Nat Prod Sci.
2019 Jun;25(2):165-171. 10.20307/nps.2019.25.2.165.
Identification of a Novel Function of Extract of Gingko biloba (EGb 761®) as a Regulator of PYY Secretion and FFA4 Activation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Group of Natural Material and Metabolism, Division of Functional Food Research, Korea Food Research Institute, 245 Nongsaengmyeong-ro, Iseo-myeon, Wanju-gun, Jeollabuk-do 55365, Korea. khyey@kfri.re.kr
- KMID: 2452787
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2019.25.2.165
Abstract
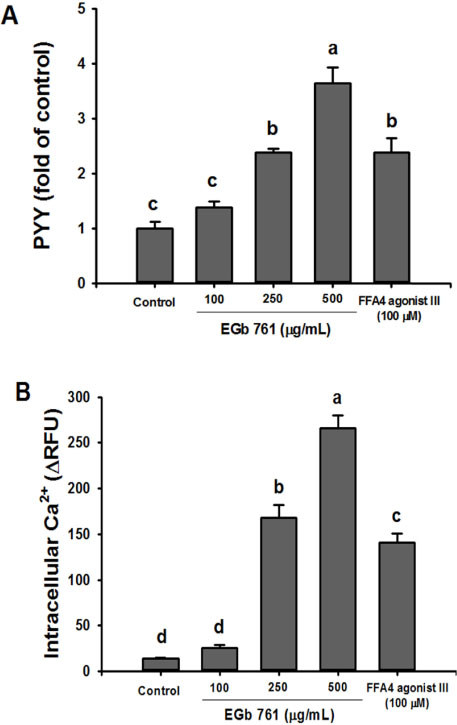
- Although the functions of a standardized extract of Gingko biloba leaves (EGb 761®) has been reported with regard to neurobiological properties, no attention has been paid to the impact of EGb 761® on the neuronal regulation of energy homeostasis. To evaluate the hypothesis that EGb 761® affect the secretion of peptide tyrosine tyrosine (PYY) and the activation of free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4), which are involved in the neuronal circuitries that control energy homeostasis by inducing the transfer of information about the influx of energy to the brain, we examined whether EGb 761® can stimulate PYY secretion in the enteroendocrine NCI-H716 cells and if EGb 761® can activate FFA4 in FFA4-expressing cells. In NCI-H716 cells, EGb 761® stimulated PYY secretion and the EGb 761®-induced PYY secretion was involved in the increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration and the activation of FFA4. Furthermore, in FFA4-expressing cells, EGb 761® activated FFA4. These results suggest that EGb 761® may affect the control of energy homeostasis via the regulation of PYY secretion and FFA4 activation.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clemmensen C, Müller TD, Woods SC, Berthoud HR, Seeley RJ, Tschöp MH. Cell. 2017; 168:758–774.2. Brooks L, Viardot A, Tsakmaki A, Stolarczyk E, Howard JK, Cani PD, Everard A, Sleeth ML, Psichas A, Anastasovskaj J, Bell JD, Bell-Anderson K, Mackay CR, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Frost G, Bewick GA. Mol Metab. 2016; 6:48–60.3. Lousie P, Herbert H. Kastin AJ, editor. Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides (Second Edition): PYY. United States of America: Academic press;2013. p. 1307–1313.4. Depoortere I. Peptides. 2015; 66:9–12.5. Im DS. Mol Aspects Med. 2018; 64:92–108.6. Gribble FM, Diakogiannaki E, Reimann F. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017; 236:181–203.7. Hansen SV, Ulven T. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017; 236:33–56.8. Liu HD, Wang WB, Xu ZG, Liu CH, He DF, Du LP, Li MY, Yu X, Sun JP. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015; 763(Pt. B):160–168.9. Auguste S, Fisette A, Fernandes MF, Hryhorczuk C, Poitout V, Alquier T, Fulton S. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016; 19:1–10.10. Cintra DE, Ropelle ER, Moraes JC, Pauli JR, Morari J, Souza CT, Grimaldi R, Stahl M, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ, Velloso LA. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e30571.11. Moodaley R, Smith DM, Tough IR, Schindler M, Cox HM. Br J Pharmacol. 2017; 174:4508–4522.12. Cox HM. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016; 31:50–56.13. Moniri NH. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016; 110-111:1–15.14. Song WY, Aihara Y, Hashimoto T, Kanazawa K, Mizuno M. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015; 57:164–169.15. Kim MJ, Son HJ, Song SH, Jung M, Kim Y, Rhyu MR. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e71603.16. Schiess S, Platz S, Kemper M, Schreiner M, Mewis I, Rohn S, Bumke-Vogt C, Pivovarova O, Pfeiffe AFH. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017; 61:1600886.17. Zanzer YC, Plaza M, Dougkas A, Turner C, Björck I, Östman E. J Funct Food. 2017; 35:574–583.18. Hara T, Hirasawa A, Sun Q, Sadakane K, Itsubo C, Iga T, Adachi T, Koshimizu TA, Hashimoto T, Asakawa Y, Tsujimoto G. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. 2009; 380:247–255.19. Mahadevan S, Park Y. J Food Sci. 2008; 73:R14–R19.20. Ramassamy C, Longpré F, Christen Y. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007; 4:253–262.21. Hsieh SK, Chung TY, Li YC, Lo YH, Lin NH, Kuo PC, Chen WY, Tzen JT. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016; 193:237–247.22. Kim K, Park M, Lee YM, Rhyu MR, Kim HY. Arch Pharm Res. 2014; 37:1193–1200.23. Reimer RA, Darimont C, Gremlich S, Nicolas-Méttral V, Rüegg UT, Macé K. J Endocrinology. 2001; 142:4522–4528.24. Nakajima S, Hira T, Yahagi A, Nishiyama C, Yamashita T, Imagi J, Hara H. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014; 58:1042–1051.25. Hirasawa A, Tsumaya K, Awaji T, Katsuma S, Adachi T, Yamada M, Sugimoto Y, Miyazaki S, Tsujimoto G. Nat Med. 2005; 11:90–94.26. Stewart JE, Feinle-Bisset C, Keast RS. Prog Lipid Res. 2011; 50:225–233.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Ginkgo Biloba to Retinal Microcirculation
- Gingko biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates ischemic brain injury-induced reduction in Ca2+ sensor protein hippocalcin
- The Effect of Gingko Biloba on Hearing in Mice with Noise-Induced Temporary Threshold Shift
- Effects of Ginkgo Biloba Extract on Experimentally Induced Hearing Loss by Noise
- Protective Effect of Ginkgo biloba Extract (Ginexin(R)) on a Variety of Damage on Cultured RPE