Investig Clin Urol.
2016 Jul;57(4):260-267. 10.4111/icu.2016.57.4.260.
Complications and oncologic outcomes following robot-assisted radical cystectomy: What is the real benefit?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. tgkwon@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2426503
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2016.57.4.260
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to assess the advantages of robotic surgery, comparing perioperative and oncological outcomes between robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) and open radical cystectomy (ORC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
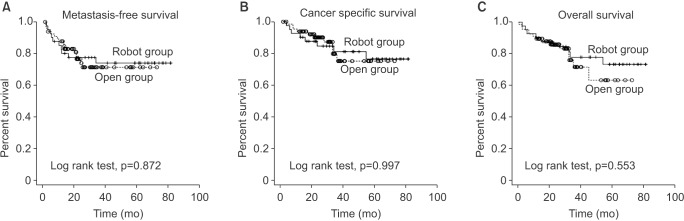
Between August 2008 and May 2014, 112 radical cystectomies (42 RARCs and 70 ORCs) were performed at a single academic institution following Institutional Review Board approval. Patient demographics, perioperative variables (e.g., complications), and oncologic outcomes including metastasis-free survival (MFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and overall survival (OS) were reported using the Kaplan-Meier analyses.
RESULTS
The median follow-up period was 40 months (range, 0-70 months) vs. 42 months (range, 0-74 months) in RARC and ORC, respectively. Baseline characteristics of both groups were balanced. Blood loss (median, [range]; 300 mL [125-925 mL] vs. 598 mL [150-2,000 mL], p=0.001) and perioperative transfusion rates (23.8% vs. 45.7%, p=0.020) were significantly lower in the RARC group than in the ORC group. The overall complication rates were greater in the ORC group, but this was not statistically significant (65.7% vs. 64.3%, p=0.878). However, there were significantly higher major complication rates in the ORC group (45.7% vs. 26.2%, p=0.040). No significant differences were found with regards to MFS, CSS, and OS.
CONCLUSIONS
While histopathological findings, overall complications, and survival rates do not reveal definite differences, RARC has more advantages compared to ORC in terms of estimated blood loss, perioperative transfusion rates and fewer perioperative major complications. We propose that RARC is a safer treatment modality with equivalent oncological outcomes compared to ORC.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Blood Loss, Surgical
Blood Transfusion
Cystectomy/adverse effects/*methods
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Grading
Neoplasm Staging
Perioperative Care/methods
Robotic Surgical Procedures/adverse effects/*methods
Treatment Outcome
Urinary Bladder Neoplasms/pathology/*surgery
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A preliminary oncologic outcome and postoperative complications in patients undergoing robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Initial experience
Satoru Muto, Kousuke Kitamura, Takeshi Ieda, Fumitaka Shimizu, Masayoshi Nagata, Shuji Isotani, Hisamitsu Ide, Raizo Yamaguchi, Shigeo Horie
Investig Clin Urol. 2017;58(3):171-178. doi: 10.4111/icu.2017.58.3.171.
Reference
-
1. Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M, Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, Ribal MJ, et al. Treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: update of the EAU guidelines. Eur Urol. 2011; 59:1009–1018. PMID: 21454009.
Article2. Cookson MS, Chang SS, Wells N, Parekh DJ, Smith JA Jr. Complications of radical cystectomy for nonmuscle invasive disease: comparison with muscle invasive disease. J Urol. 2003; 169:101–104. PMID: 12478113.
Article3. Sterrett S, Mammen T, Nazemi T, Galich A, Peters G, Smith L, et al. Major urological oncological surgeries can be performed using minimally invasive robotic or laparoscopic methods with similar early perioperative outcomes compared to conventional open methods. World J Urol. 2007; 25:193–198. PMID: 17171562.
Article4. Menon M, Hemal AK, Tewari A, Shrivastava A, Shoma AM, El-Tabey NA, et al. Nerve-sparing robot-assisted radical cystoprostatectomy and urinary diversion. BJU Int. 2003; 92:232–236. PMID: 12887473.
Article5. Galich A, Sterrett S, Nazemi T, Pohlman G, Smith L, Balaji KC. Comparative analysis of early perioperative outcomes following radical cystectomy by either the robotic or open method. JSLS. 2006; 10:145–150. PMID: 16882409.6. Wang GJ, Barocas DA, Raman JD, Scherr DS. Robotic vs open radical cystectomy: prospective comparison of perioperative outcomes and pathological measures of early oncological efficacy. BJU Int. 2008; 101:89–93. PMID: 17888044.
Article7. Ng CK, Kauffman EC, Lee MM, Otto BJ, Portnoff A, Ehrlich JR, et al. A comparison of postoperative complications in open versus robotic cystectomy. Eur Urol. 2010; 57:274–281. PMID: 19560255.
