J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2019 Aug;45(4):180-185. 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.4.180.
Huge central intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia of the mandible: a case report and review of the literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Dental School, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. dr.f.latifi@gmail.com
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Dental School, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- KMID: 2456035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.4.180
Abstract
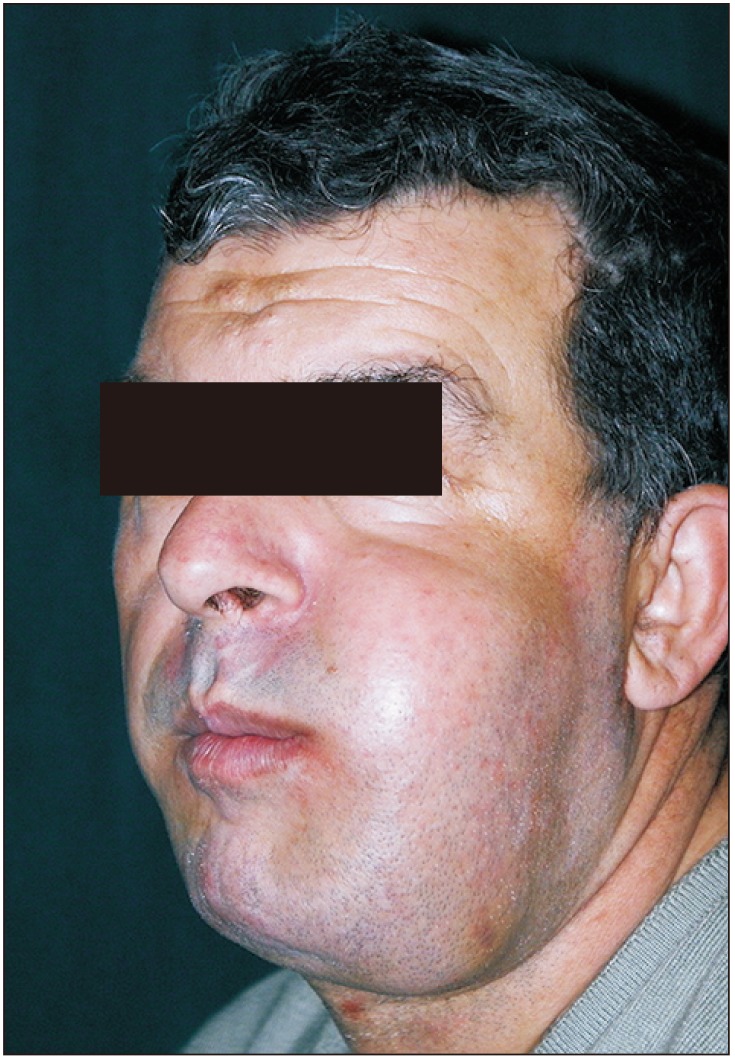
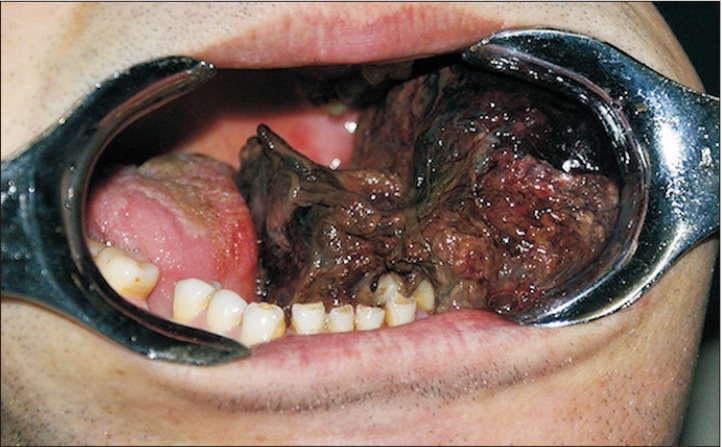
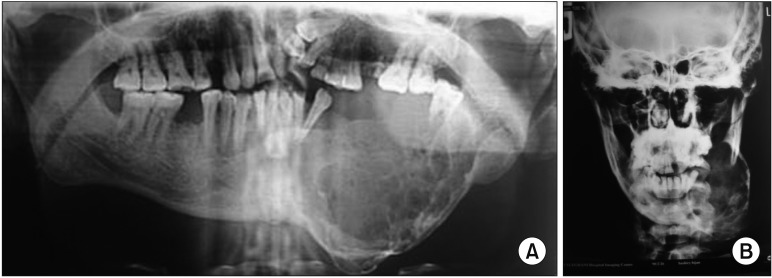
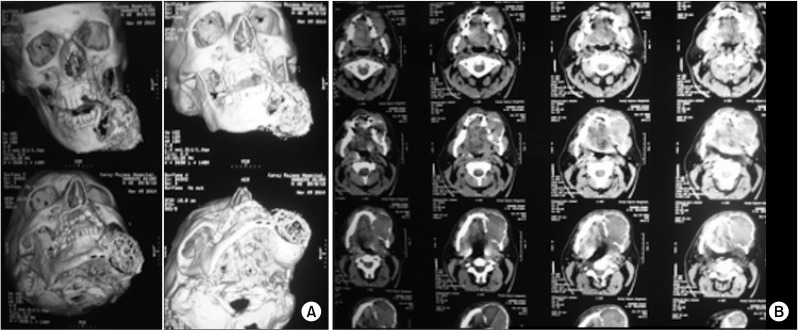
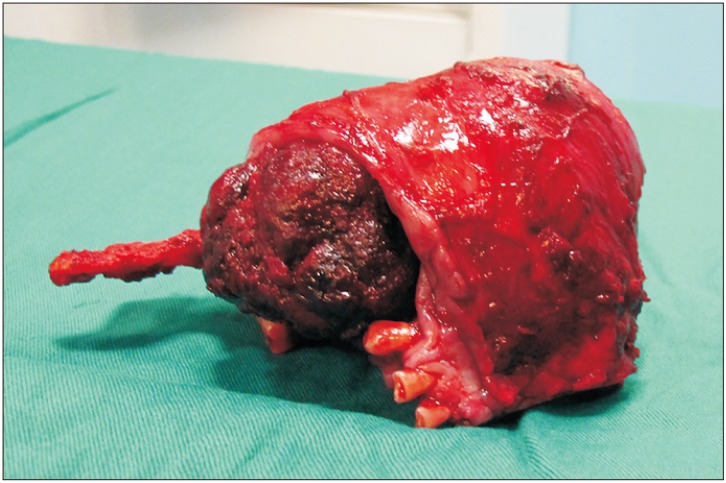
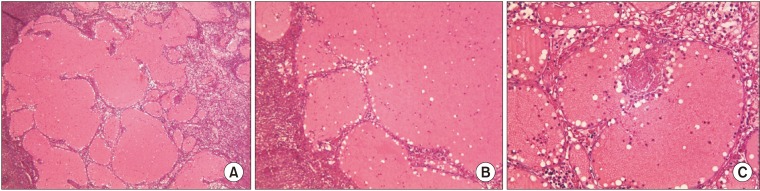
- Masson's tumor or intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia is an inflammatory soft tissue lesion that rarely occurs in the maxillofacial region and skeletal system. Precise clinical and para-clinical investigation is necessary for the accurate diagnosis and correct treatment of this lesion. This paper presents a massive intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia lesion in the bony tissue of the mandible. Histopathology features, clinical appearance, and suitable management are discussed, with a complete review of the literature. The patient underwent composite resection of the lesion as well as reconstruction. No recurrence was observed during 6 years of follow-up. To the best of our knowledge, this is the fourth case of Masson's tumor in mandibular skeletal tissue, which has unique and distinctive features due to its size and location. A rare occurrence in skeletal tissue, complex clinical presentations, and complicated histopathologic findings present diagnostic challenges for treatment of this lesion.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Masson P. Hemangioendotheliome vegetant intravasculaire. Bull Soc Anat (Paris). 1923; 93:517–523.2. Makos CP, Nikolaidou AJ. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson’s tumor) of the oral mucosa. Presentation of two cases and review. Oral Oncol Extra. 2004; 40:59–62.
Article3. Komori A, Koike M, Kinjo T, Azuma T, Yoshinari M, Inaba H, et al. Central intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia of the mandible. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1984; 403:453–459. PMID: 6429945.
Article4. Xu SS, Li D. Radiological imaging of florid intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia in the mandibule: case report and literature review. Clin Imaging. 2014; 38:364–366. PMID: 24461559.
Article5. Tanio S, Okamoto A, Majbauddin A, Sonoda M, Kodani I, Doi R, et al. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia associated with hemangioma of the mandible: a rare case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 2016; 28:55–60.
