Korean J Ophthalmol.
2019 Dec;33(6):528-538. 10.3341/kjo.2019.0088.
Effect of Sequential Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segment Implantation and Corneal Collagen Crosslinking in Corneal Ectasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmk9@snu.ac.kr
- 2Laboratory of Ocular Regenerative Medicine and Immunology, Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2465133
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2019.0088
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To assess the clinical efficacy of sequential intrastromal corneal ring segment (ICRS) implantation and corneal crosslinking (CXL) in corneal ectasia.
METHODS
To assess the clinical efficacy of sequential intrastromal corneal ring segment (ICRS) implantation and corneal crosslinking (CXL) in corneal ectasia.
RESULTS
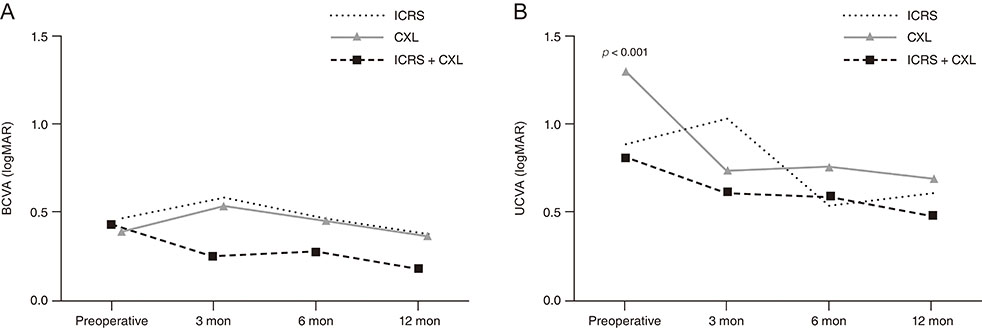
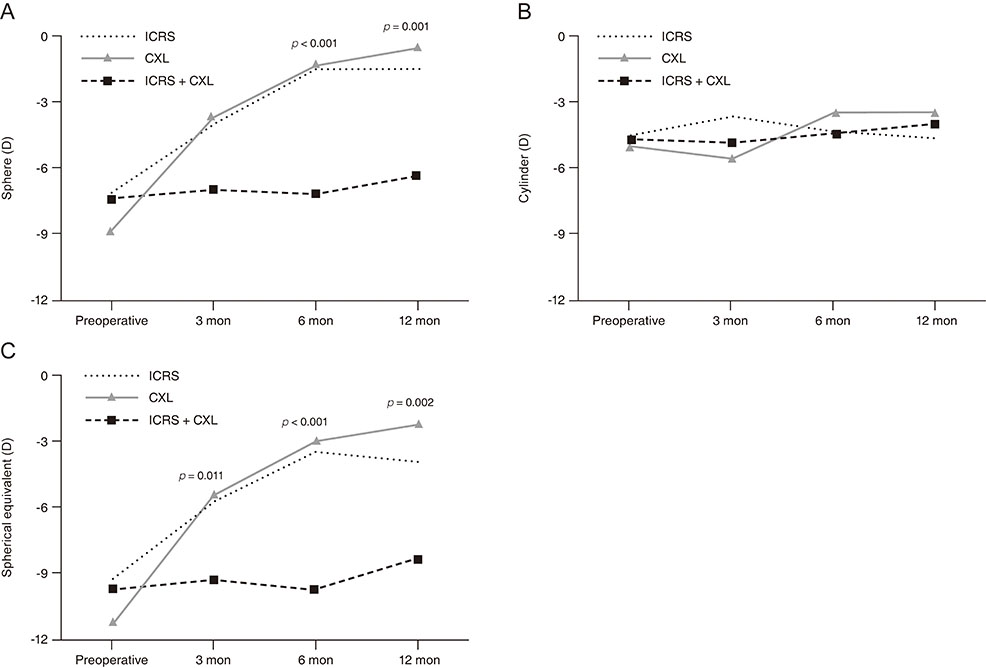
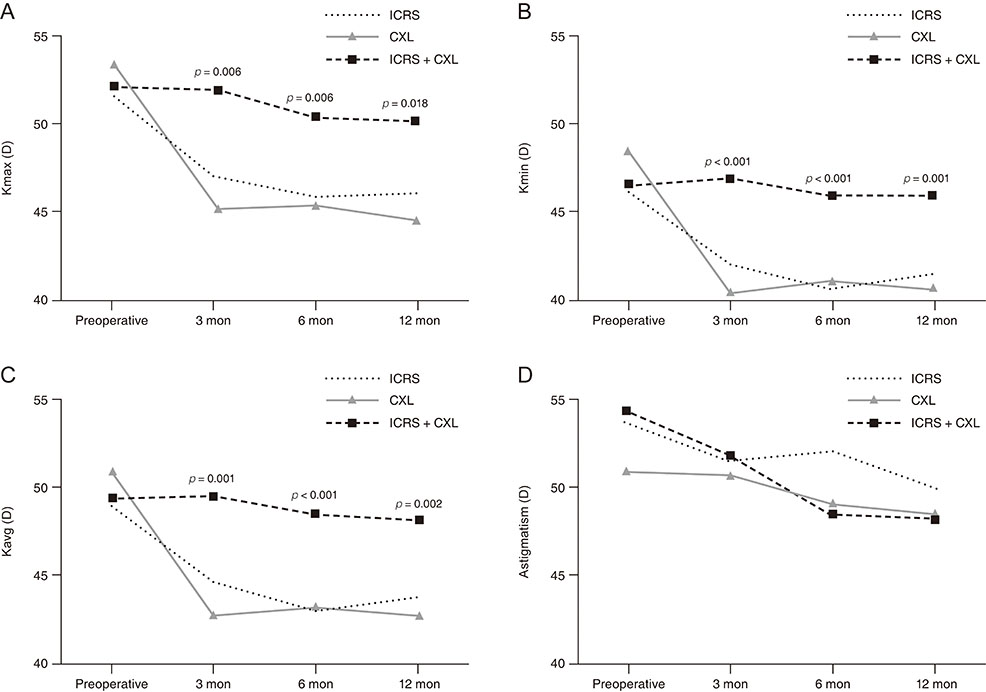
Greater improvement in uncorrected visual acuity was observed in the ICRS + CXL group than in the ICRS or CXL alone groups at both 6 (p = 0.008) and 12 months (p = 0.028). Refractive errors of sphere and spherical equivalent were significantly reduced in both the ICRS (p = 0.002 at 6 months, p = 0.004 at 12 months) and ICRS + CXL groups (p < 0.001 at both 6 and 12 months). Keratometric values including the maximum, minimum, and average were significantly reduced in all 3 groups at postoperative 6 and 12 months; however, the greatest reductions were observed in the ICRS + CXL group (all p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
ICRS implantation followed by CXL within 1 month seems to be effective, and may be superior to ICRS or CXL alone in improving visual acuity and reducing refractive errors and keratometric values.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parker JS, van Dijk K, Melles GR. Treatment options for advanced keratoconus: a review. Surv Ophthalmol. 2015; 60:459–480.2. Rabinowitz YS. Intacs for keratoconus. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007; 18:279–283.3. Raiskup F, Theuring A, Pillunat LE, Spoerl E. Corneal collagen crosslinking with riboflavin and ultraviolet-A light in progressive keratoconus: ten-year results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:41–46.4. Spoerl E, Huhle M, Seiler T. Induction of cross-links in corneal tissue. Exp Eye Res. 1998; 66:97–103.5. Wollensak G, Spoerl E, Seiler T. Riboflavin/ultraviolet-a-induced collagen crosslinking for the treatment of keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:620–627.6. Burris TE. Intrastromal corneal ring technology: results and indications. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1998; 9:9–14.7. Ibrahim O, Elmassry A, Said A, et al. Combined femtosecond laser-assisted intracorneal ring segment implantation and corneal collagen cross-linking for correction of keratoconus. Clin Ophthalmol. 2016; 10:521–526.8. Cakir H, Pekel G, Perente I, Genc S. Comparison of intrastromal corneal ring segment implantation only and in combination with collagen crosslinking for keratoconus. