Blood Res.
2018 Sep;53(3):189-197. 10.5045/br.2018.53.3.189.
Clinical features and survival outcomes of patients with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, including non-IgM type, in Korea: a single-center experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. csuh@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2429317
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2018.53.3.189
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The incidence of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL) is lower in Asian than in Western populations. Few studies have described the clinical features and treatment outcomes of patients with LPL, including non-IgM LPL, in East Asia.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed patients diagnosed with LPL at Asan Medical Center between January 2001 and March 2016. We evaluated the clinical features and survival outcomes of patients with LPL and non-IgM LPL and compared these data with those of patients with LPL/Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM).
RESULTS
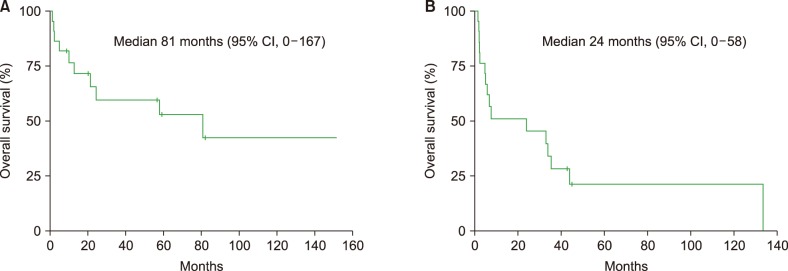
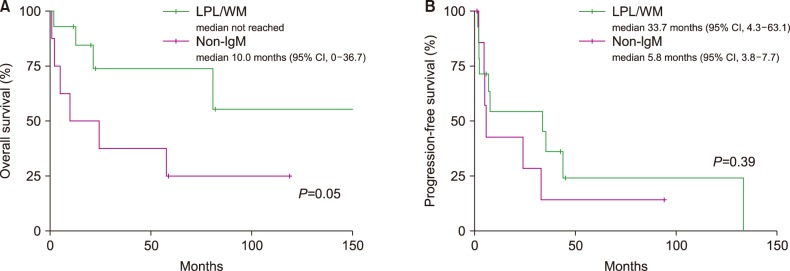
The median age at diagnosis of patients with LPL was 61.5 years (range, 34-77 yr); most patients were male (91%). Approximately three-quarters of the 22 patients with LPL were in the low or intermediate risk groups according to the International Prognostic Scoring System for Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia classification. The median follow-up duration was 75 months [95% confidence interval (CI), 48-102 mo], and the median overall survival (OS) was 81 months (95% CI, 0-167 mo). The number of patients in the non-IgM LPL group who exhibited extramedullary involvement was higher than in the LPL/WM group. OS of the LPL/WM group was improved compared with that of the non-IgM LPL group [median not reached vs. 10.0 mo (95% CI, 0-36.7); P=0.05].
CONCLUSION
We present a single-center experience of 22 patients with LPL, including a non-IgM cohort, in Korea. The treatment of non-IgM LPL was heterogeneous, and patients with non-IgM LPL showed a higher 5-year mortality rate and more adverse prognostic factors than those with LPL/WM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Successful treatment of non-IgM lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma by bortezomib-containing regimen: case reports and review of literature
Kenichi Ito, Risa Nishiyama, Kazuhiko Hirano, Kazuaki Yamada, Naohiro Sekiguchi
Blood Res. 2019;54(3):236-240. doi: 10.5045/br.2019.54.3.236.A Case of Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia with IgM-κ and IgA-λ Biclonal Gammopathy
Woo Yong Shin, Hae In Bang, Jieun Kim, Rojin Park, Jeong Won Shin, Tae Youn Choi
Lab Med Online. 2019;9(4):263-268. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.4.263.
Reference
-
1. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016; 127:2375–2390. PMID: 26980727.
Article2. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2008.3. Cao X, Medeiros LJ, Xia Y, et al. Clinicopathologic features and outcomes of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma patients with monoclonal IgG or IgA paraprotein expression. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016; 57:1104–1113. PMID: 26421453.
Article4. Iwanaga M, Chiang CJ, Soda M, et al. Incidence of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia in Japan and Taiwan population-based cancer registries, 1996–2003. Int J Cancer. 2014; 134:174–180. PMID: 23784625.
