, Lee-Kong SA, Migaly J, Feingold DL, Steele SR. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of hemorrhoids. Dis Colon Rectum. 2018; 61:284–292.
Article6. Brown SR. Haemorrhoids: an update on management. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2017; 8:141–147.
Article7. Yano T, Yano K. Comparison of injection sclerotherapy between 5% phenol in almond oil and aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid for grade 3 hemorrhoids. Ann Coloproctol. 2015; 31:103–105.
Article8. Lim SW. Aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid injection for hemorrhoids. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2012; 28:73–77.
Article9. Tomiki Y, Ono S, Aoki J, Takahashi R, Sakamoto K. Endoscopic sclerotherapy with aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid for internal hemorrhoids. Endoscopy. 2014; 46 Suppl 1 UCTN:E114.
Article10. Tomiki Y, Ono S, Aoki J, et al. Treatment of internal hemorrhoids by endoscopic sclerotherapy with aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2015; 2015:517690.
Article11. Yano T, Nogaki T, Asano M, Tanaka S, Kawakami K, Matsuda Y. Outcomes of case-matched injection sclerotherapy with a new agent for hemorrhoids in patients treated with or without blood thinners. Surg Today. 2013; 43:854–858.
Article12. ASGE Technology Committee, Siddiqui UD, Barth BA, et al. Devices for the endoscopic treatment of hemorrhoids. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79:8–14.
Article13. Zhang T, Xu LJ, Xiang J, et al. Cap-assisted endoscopic sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids: methods, feasibility and efficacy. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:1334–1340.
Article14. Tomiki Y, Higashiyama A, Okada T, et al. Evaluation of endoscopic hemorrhoidal ligation in 119 patients. Dig Endosc. 2003; 15:30–34.
Article15. Abe T, Hachiro Y, Ebisawa Y, Hishiyama H, Kunimoto M. Distal hemorrhoidectomy with ALTA injection: a new method for hemorrhoid surgery. Int Surg. 2014; 99:295–298.
Article16. Albuquerque A. Rubber band ligation of hemorrhoids: a guide for complications. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2016; 8:614–620.
Article17. Yano T, Asano M, Tanaka S, Oda N, Matsuda Y. Prospective study comparing the new sclerotherapy and hemorrhoidectomy in terms of therapeutic outcomes at 4 years after the treatment. Surg Today. 2014; 44:449–453.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Sclerotherapy with Aluminum Potassium Sulfate and Tannic Acid: An Effective and Less Invasive Strategy for Internal Hemorrhoids
- Aluminum Potassium Sulfate and Tannic Acid Injection for Hemorrhoids
- Comparison of Injection Sclerotherapy Between 5% Phenol in Almond Oil and Aluminum Potassium Sulfate and Tannic Acid for Grade 3 Hemorrhoids
- Aluminum Potassium Sulfate and Tannic Acid - A New Option for the Treatment of Grade 3 Hemorrhoids
- Early postoperative outcomes of a novel nonexcisional technique using aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid sclerotherapy with mucopexy on patients with grade III hemorrhoids