Diabetes Metab J.
2019 Jun;43(3):276-286. 10.4093/dmj.2018.0051.
Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. drshchoi@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 11Diabetes Center, Endocrinology and Metabolism, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 13Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 15Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 16Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 17Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 18Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. endoswpark@gmail.com
- KMID: 2454057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0051
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Combination of metformin to reduce the fasting plasma glucose level and an α-glucosidase inhibitor to decrease the postprandial glucose level is expected to generate a complementary effect. We compared the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of voglibose plus metformin (vogmet) with metformin monotherapy in drug-naïve newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.
METHODS
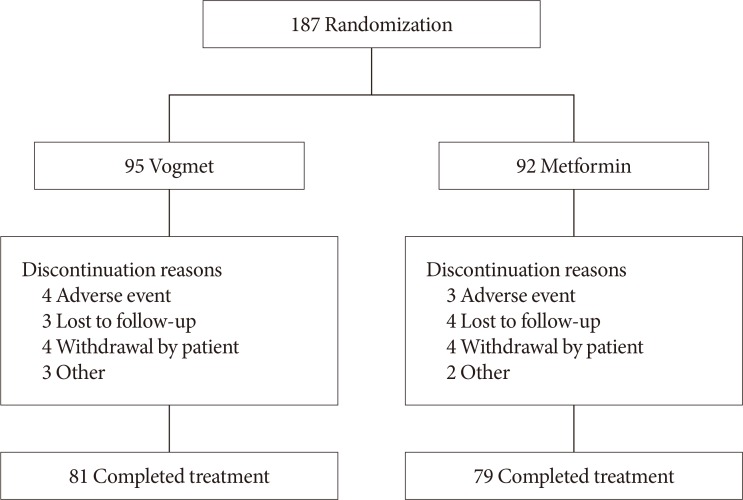
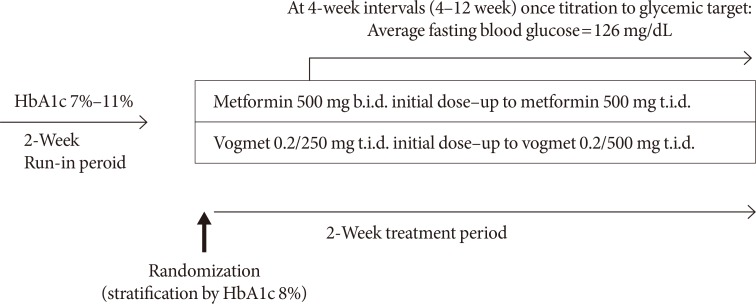
A total of 187 eligible patients aged 20 to 70 years, with a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 7.0% to 11.0%, were randomized into either vogmet or metformin treatments for 24 weeks. A change in the HbA1c level from baseline was measured at week 24.
RESULTS
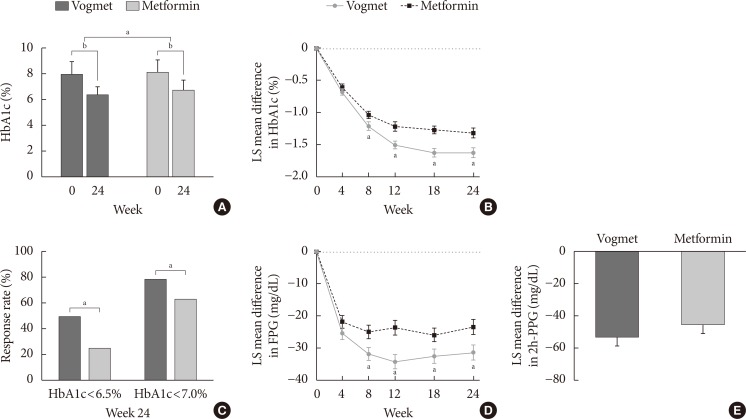
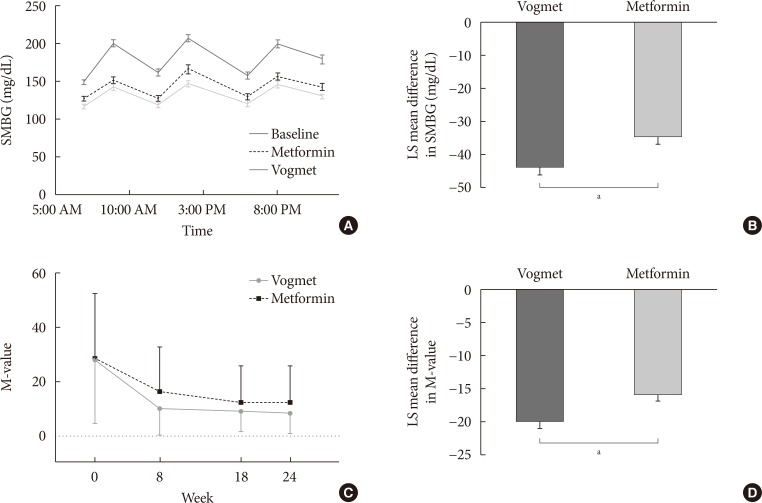
The reduction in the levels of HbA1c was −1.62%±0.07% in the vogmet group and −1.31%±0.07% in the metformin group (P=0.003), and significantly more vogmet-treated patients achieved the target HbA1c levels of <6.5% (P=0.002) or <7% (P=0.039). Glycemic variability was also significantly improved with vogmet treatment, estimated by M-values (P=0.004). Gastrointestinal adverse events and hypoglycemia (%) were numerically lower in the vogmet-treated group. Moreover, a significant weight loss was observed with vogmet treatment compared with metformin (−1.63 kg vs. −0.86 kg, P=0.039).