Article5. Kristinsson SY, Björkholm M, Goldin LR, McMaster ML, Turesson I, Landgren O. Risk of lymphoproliferative disorders among first-degree relatives of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia patients: a population-based study in Sweden. Blood. 2008; 112:3052–3056. PMID: 18703425.6. Treon SP, Xu L, Yang G, et al. MYD88 L265P somatic mutation in Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:826–833. PMID: 22931316.
Article7. King RL, Gonsalves WI, Ansell SM, et al. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma with a non-IgM paraprotein shows clinical and pathologic heterogeneity and may harbor MYD88 L265P mutations. Am J Clin Pathol. 2016; 145:843–851. PMID: 27329639.8. Owen RG, Kyle RA, Stone MJ, et al. Response assessment in Waldenström macroglobulinaemia: update from the VIth International Workshop. Br J Haematol. 2013; 160:171–176. PMID: 23150997.
Article9. Sant M, Allemani C, Tereanu C, et al. Incidence of hematologic malignancies in Europe by morphologic subtype: results of the HAEMACARE project. Blood. 2010; 116:3724–3734. PMID: 20664057.
Article10. Ko YH, Kim CW, Park CS, et al. REAL classification of malignant lymphomas in the Republic of Korea: incidence of recently recognized entities and changes in clinicopathologic features. Hematolymphoreticular Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists. Revised European-American lymphoma. Cancer. 1998; 83:806–812. PMID: 9708949.11. Won YW, Kim SJ, Kim K, Ko YH, Kim WS. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma: a single center experience in Korea. Ann Hematol. 2010; 89:1011–1018. PMID: 20449747.
Article12. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines for patients. Waldenström's macroglobulinemia: lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. Version 1. Fort Washington, PA: NCCN;2017. Accessed November 25, 2017. at https://www.nccn.org/patients/guidelines/waldenstroms/files/assets/common/downloads/files/waldenstroms.pdf.13. Vitolo U, Ferreri AJ, Montoto S. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma-Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008; 67:172–185. PMID: 18499469.
Article14. Bang SM, Seo JW, Park KU, et al. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of Korean patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2010; 197:117–121. PMID: 20193844.
Article15. Lee HS, Kim K, Yoon DH, et al. Clinical factors associated with response or survival after chemotherapy in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia in Korea. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:253243. PMID: 24995279.
Article16. Tursz T, Brouet JC, Flandrin G, Danon F, Clauvel JP, Seligmann M. Clinical and pathologic features of Waldenström's macroglobulinemia in seven patients with serum monoclonal IgG or IgA. Am J Med. 1977; 63:499–502. PMID: 410294.
Article17. Braggio E, Fonseca R. Genomic abnormalities of Waldenström macroglobulinemia and related low-grade B-cell lymphomas. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013; 13:198–201. PMID: 23477936.
Article18. Heerema-McKenney A, Waldron J, Hughes S, et al. Clinical, immunophenotypic, and genetic characterization of small lymphocyte-like plasma cell myeloma: a potential mimic of mature B-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010; 133:265–270. PMID: 20093236.19. Dimopoulos MA, García-Sanz R, Gavriatopoulou M, et al. Primary therapy of Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM) with weekly bortezomib, low-dose dexamethasone, and rituximab (BDR): long-term results of a phase 2 study of the European Myeloma Network (EMN). Blood. 2013; 122:3276–3282. PMID: 24004667.20. Treon SP, Ioakimidis L, Soumerai JD, et al. Primary therapy of Waldenström macroglobulinemia with bortezomib, dexamethasone, and rituximab: WMCTG clinical trial 05-180. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3830–3835. PMID: 19506160.
Article21. Owen RG, Barrans SL, Richards SJ, et al. Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Development of diagnostic criteria and identification of prognostic factors. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001; 116:420–428. PMID: 11554171.22. Morel P, Monconduit M, Jacomy D, et al. Prognostic factors in Waldenström macroglobulinemia: a report on 232 patients with the description of a new scoring system and its validation on 253 other patients. Blood. 2000; 96:852–858. PMID: 10910896.23. Morel P, Duhamel A, Gobbi P, et al. International prognostic scoring system for Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood. 2009; 113:4163–4170. PMID: 19196866.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia with IgM-κ and IgA-λ Biclonal Gammopathy
- Electrophysiological features and prognosis of peripheral neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathy: a single-center analysis in South Korea
- Successful treatment of non-IgM lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma by bortezomib-containing regimen: case reports and review of literature
- Primary well differentiated lymphocytic lymphoma of the lung: a clinical and immunohistochemical study of four cases
- Rare Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Childhood; A Single Center Experience