Article6. Mahapatra QS, Sahai K, Malik A, Mani NS. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia: an unusual histopathological entity. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015; 6:277–279. PMID: 26225335.
Article7. Tarallo M, Spagnoli AM, Fino P, Lo Torto F, Scuderi N. Masson's tumor: a soft tissue tumor simulating a tendon cyst: case report. G Chir. 2012; 33:34–37. PMID: 22357437.8. Kim D, Israel H, Friedman M, Kuhel W, Langevin CJ, Plansky T. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia manifesting as a submandibular mass: an unusual presentation in an uncommon location. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:786–790. PMID: 17368381.
Article9. Bologna-Molina R, Amezcua-Rosas G, Guardado-Luevanos I, Mendoza-Roaf PL, González-Montemayor T, Molina-Frechero N. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson's tumor) of the mouth - a case report. Case Rep Dermatol. 2010; 2:22–26. PMID: 21173922.
Article10. Korkolis DP, Papaevangelou M, Koulaxouzidis G, Zirganos N, Psichogiou H, Vassilopoulos PP. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson's hemangioma) presenting as a soft-tissue sarcoma. Anticancer Res. 2005; 25:1409–1412. PMID: 15865098.11. Pins MR, Rosenthal DI, Springfield DS, Rosenberg AE. Florid extravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson's pseudoangiosarcoma) presenting as a soft-tissue sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993; 117:259–263. PMID: 8442671.12. Liu DT, Shields CL, Tse GM, Lam DS. Periocular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson's tumour) in Behçet's disease. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012; 90:e413–e415. PMID: 22008471.
Article13. Sarode GS, Sarode SC, Karmarkar SP. Oral intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson's tumor): a review of literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 2014; 26:73–79.
Article14. Hashimoto H, Daimaru Y, Enjoji M. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. A clinicopathologic study of 91 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983; 5:539–546. PMID: 6666836.15. Ginat DT, Walcott BP, Mordes D, Schaefer PW, Nahed B. Intracranial organizing hematoma with papillary endothelial hyperplasia features after resection and involved field radiotherapy for cerebellar juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma. Clin Imaging. 2014; 38:322–325. PMID: 24456989.
Article16. Fomete B, Samaila M, Edaigbini S, Agbara R, Okeke UA. Primary oral soft tissue angiosarcoma of the cheek: a case report and literature review. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 41:273–277. PMID: 26568931.
Article17. Cohen A, Maly A, Azaz B. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia of the lower lip: surgical approach and review of the literature. Gerodontology. 2009; 26:305–308. PMID: 19702673.
Article18. Wang ZH, Hsin CH, Chen SY, Lo CY, Cheng PW. Sinonasal intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia successfully treated by endoscopic excision: a case report and review of the literature. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2009; 36:363–366. PMID: 18783901.
Article19. Shih CS, Burgett R, Bonnin J, Boaz J, Ho CY. Intracranial Masson tumor: case report and literature review. J Neurooncol. 2012; 108:211–217. PMID: 22278666.
Article20. Jain S, Khurana N, Gulati A. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia of the palate masquerading as adenoid cystic carcinoma on fine needle aspiration cytology: a potential diagnostic pitfall. Cytopathology. 2012; 23:198–200. PMID: 21385237.
Article21. Higashi Y, Uchida Y, Yoshii N, Kubo H, Kanzaki T, Yokouchi M, et al. Multiple intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia affecting skin and bone. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009; 34:e740–e743. PMID: 19663847.
Article22. Petry M, Brown MA, Hesselink JR, Imbesi SG. Multifocal intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia in the retroperitoneum and spine: a case report and review of the literature. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 29:957–961. PMID: 19306442.
Article23. Lee SK, Jung TY, Baek HJ, Kim SK. Destructive radiologic development of intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia on skull bone. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 52:48–51. PMID: 22993678.
Article24. Park KK, Won YS, Yang JY, Choi CS, Han KY. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson tumor) of the skull: case report and literature review. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 52:52–54. PMID: 22993679.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Intravascular Papillary Endothelial Hyperplasia Developing on the Sole
- A Case of Intavascular Papillary Endothelial Hyperplasia on Dorsum of Tongue
- A Case of Intravascular Papillary Endothelial Hyperplasia on the Finger
- A Case of Intravascular Papillary Endothelial Hyperplasia on the Lip
- A Case of Intravascular Papillary Endothelial Hyperplasia with Angioleiomyoma