Nat Prod Sci.
2018 Dec;24(4):247-252. 10.20307/nps.2018.24.4.247.
Comparison of Biological Activities of Korean Halophytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Applied Research, National Marine Biodiversity Institute of Korea, Seocheon 33662, Republic of Korea. gchoi@mabik.re.kr
- KMID: 2432419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2018.24.4.247
Abstract
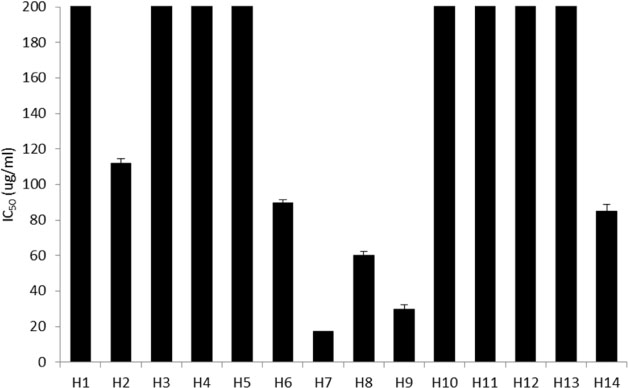
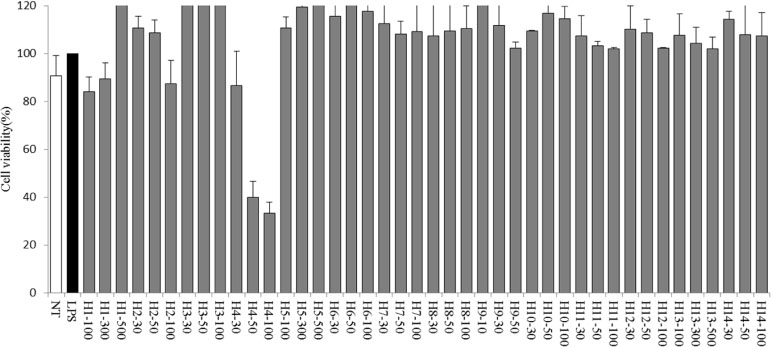
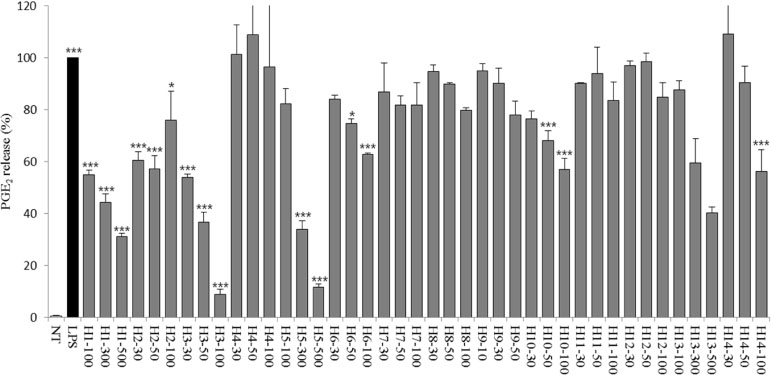
- Halophytes are expected to possess abundant secondary metabolites and various biological activities because of habitat in extreme environments. In this study, we collected 14 halophytes (Asparagus oligoclonos, Calystegia soldanella, Carex pumila, Chenopodium glaucum, Elymus mollis, Glehnia littoralis, Limonium tetragonum, Messerschmidia sibirica, Rosa rugosa, Salsola komarovii, Spergularia marina, Suaeda glauca, Suaeda maritima, and Vitex rotundifolia) native to Korea and compared their total polyphenol contents, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. The total polyphenol contents of R. rugosa (27.28%) and L. tetragonum (13.17%) were significantly higher than those of the other 12 halophytes and L. tetragonum, R. rugosa, and M. sibirica showed significantly greater antioxidant activities than the other 11 halophytes, as determined by DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl). A. oligoclonos, E. mollis, and C. pumila showed significantly greater anti-inflammatory activities than the other 11, as determined by NO (Nitric oxide) and PGEâ‚‚ (Prostaglandin Eâ‚‚) levels. In contrast, these three extracts had normal and low total polyphenol contents among the 14 halophytes. Consequently, the total polyphenol content in the 14 studied halophytes appeared to be related to antioxidant, but not anti-inflammatory activity levels.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Liebezeit G, Künnemann TD, Gad G. J Biotech. 1999; 70:77–84.2. Abdelly C, Barhoumi Z, Ghnaya T, Debez A, Ben Hamed K, Ksouri R, Talbi O, Zribi F, Ouerghi Z, Smaoui A, Huchzernmeyer B, Grignon C. Potential utilization of halophytes for the rehabilitation and valorization of salt-affected areas in Tunisia. In : Öztürk M, Waisel Y, Khan MA, Görk G, editors. Biosaline Agriculture and Salinity Tolerance in Plants. New York: Springer;2006. p. 161–170.3. Ksouri R, Ksouri WM, Jallali I, Debez A, Magné C, Hiroko I, Abdelly C. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2012; 32:289–326.4. Virág L, Szabó E, Gergely P, Szabó C. Toxicol Lett. 2003; 140-141:113–124.5. Wang B, Lüttge U, Ratajczak R. J Plant Physiol. 2004; 161:285–293.6. Drel VR, Pacher P, Vareniuk I, Pavlov I, Ilnytska O, Lyzogubov VV, Tibrewala J, Groves JT, Obrosova IG. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007; 569:48–58.7. Korda M, Kubant R, Patton S, Malinski T. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008; 295:H1514–H1521.8. Jaleel CA, Gopi R, Manivannan P, Panneerselvam R. Turk J Bot. 2007; 31:245–251.9. Manikandan T, Neelakandan T, Usha Rani G. J Phytol. 