Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2019 Nov;23(4):397-402. 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.397.
The drain fluid amylase level on the first postoperative day predicts pancreatic fistula in chronic pancreatitis patients undergoing Frey procedure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgical Gastroenterology, JIPMER, Puducherry, India. kalayarasanraja@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2464331
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.397
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
Abdominal drains are routinely placed following Frey procedure for chronic pancreatitis (CP) despite the low incidence of pancreatic fistula (PF). The utility of the first postoperative day (POD1) drain fluid amylase (DFA) value in predicting PF in CP patients undergoing Frey procedure has not been previously reported.
METHODS
A prospective study of patients with CP who underwent Frey procedure between August 2014 and April 2018. A standard technique of head coring with single layer continuous pancreatojejunostomy was done in all the patients. Amylase level of the drain placed close to the pancreatojejunostomy was recorded on POD1 and 3. Postoperative PF was defined and graded as per the updated International Study Group of Pancreatic Fistula (ISGPF) guidelines.
RESULTS
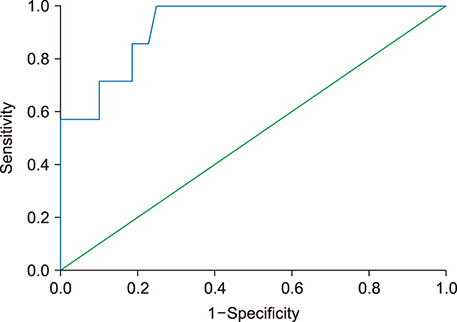
Fifty-five patients with CP who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were included in the study. All had normal preoperative serum amylase level. Three patients developed a biochemical leak and four patients developed postoperative PF (Grade B - 3 and Grade C - 1). Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve identified a POD1 DFA cut-off value of 326 U/L that predicted a postoperative PF with sensitivity, specificity and negative predictive value of 100%, 70%, and 100% respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The POD1 DFA is a reliable predictor of postoperative PF in CP patients who have undergone Frey procedure. The PF can be confidently excluded in patients who have a POD1 DFA less than 326 U/L.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Frey’s plus versus Frey’s procedure for chronic pancreatitis: Analysis of postoperative outcomes and quality of life
Gunasekaran Gopalakrishnan, Raja Kalayarasan, Senthil Gnanasekaran, Biju Pottakkat
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2020;24(4):496-502. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.4.496.
Reference
-
1. El Nakeeb A, Salah T, Sultan A, El Hemaly M, Askr W, Ezzat H, et al. Pancreatic anastomotic leakage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Risk factors, clinical predictors, and management (single center experience). World J Surg. 2013; 37:1405–1418.2. Molinari E, Bassi C, Salvia R, Butturini G, Crippa S, Talamini G, et al. Amylase value in drains after pancreatic resection as predictive factor of postoperative pancreatic fistula: results of a prospective study in 137 patients. Ann Surg. 2007; 246:281–287.3. Sutcliffe RP, Battula N, Haque A, Ali A, Srinivasan P, Atkinson SW, et al. Utility of drain fluid amylase measurement on the first postoperative day after pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Surg. 2012; 36:879–883.4. Roch A, Teyssedou J, Mutter D, Marescaux J, Pessaux P. Chronic pancreatitis: a surgical disease? Role of the Frey procedure. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2014; 6:129–135.5. Izbicki JR, Bloechle C, Broering DC, Knoefel WT, Kuechler T, Broelsch CE. Extended drainage versus resection in surgery for chronic pancreatitis: a prospective randomized trial comparing the longitudinal pancreaticojejunostomy combined with local pancreatic head excision with the pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 1998; 228:771–779.6. Bachmann K, Tomkoetter L, Kutup A, Erbes J, Vashist Y, Mann O, et al. Is the Whipple procedure harmful for long-term outcome in treatment of chronic pancreatitis? 15-years follow-up comparing the outcome after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy and Frey procedure in chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2013; 258:815–820. discussion 820–821.7. Sudo T, Murakami Y, Uemura K, Hashimoto Y, Kondo N, Nakagawa N, et al. Short- and long-term results of lateral pancreaticojejunostomy for chronic pancreatitis: a retrospective Japanese single-center study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014; 21:426–432.8. Ljungqvist O, Scott M, Fearon KC. Enhanced recovery after surgery: a review. JAMA Surg. 2017; 152:292–298.9. Saluja SS, Kalayarasan R, Mishra PK, Srivastava S, Chandrasekar S, Godhi S. Chronic pancreatitis with benign biliary obstruction: management issues. World J Surg. 2014; 38:2455–2459.10. Bassi C, Marchegiani G, Dervenis C, Sarr M, Abu Hilal M, Adham M, et al. International Study Group on Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS). The 2016 update of the International Study Group (ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula: 11 years after. Surgery. 