CONCLUSION
Vogmet is a safe antihyperglycemic agent that controls blood glucose level effectively, yields weight loss, and is superior to metformin in terms of various key glycemic parameters without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Voglibose
In Vitro andIn Vivo
Mahesh Raj Nepal, Mi Jeong Kang, Geon Ho Kim, Dong Ho Cha, Ju-Hyun Kim, Tae Cheon Jeong
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):908-918. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0147.
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 6th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation;2013.2. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. American Diabetes Association (ADA). European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1364–1379. PMID: 22517736.
Article3. Ko SH, Hur KY, Rhee SY, Kim NH, Moon MK, Park SO, Lee BW, Kim HJ, Choi KM, Kim JH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Diabetes Association. Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2017; 41:337–348. PMID: 29086531.
Article4. Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, Dagogo-Jack S, DeFronzo RA, Einhorn D, Fonseca VA, Garber JR, Garvey WT, Grunberger G, Handelsman Y, Hirsch IB, Jellinger PS, McGill JB, Mechanick JI, Rosenblit PD, Umpierrez GE. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm: 2018 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2018; 24:91–120. PMID: 29368965.5. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Lipscombe L, Booth G, Butalia S, Dasgupta K, Eurich DT, Goldenberg R, Khan N, MacCallum L, Shah BR, Simpson S. Pharmacologic glycemic management of type 2 diabetes in adults. Can J Diabetes. 2018; 42(Suppl 1):S88–S103. PMID: 29650116.
Article6. IDF Clinical Guidelines Task Force. Global guideline for type 2 diabetes. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation;2012.7. Derosa G, Maffioli P. α-Glucosidase inhibitors and their use in clinical practice. Arch Med Sci. 2012; 8:899–906. PMID: 23185202.8. Hanefeld M, Schaper F. Acarbose: oral anti-diabetes drug with additional cardiovascular benefits. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2008; 6:153–163. PMID: 18248270.
Article9. Monnier L, Colette C, Dunseath GJ, Owens DR. The loss of postprandial glycemic control precedes stepwise deterioration of fasting with worsening diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:263–269. PMID: 17259492.
Article10. Schrot RJ. Targeting plasma glucose: preprandial versus postprandial. Clin Diabetes. 2004; 22:169–172.
Article11. Chiasson JL, Naditch L. Miglitol Canadian University Investigator Group. The synergistic effect of miglitol plus metformin combination therapy in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:989–994. PMID: 11375358.
Article12. Halimi S, Le Berre MA, Grange V. Efficacy and safety of acarbose add-on therapy in the treatment of overweight patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000; 50:49–56. PMID: 10936668.
Article13. Phillips P, Karrasch J, Scott R, Wilson D, Moses R. Acarbose improves glycemic control in overweight type 2 diabetic patients insufficiently treated with metformin. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:269–273. PMID: 12547847.
Article14. Van Gaal L, Maislos M, Schernthaner G, Rybka J, Segal P. Miglitol combined with metformin improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2001; 3:326–331. PMID: 11703422.
Article15. Wang JS, Huang CN, Hung YJ, Kwok CF, Sun JH, Pei D, Yang CY, Chen CC, Lin CL, Sheu WH. acarbose/metformin fixed-dose combination study investigators. Acarbose plus metformin fixed-dose combination outperforms acarbose monotherapy for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 102:16–24. PMID: 23993469.
Article16. Ismail TSES, Deshmukh SA. Comparative study of effect of alpha glucosidase inhibitors: miglitol, acarbose and voglibose on postprandial hyperglycemia and glycosylated hemoglobin in type-2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Pharma Bio Sci. 2012; 3:337–343.17. Benford M, Milligan G, Pike J, Anderson P, Piercy J, Fermer S. Fixed-dose combination antidiabetic therapy: real-world factors associated with prescribing choices and relationship with patient satisfaction and compliance. Adv Ther. 2012; 29:26–40. PMID: 22246944.
