Korean J Gastroenterol.
2018 Nov;72(5):267-270. 10.4166/kjg.2018.72.5.267.
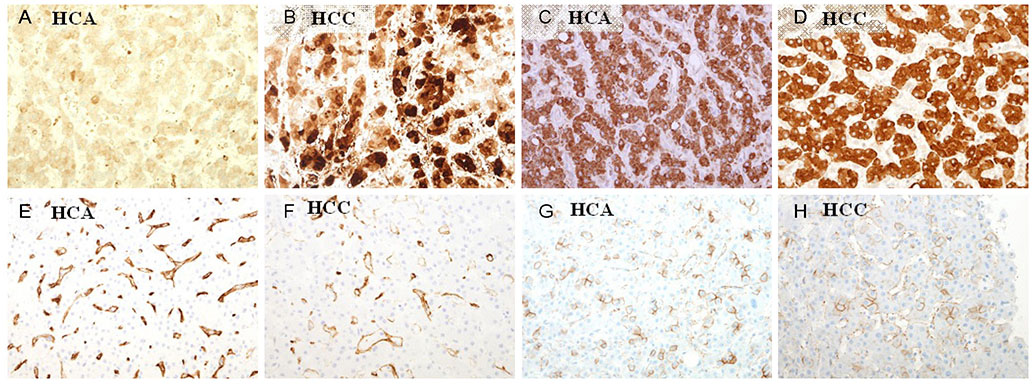
Malignant Transformation of Inflammatory Hepatocellular Adenoma into Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. DRPJY@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2426869
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2018.72.5.267
Abstract
- No abstract available.
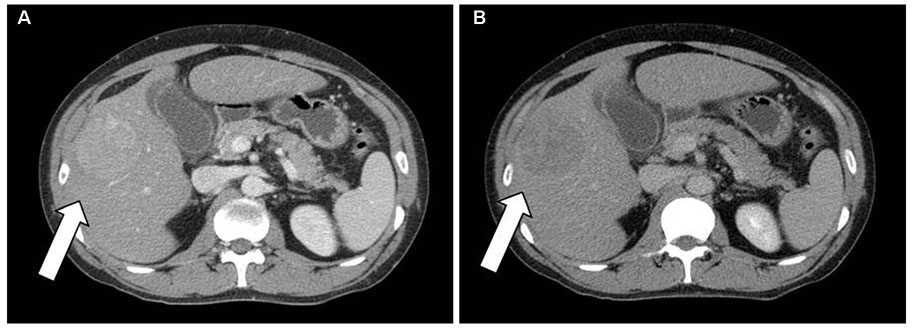
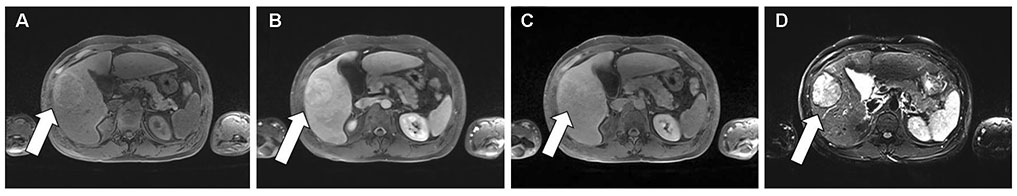
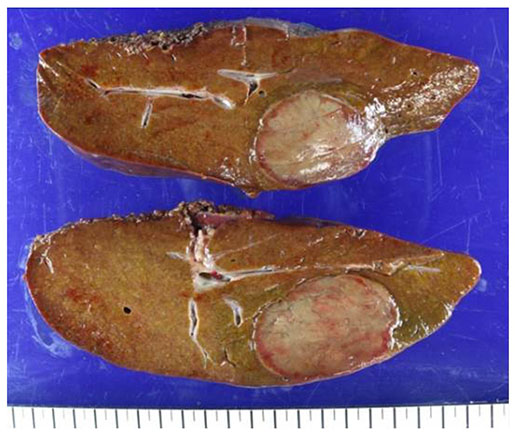
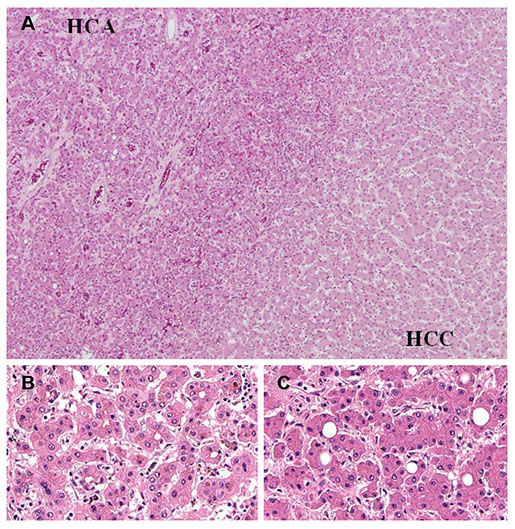
Figure
Reference
-
1. Belghiti J, Cauchy F, Paradis V, Vilgrain V. Diagnosis and management of solid benign liver lesions. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 11:737–749.
Article2. Agrawal S, Agarwal S, Arnason T, Saini S, Belghiti J. Management of hepatocellular adenoma: recent advances. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:1221–1230.
Article3. Stoot JH, Coelen RJ, De Jong MC, Dejong CH. Malignant transformation of hepatocellular adenomas into hepatocellular carcinomas: a systematic review including more than 1600 adenoma cases. HPB (Oxford). 2010; 12:509–522.
Article4. Grazioli L, Federle MP, Brancatelli G, Ichikawa T, Olivetti L, Blachar A. Hepatic adenomas: imaging and pathologic findings. Radiographics. 2001; 21:877–892.
Article5. Arif-Tiwari H, Kalb B, Chundru S, et al. MRI of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update of current practices. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014; 20:209–221.
Article6. Bioulac-Sage P, Laumonier H, Couchy G, et al. Hepatocellular adenoma management and phenotypic classification: the Bordeaux experience. Hepatology. 2009; 50:481–489.
Article7. Bioulac-Sage P, Rebouissou S, Thomas C, et al. Hepatocellular adenoma subtype classification using molecular markers and immunohistochemistry. Hepatology. 2007; 46:740–748.
Article8. Farges O, Ferreira N, Dokmak S, Belghiti J, Bedossa P, Paradis V. Changing trends in malignant transformation of hepatocellular adenoma. Gut. 2011; 60:85–89.
Article9. Atwell TD, Brandhagen DJ, Charboneau JW, Nagorney DM, Callstrom MR, Farrell MA. Successful treatment of hepatocellular adenoma with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:828–831.
Article10. Erdogan D, Busch OR, van Delden OM, Ten Kate FJ, Gouma DJ, van Gulik TM. Management of spontaneous haemorrhage and rupture of hepatocellular adenomas. A single centre experience. Liver Int. 2006; 26:433–438.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Arising from Hepatocellular Adenoma in an Elderly Male Patient
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Arising in Hepatocellular Adenoma
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Arising in a Huge Hepatocellular Adenoma with Bone Marrow Metaplasia
- Molecular classification of hepatocellular adenoma: A single-center experience
- Hepatocellular Adenoma and Focal Nodular Hyperplasia