J Neurocrit Care.
2018 Jun;11(1):39-42. 10.18700/jnc.180041.
Sudden Bispectral Index Reduction and Suppression Ratio Increase Associated with Bradycardia in a Patient Undergoing Breast Conserving Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shkimans@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Health Innovation Bigdata Center, Asan Institute for Lifesciences, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2426212
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.180041
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The bispectral index (BIS) is a valuable indicator for measuring sedation levels and patient consciousness. Recent reports have highlighted its clinical value as an indicator for anesthesia-related cerebral hypoperfusion and ischemic brain damage.
CASE REPORT
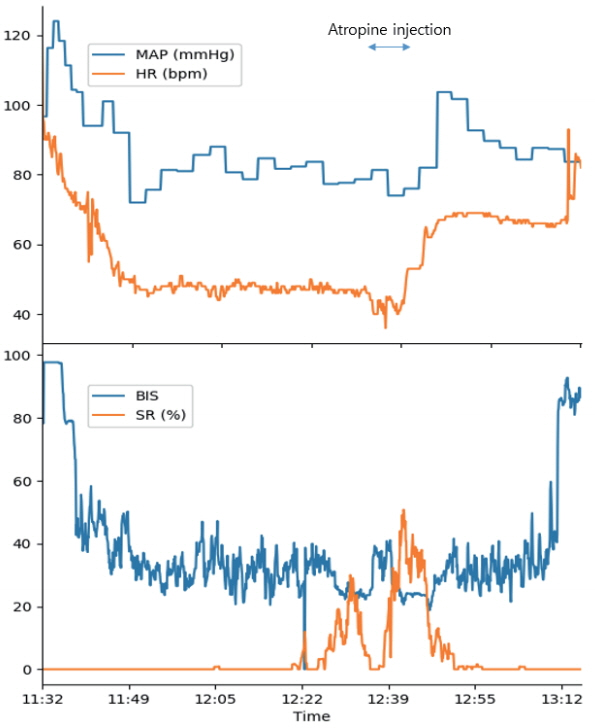
A 55-year-old female patient underwent right breast conservation surgery during general anesthesia. During surgery, the patient experienced abrupt bradycardia (heart rate of 36 bpm) without hypotension. During bradycardia, her BIS was severely reduced from 45 to 20 along with elvated suppression ratio (50). After injection of 0.5mg of atropine, her BIS level was recovered, her heart rate was increased, and her suppression ratio was decreased.
CONCLUSION
The patient recovered from anesthesia without showing any signs of neurological sequelae based on BIS level monitoring.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mérat S, Lévecque JP, Le Gulluche Y, Diraison Y, Brinquin L, Hoffmann JJ. BIS monitoring may allow the detection of severe cerebral ischemia. Can J Anaesth. 2001; 48:1066–9.2. Rampil IJ. A primer for EEG signal processing in anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1998; 89:980–1002.
Article3. Myles PS, Daly D, Silvers A, Cairo S. Prediction of neurological outcome using bispectral index monitoring in patients with severe Ischemic-Hypoxic brain injury undergoing emergency surgery. Anesthesiology. 2009; 110:1106–15.
Article4. Hayashida M, Chinzei M, Komatsu K, Yamamoto H, Tamai H, Orii R, et al. Detection of cerebral hypoperfusion with bispectral index during paediatric cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2003; 90:694–8.
Article5. Hemmerling TM, Olivier JF, Basile F, Le N, Prieto I. Bispectral index as an indicator of cerebral hypoperfusion during off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Anesth Analg. 2005; 100:354–6.
Article6. Hashimoto H, Nakamura H, Hirota K. Marked reduction in bispectral index with severe bradycardia without hypotension in a diabetic patient undergoing ophthalmic surgery. J Anesth. 2008; 22:300–3.
Article7. Lagergren K. Effect of exogenous changes in heart rate upon mental performance in patients treated with artificial pacemakers for complete heart block. Br Heart J. 1974; 36:1126–32.
Article8. Isaksson A, Lagergren K, Wennberg A. Visible and non-visible EEG changes demonstrated by spectral parameter analysis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1976; 41:225–36.
Article9. Shapiro W, Chawla NP. Observations on the regulation of cerebral blood flow in complete heart block. Circulation. 1969; 40:863–70.
Article10. Hering W, Geisslinger G, Kamp HD, Dinkel M, Tschaikowsky K, Rügheimer E, et al. Changes in the EEG power spectrum after midazolam anaesthesia combined with racemic or S- (+) ketamine. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1994; 38:719–23.11. Rampil IJ, Kim JS, Lenhardt R, Negishi C, Sessler DI. Bispectral EEG index during nitrous oxide administration. Anesthesiology. 1998; 89:671–7.
Article12. Hemmerling TM, Migneault B. Falsely increased bispectral index during endoscopic shoulder surgery attributed to interferences with the endoscopic shaver device. Anesth Analg. 2002; 95:1678–9. table of contents.
Article13. Koide H, Kobayashi S, Kitani M, Tsunematsu T, Nakazawa Y. Improvement of cerebral blood flow and cognitive function following pacemaker implantation in patients with bradycardia. Gerontology. 1994; 40:279–85.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Outcomes of Standard and Oncoplastic Breast-Conserving Surgery
- Pitfall of bispectral index during intraoperative seizure: a case report
- Comparison of Psychiatric Symptoms between Total Mastectomy and Breast Conserving Surgery in Breast Cancer Patients
- Dose fentanyl injection for blunting the hemodynamic response to intubation increase the risk of reflex bradycardia during major abdominal surgery?
- Aesthetic outcomes of breast-conserving surgery and oncoplastic surgery with the new scale named Quality of Life Questionnaire Breast Reconstruction Module-23