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2013; 23:629–634.9. Coskunseven E, Jankov MR 2nd, Hafezi F, et al. Effect of treatment sequence in combined intrastromal corneal rings and corneal collagen crosslinking for keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:2084–2091.10. Legare ME, Iovieno A, Yeung SN, et al. Intacs with or without same-day corneal collagen cross-linking to treat corneal ectasia. Can J Ophthalmol. 2013; 48:173–178.11. Liu XL, Li PH, Fournie P, Malecaze F. Investigation of the efficiency of intrastromal ring segments with cross-linking using different sequence and timing for keratoconus. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015; 8:703–708.12. Benoist d'Azy C, Pereira B, Chiambaretta F, Dutheil F. Efficacy of different procedures of intra-corneal ring segment implantation in keratoconus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2019; 8:38.13. Kim JA, Kim DH, Wee WR, Kim MK. Clinical results of intacs(R) ring implantation in keratoconus or keratectasia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:499–508.14. Kim CY, Kim MK. Effect of the retention ring-assisted continuous application of riboflavin in pulsed-light accelerated corneal collagen cross-linking on the progression of keratoconus. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019; 19:72.15. Park J, Gritz DC. Evolution in the use of intrastromal corneal ring segments for corneal ectasia. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013; 24:296–301.16. Kilic A, Kamburoglu G, Akinci A. Riboflavin injection into the corneal channel for combined collagen crosslinking and intrastromal corneal ring segment implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:878–883.17. Saelens IE, Bartels MC, Bleyen I, Van Rij G. Refractive, topographic, and visual outcomes of same-day corneal cross-linking with Ferrara intracorneal ring segments in patients with progressive keratoconus. Cornea. 2011; 30:1406–1408.18. Hashemi H, Alvani A, Seyedian MA, et al. Appropriate sequence of combined intracorneal ring implantation and corneal collagen cross-linking in keratoconus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cornea. 2018; 37:1601–1607.19. Soeters N, Muijzer MB, Molenaar J, et al. Autorefraction versus manifest refraction in patients with keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 2018; 34:30–34.20. Ozerturk Y, Sari ES, Kubaloglu A, et al. Comparison of deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty and intrastromal corneal ring segment implantation in advanced keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:324–332.21. Elsaftawy HS, Ahmed MH, Saif MY, Mousa R. Sequential intracorneal ring segment implantation and corneal transepithelial collagen cross-linking in keratoconus. Cornea. 2015; 34:1420–1426.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments (KeraRing(R)) Implantation for the Correction of Keratoconus
- The Clinical Results of Intacs(R) Ring Implantation by Manual Tunnel Creation in Patients with Keratoconus
- Sequential Intrastromal Corneal Ring Implantation and Cataract Surgery in a Severe Keratoconus Patient with Cataract
- Clinical Results of Intacs(R) Ring Implantation in Keratoconus or Keratectasia
- The Clinical Results of Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segment Implantation Using a Femtosecond Laser in Keratectasia