Article18. Choi HK, Oh M, Kim EJ, Song GS, Ghim JL, Shon JH, Kim HS, Shin JG. Pharmacokinetic study of metformin to compare voglibose/metformin fixed-dose combination with coadministered voglibose and metformin. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 53:147–153. PMID: 25546164.
Article19. Kim HS, Oh M, Kim EJ, Song GS, Ghim JL, Shon JH, Kim DH, Shin JG. Effect of voglibose on the pharmacokinetics of metformin in healthy Korean subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 52:1005–1011. PMID: 25161160.20. Monnier L, Colette C, Owens DR. Glycemic variability: the third component of the dysglycemia in diabetes. Is it important? How to measure it? J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2008; 2:1094–1100. PMID: 19885298.
Article21. Schlichtkrull J, Munck O, Jersild M. The M-valve, an index of blood-sugar control in diabetics. Acta Med Scand. 1965; 177:95–102. PMID: 14251860.22. Goldstein BJ, Feinglos MN, Lunceford JK, Johnson J, Williams-Herman DE. Sitagliptin 036 Study Group. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and metformin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:1979–1987. PMID: 17485570.
Article23. Rosak C, Mertes G. Critical evaluation of the role of acarbose in the treatment of diabetes: patient considerations. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012; 5:357–367. PMID: 23093911.
Article24. Pan C, Yang W, Barona JP, Wang Y, Niggli M, Mohideen P, Wang Y, Foley JE. Comparison of vildagliptin and acarbose monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, double-blind, randomized trial. Diabet Med. 2008; 25:435–441. PMID: 18341596.
Article25. Viljanen AP, Iozzo P, Borra R, Kankaanpaa M, Karmi A, Lautamaki R, Jarvisalo M, Parkkola R, Ronnemaa T, Guiducci L, Lehtimaki T, Raitakari OT, Mari A, Nuutila P. Effect of weight loss on liver free fatty acid uptake and hepatic insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:50–55. PMID: 18957499.
Article26. Monnier L, Lapinski H, Colette C. Contributions of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose increments to the overall diurnal hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetic patients: variations with increasing levels of HbA(1c). Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:881–885. PMID: 12610053.27. Monnier L, Colette C. Glycemic variability: should we and can we prevent it. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31(Suppl 2):S150–S154. PMID: 18227477.28. Nalysnyk L, Hernandez-Medina M, Krishnarajah G. Glycaemic variability and complications in patients with diabetes mellitus: evidence from a systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010; 12:288–298. PMID: 20380649.
Article29. Koyama H, Ohguchi H, Yagi T, Imaeda K. Nocturnal reactive hypoglycaemia well treated subjectively and objectively with voglibose. BMJ Case Rep. 2017; 2017:220295.
Article30. Peter S. Acarbose and idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia. Horm Res. 2003; 60:166–167. PMID: 14530603.
Article31. Holman RR, Cull CA, Turner RC. A randomized double-blind trial of acarbose in type 2 diabetes shows improved glycemic control over 3 years (U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 44). Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:960–964. PMID: 10372249.
Article32. Meneghini LF, Orozco-Beltran D, Khunti K, Caputo S, Damci T, Liebl A, Ross SA. Weight beneficial treatments for type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:3337–3353. PMID: 21900381.
Article33. DeFronzo RA, Goodman AM. Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Multicenter Metformin Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:541–549. PMID: 7623902.34. Ohmura C, Tanaka Y, Mitsuhashi N, Atsum Y, Matsuoka K, Onuma T, Kawamori R. Efficacy of low-dose metformin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Ther Res. 1998; 59:889–895.
Article35. Yang W, Liu J, Shan Z, Tian H, Zhou Z, Ji Q, Weng J, Jia W, Lu J, Liu J, Xu Y, Yang Z, Chen W. Acarbose compared with metformin as initial therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: an open-label, non-inferiority randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:46–55. PMID: 24622668.
Article36. Wolever TM, Chiasson JL, Josse RG, Hunt JA, Palmason C, Rodger NW, Ross SA, Ryan EA, Tan MH. Small weight loss on long-term acarbose therapy with no change in dietary pattern or nutrient intake of individuals with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1997; 21:756–763. PMID: 9376887.
Article37. Jeong IK, Chung JH, Min YK, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim KW, Chung YE, Park JY, Hong SK, Lee KU. Comparative study about the effects of acarbose and voglibose in type 2 diabetic patients. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2002; 26:134–145.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
- Response: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes metab J 2019;43;276-86)
- A Pregnant Woman with Type 2 Diabetes Unintentionally Exposed to Metformin and Voglibose until the Second Trimester of Pregnancy: A Case Report
- Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Pharmacothearpy of Adolescents with Diabetes