J Korean Fract Soc.
2017 Jul;30(3):117-123. 10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.117.
Posterior Dual Plating for Distal Shaft Fractures of the Humerus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. oscho5362@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2424119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.117
Abstract
- PURPOSE
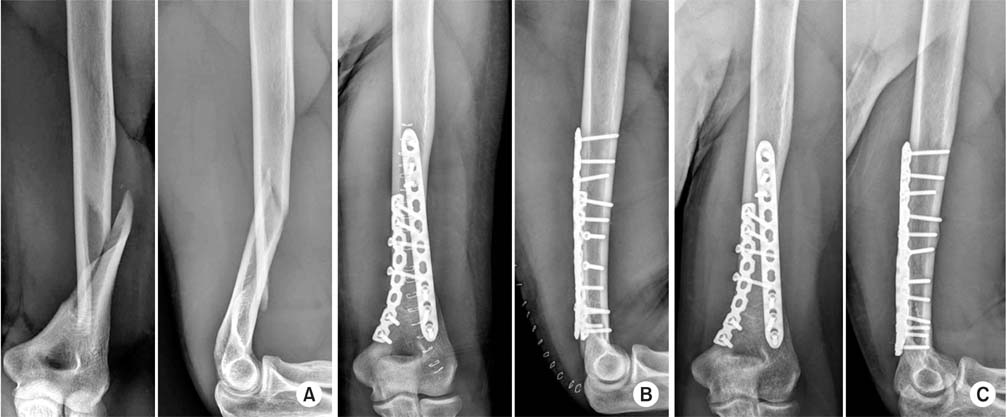
To evaluate the results and efficacy of posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 12 patients, who underwent open reduction and internal fixation using posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus, between July 2007 and July 2015, with at least 6 months of follow-up. After locating the radial nerve without dissection via posterior triceps splitting, the fracture was stabilized using a short 3.5 mm locking compression plate. Then additional fixation, using a long 3.5 mm locking compression plate, was performed. The clinical outcomes were assessed in accordance with the Mayo Elbow Performance Index (MEPI) scoring system, and the radiological outcomes were assessed using serial plain radiographs.
RESULTS
Eleven patients (91.7%) had bony union, and the mean union period was 13.9 weeks. In one patient, delayed union was treated by autogenous iliac bone graft at 8 months after surgery, which resulted in bony union. The mean MEPI score was 95.8, and the clinical outcomes were excellent in 9 patients and good in 3 patients. Postoperative complications included 1 elbow stiffness by heterotopic ossification and 1 temporary radial nerve palsy. One patient with temporary radial nerve palsy was completely recovered within the first 4 days after surgery.
CONCLUSION
Posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus revealed satisfactory clinical and radiological outcomes. It can be a useful alternative to provide stable fixation without the need for a dissection of the radial nerve.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rhee SK, Lee JY, Suh YJ, Lee JH, Ahn NK. Lateral approach for internal fixation of the distal humeral shaft fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004; 17:83–89.
Article2. Kwon DG, Moon KH, Na SI, Shin BK, Lee TJ. Combined anterolateral and lateral approaches in treatment of extra-articular fracture of the distal humerus. J Korean Fract Soc. 2012; 25:185–190.3. Parmaksızoğlu AS, Özkaya U, Bilgili F, Mutlu H, Çetin Ü. Fixation of extra-articular distal humeral fractures with a lateral approach and a locked plate: an alternative method. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016; 50:132–138.4. Prasarn ML, Ahn J, Paul O, et al. Dual plating for fractures of the distal third of the humeral shaft. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25:57–63.
Article5. Rubel IF, Kloen P, Campbell D, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral nonunions: a biomechanical and clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A:1315–1322.6. Tejwani NC, Murthy A, Park J, McLaurin TM, Egol KA, Kummer FJ. Fixation of extra-articular distal humerus fractures using one locking plate versus two reconstruction plates: a laboratory study. J Trauma. 2009; 66:795–799.
Article7. Watts A, Weinhold P, Kesler W, Dahners L. A biomechanical comparison of short segment long bone fracture fixation techniques: single large fragment plate versus 2 small fragment plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26:528–532.
Article8. Browner BD, Jupiter JB, Levine AM, et al. Skeletal trauma. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2003. p. 1436–1511.9. Jawa A, McCarty P, Doornberg J, Harris M, Ring D. Extraarticular distal-third diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. A comparison of functional bracing and plate fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:2343–2347.10. Schatzker J. Fractures of the humerus. In : Schatzker J, editor. The rationale of operative fracture care. New York: Springer Verlag;1987. p. 61–70.11. Aitken GK, Rorabeck CH. Distal humeral fractures in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (207):191–197.
Article12. Scolaro JA, Voleti P, Makani A, Namdari S, Mirza A, Mehta S. Surgical fixation of extra-articular distal humerus fractures with a posterolateral plate through a triceps-reflecting technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23:251–257.
Article13. Archdeacon MT, Wyrick JD. Reduction plating for provisional fracture fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20:206–211.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medial Transposition of Radial Nerve in Distal Humerus Shaft Fracture: A Report of Six Cases
- Posterior-Posterior Dual Plates Fixation for the Distal Humerus Fractures
- Ulnar Nerve Injury Caused by the Incomplete Insertion of a Screw Head after Internal Fixation with Dual Locking Plates in AO/OTA Type C2 Distal Humerus Fractures
- Plain Radiograph Analysis of the Distal Humerus Posterior Bowing That May Affect Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for Humerus Shaft Fracture
- Surgical Treatment Strategy for Distal Humerus Intra-articular Fractures