Article8. Nix J, Smith A, Kurpad R, Nielsen ME, Wallen EM, Pruthi RS. Prospective randomized controlled trial of robotic versus open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: perioperative and pathologic results. Eur Urol. 2010; 57:196–201. PMID: 19853987.
Article9. Gondo T, Yoshioka K, Nakagami Y, Okubo H, Hashimoto T, Satake N, et al. Robotic versus open radical cystectomy: prospective comparison of perioperative and pathologic outcomes in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012; 42:625–631. PMID: 22581913.
Article10. Khan MS, Challacombe B, Elhage O, Rimington P, Coker B, Murphy D, et al. A dual-centre, cohort comparison of open, laparoscopic and robotic-assisted radical cystectomy. Int J Clin Pract. 2012; 66:656–662. PMID: 22507234.
Article11. Styn NR, Montgomery JS, Wood DP, Hafez KS, Lee CT, Tallman C, et al. Matched comparison of robotic-assisted and open radical cystectomy. Urology. 2012; 79:1303–1308. PMID: 22516354.
Article12. Sung HH, Ahn JS, Seo SI, Jeon SS, Choi HY, Lee HM, et al. A comparison of early complications between open and robotassisted radical cystectomy. J Endourol. 2012; 26:670–675. PMID: 22011001.
Article13. Nepple KG, Strope SA, Grubb RL 3rd, Kibel AS. Early oncologic outcomes of robotic vs. open radical cystectomy for urothelial cancer. Urol Oncol. 2013; 31:894–898. PMID: 21803615.
Article14. Martin AD, Nunez RN, Castle EP. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy: a complete cost analysis. Urology. 2011; 77:621–625. PMID: 21122900.
Article15. Abaza R, Dangle PP, Gong MC, Bahnson RR, Pohar KS. Quality of lymphadenectomy is equivalent with robotic and open cystectomy using an extended template. J Urol. 2012; 187:1200–1204. PMID: 22341295.
Article16. Ahdoot M, Almario L, Araya H, Busch J, Conti S, Gonzalgo ML. Oncologic outcomes between open and robotic-assisted radical cystectomy: a propensity score matched analysis. World J Urol. 2014; 32:1441–1446. PMID: 24469858.
Article17. Li K, Lin T, Fan X, Xu K, Bi L, Duan Y, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies reporting early outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013; 39:551–560. PMID: 23273846.
Article18. Parekh DJ, Messer J, Fitzgerald J, Ercole B, Svatek R. Perioperative outcomes and oncologic efficacy from a pilot prospective randomized clinical trial of open versus robotic assisted radical cystectomy. J Urol. 2013; 189:474–479. PMID: 23017529.
Article19. Musch M, Janowski M, Steves A, Roggenbuck U, Boergers A, Davoudi Y, et al. Comparison of early postoperative morbidity after robot-assisted and open radical cystectomy: results of a prospective observational study. BJU Int. 2014; 113:458–467. PMID: 24053793.
Article20. Knox ML, El-Galley R, Busby JE. Robotic versus open radical cystectomy: identification of patients who benefit from the robotic approach. J Endourol. 2013; 27:40–44. PMID: 22788707.
Article21. Kader AK, Richards KA, Krane LS, Pettus JA, Smith JJ, Hemal AK. Robot-assisted laparoscopic vs open radical cystectomy: comparison of complications and perioperative oncological outcomes in 200 patients. BJU Int. 2013; 112:E290–E294. PMID: 23815802.
Article22. Kwon SY, Kim BS, Kim TH, Yoo ES, Kwon TG. Initial experiences with robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy. Korean J Urol. 2010; 51:178–182. PMID: 20414393.
Article23. Osunkoya AO, Grignon DJ. Practical issues and pitfalls in staging tumors of the genitourinary tract. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:154–166. PMID: 23062422.
Article24. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:205–213. PMID: 15273542.25. Pyun JH, Kim HK, Kim JY, Kim SB, Cho S, Kang SG, et al. Standardized analysis of complications after robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Korea University Hospital experience. Korean J Urol. 2015; 56:48–55. PMID: 25598936.
Article26. Stein JP, Quek ML, Skinner DG. Lymphadenectomy for invasive bladder cancer. II. technical aspects and prognostic factors. BJU Int. 2006; 97:232–237. PMID: 16430619.
Article27. Stein JP, Skinner DG. Surgical atlas: radical cystectomy. BJU Int. 2004; 94:197–221. PMID: 15217471.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy
- Erectile Function and Long-term Oncologic Outcomes of Nerve-Sparing Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy: Comparison With Open Radical Cystectomy
- A preliminary oncologic outcome and postoperative complications in patients undergoing robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Initial experience
- Gender-related outcomes in robot-assisted radical cystectomy: A multi-institutional study
- Initial experience with Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy compared to the conventional method: is it a suitable option for robotic prostatectomy beginners?