2017; 161:584–591.11. Wente MN, Veit JA, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fingerhut A, Gouma DJ, et al. Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (PPH): an International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) definition. Surgery. 2007; 142:20–25.12. Yang CJ, Bliss LA, Schapira EF, Freedman SD, Ng SC, Windsor JA, et al. Systematic review of early surgery for chronic pancreatitis: impact on pain, pancreatic function, and re-intervention. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014; 18:1863–1869.13. Bhutiani N, Cheadle GA, Bahr MH, Vitale GC. Comparative efficacy of bilateral thoracoscopic splanchnicectomy for intractable pain secondary to pancreatic cancer vs chronic pancreatitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2017; 224:566–571.14. Ahmed Ali U, Pahlplatz JM, Nealon WH, van Goor H, Gooszen HG, Boermeester MA. Endoscopic or surgical intervention for painful obstructive chronic pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; (3):CD007884.15. Wang Q, Jiang YJ, Li J, Yang F, Di Y, Yao L, et al. Is routine drainage necessary after pancreaticoduodenectomy? World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:8110–8118.16. van der Wilt AA, Coolsen MM, de Hingh IH, van der Wilt GJ, Groenewoud H, Dejong CH, et al. To drain or not to drain: a cumulative meta-analysis of the use of routine abdominal drains after pancreatic resection. HPB (Oxford). 2013; 15:337–344.17. Conlon KC, Labow D, Leung D, Smith A, Jarnagin W, Coit DG, et al. Prospective randomized clinical trial of the value of intraperitoneal drainage after pancreatic resection. Ann Surg. 2001; 234:487–493. discussion 493–494.18. Fisher WE, Hodges SE, Silberfein EJ, Artinyan A, Ahern CH, Jo E, et al. Pancreatic resection without routine intraperitoneal drainage. HPB (Oxford). 2011; 13:503–510.19. Van Buren G 2nd, Bloomston M, Hughes SJ, Winter J, Behrman SW, Zyromski NJ, et al. A randomized prospective multicenter trial of pancreaticoduodenectomy with and without routine intraperitoneal drainage. Ann Surg. 2014; 259:605–612.20. Kawai M, Tani M, Terasawa H, Ina S, Hirono S, Nishioka R, et al. Early removal of prophylactic drains reduces the risk of intra-abdominal infections in patients with pancreatic head resection: prospective study for 104 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 2006; 244:1–7.21. Gestic MA, Callejas-Neto F, Chaim EA, Utrini MP, Cazzo E, Pareja JC. Surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis using Frey's procedure: a Brazilian 16-year single-centre experience. HPB (Oxford). 2011; 13:263–271.22. Tan CL, Zhang H, Yang M, Li SJ, Liu XB, Li KZ. Role of original and modified Frey's procedures in chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:10415–10423.23. Yamaguchi M, Nakano H, Midorikawa T, Yoshizawa Y, Sanada Y, Kumada K. Prediction of pancreatic fistula by amylase levels of drainage fluid on the first day after pancreatectomy. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003; 50:1155–1158.24. Bassi C, Molinari E, Malleo G, Crippa S, Butturini G, Salvia R, et al. Early versus late drain removal after standard pancreatic resections: results of a prospective randomized trial. Ann Surg. 2010; 252:207–214.25. Berberat PO, Ingold H, Gulbinas A, Kleeff J, Müller MW, Gutt C, et al. Fast track--different implications in pancreatic surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:880–887.26. Balzano G, Zerbi A, Braga M, Rocchetti S, Beneduce AA, Di Carlo V. Fast-track recovery programme after pancreatico- duodenectomy reduces delayed gastric emptying. Br J Surg. 2008; 95:1387–1393.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Result of Suction Pancreatic Stent in Pancreaticojejunostomy
- Changing patterns of Pancreatic enzyme after Distal Gastrectomy and the Effect of Protease Inhibitor Treatment
- The Role of External Drainage and Octreotide in Preventing Complications after Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- The Significance of Drain Amylase Level for Diagnosis of Pancreatic Leakage after Pancreatoduodenectomy
- Pancreaticopleural Fistula: CT Demonstration