2009; 1:441–443.10. Falleh H, Ksouri R, Medini F, Guyot S, Abdelly C, Magné C. Ind Crops Prod. 2011; 34:1066–1071.11. Gnanadesigan M, Ravikumar S, Inbaneson SJ. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2011; 4:462–465.12. Oueslati S, Ksouri R, Falleh H, Pichette A, Abdelly C, Legault J. Food Chem. 2012; 132:943–947.13. Kim MS, Seo JY, Oh J, Jang YK, Lee CH, Kim JS. J Med Food. 2017; 20:140–151.14. Kojima T, Akiyama H, Sasai M, Taniuchi S, Goda Y, Toyoda M, Kobayashi Y. Allergol Int. 2000; 49:69–73.15. An BJ, Kwak JH, Park JM, Lee JY, Park TS, Lee JT, Son JH, Jo C, Byun MW. Dermatol Surg. 2005; 31:848–854.16. dos Santos MD, Almeida MC, Lopes NP, de Souza GE. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006; 29:2236–2240.17. Moreno S, Scheyer T, Romano CS, Vojnov AA. Free Radic Res. 2006; 40:223–231.18. Mohan KV, Gunasekaran P, Varalakshmi E, Hara Y, Nagini S. Cell Biol Int. 2007; 31:599–608.19. Mokni M, Limam F, Elkahoui S, Amri M, Aouani E. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007; 457:1–6.20. Yamabe N, Kang KS, Matsuo Y, Tanaka T, Yokozawa T. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007; 30:1289–1296.21. Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, Quiñones Mdel M, Muguerza B, Moulay L, Miguel M, Aleixandre A. J Agric Food Chem. 2009; 57:6156–6162.22. Perron NR, Brumaghim JL. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2009; 53:75–100.23. Lee JM, Yim MJ, Choi G, Lee MS, Park YG, Lee DS. Nat Prod Sci. 2018; 24:40–46.24. Cho MS, Park WS, Jung WK, Qian ZJ, Lee DS, Choi JS, Lee DY, Park SG, Seo SK, Kim HJ, Won JY, Yu BC, Choi IW. Pharm Biol. 2014; 52:926–932.25. Ksouri R, Falleh H, Megdiche W, Trabelsi N, Mhamdi B, Chaieb K, Bakrouf A, Magné C, Abdelly C. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009; 47:2083–2091.26. Lee JI, Kong CS, Jung ME, Hong JW, Lim SY, Seo Y. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2011a; 16:992–999.27. Lee JI, Kong CS, Jung ME, Hong JW, Noh I, Seo Y. Ocean Polar Res. 2011b; 33:185–191.28. Youwei Z, Yonghong P. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci. 2007; 35:397–401.29. Ng TB, He JS, Niu SM, Zhao L, Pi ZF, Shao W, Liu F. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2004; 56:537–545.30. Kim GS, Kim HT, Seong JD, Oh SR, Bang JK, Seong NS, Song KS. J Nat Prod. 2005; 68:766–768.31. Adão CR, de Silva BP, Parente JP. Fitoterapia. 2011; 82:1175–1180.32. Balica G, Vostinaru O, Tamas M, Crisan G, Mogosan C. J Food Agric Environ. 2013; 11:106–108.33. Kurihara H, Kawabata J, Ichikawa S, Mizutani J. Agric Biol Chem. 1990; 54:1097–1099.34. Kawabata J, Mishima M, Kurihara H, Mizutani J. Phytochemistry. 1991; 30:645–647.35. Kawabata J, Mishima M, Kurihara H, Mizutani J. Phytochemistry. 1995; 40:1507–1510.36. Chung EY, Kim BH, Lee MK, Yun YP, Lee SH, Min KR, Kim Y. Planta Med. 2003; 69:710–714.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Six Halophytes in Korea
- Clinical Assessment of Aging
- Essential Oil of Marrubium vulgare: Chemical Composition and Biological Activities. A Review
- Essential Oils: Biological Activity Beyond Aromatherapy
- Endophytic Fungi Inhabiting Medicinal Plants and Their Bioactive Secondary Metabolites