J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2019 Jun;23(2):71-73. 10.14193/jkfas.2019.23.2.71.
Sural Nerve Tuberculoma: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea. osddr8151@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2449675
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2019.23.2.71
Abstract
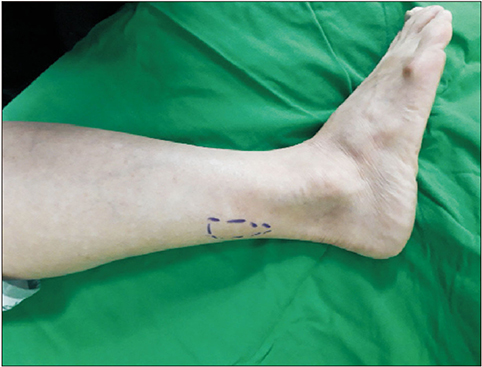
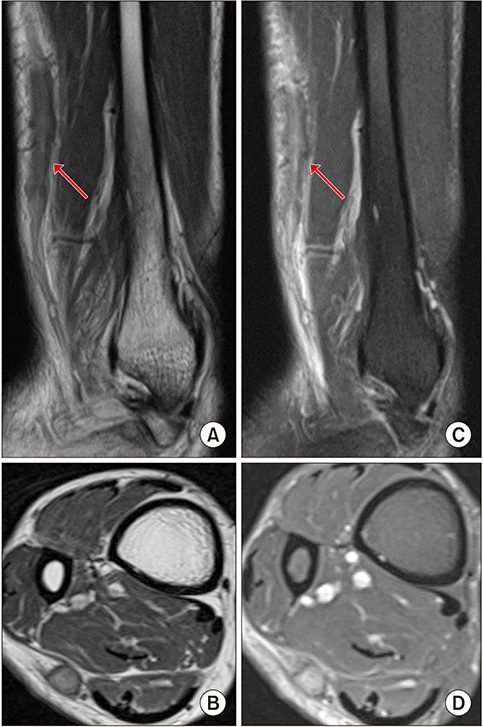
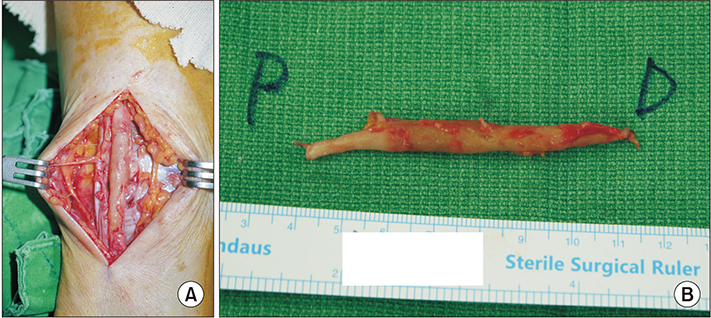
- Nearly one third of the world's population have active or latent tuberculosis, resulting in 1.5 million deaths annually. Tuberculosis involving the peripheral nerve is difficult to detect. Sural nerve tuberculoma is an extremely rare case of tuberculous involvement of the peripheral nerve that has attracted the attention of physicians. This paper reports a patient with sural nerve tuberculoma. A 58-year-old female patient presented with a palpable mass on the posterolateral calf with progressive tingling sensation on the distal area. The patient had no history of trauma and it was unclear whether the patient had any contact with individuals with active tuberculosis. The histopathologic findings revealed a granuloma-like lesion with caseous necrosis that was compatible with tuberculoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stoeckli TC, Mackin GA, DeGroote MA. Lumbosacral plexopathy in a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2000; 30:226–227. DOI: 10.1086/313622.
Article2. Song M, Sun X, Sun R, Liu T, Li G, Liu S, et al. Ulnar nerve tuberculoma: a case report and literature review. J Clin Neurosci. 2016; 32:130–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.12.047.
Article3. Orrell RW, King RH, Bowler JV, Ginsberg L. Peripheral nerve granuloma in a patient with tuberculosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002; 73:769–771. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.73.6.769.
Article4. Sinha GP. Tuberculoma of the ulnar nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975; 57:131.
Article5. Nucci F, Mastronardi L, Artico M, Ferrante L, Acqui M. Tuberculoma of the ulnar nerve: case report. Neurosurgery. 1988; 22:906–907.
Article6. Hasa , Prakashvn SA. Tuberculoma of the ulnar nerve. A new clinical entity. J Int Coll Surg. 1964; 42:30–34.7. Ramesh Chandra VV, Prasad BC, Varaprasad G. Ulnar nerve tuberculoma. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2013; 11:100–102. DOI: 10.3171/2012.9.PEDS12172.
Article8. Chatterjee D, Lath K, Sharma RK, Das A. Ulnar nerve tuberculoma masquerading as a neurofibroma. Neurol India. 2015; 63:268–270. DOI: 10.4103/0028-3886.156305.
Article9. Mauss H. Peripheral nervous system involvement in experimental tuberculosis. Pathol Microbiol (Basel). 1975; 42:103–109.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sural Nerve Graftafter Resection of a Schwannoma in the Sciatic Nerve : A Case Report
- Sural Nerve Entrapment by Fragments of Calcaneal Fracture (A Case Report)
- Entrapment of Sural Nerve in Essex-Lopresti Axial Fixation for Calcaneal Fracture: A Case Report
- Sural Nerve Entrapment and Tenosynovitis of Peroneus Longus by Hypertrophied Peroneal Tubercle: A Case Report
- Fascial entrapment of the sural nerve and its clinical relevance