J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2018 Oct;56(4):338-346. 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.4.338.
Full mouth rehabilitation of the patient with crossed occlusion using implant fixed prosthesis: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Republic of Korea. neoplasia96@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2424035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2018.56.4.338
Abstract
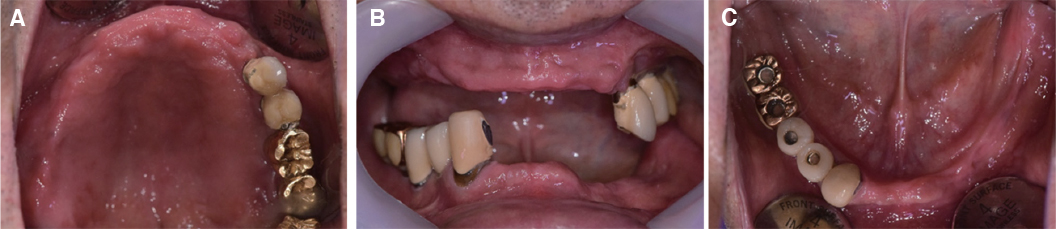
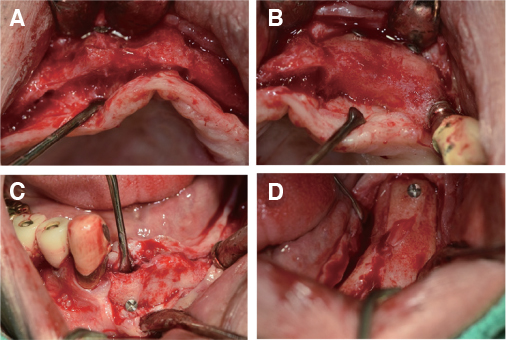
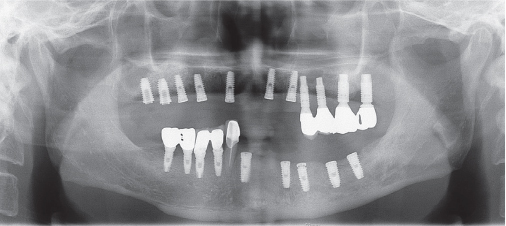
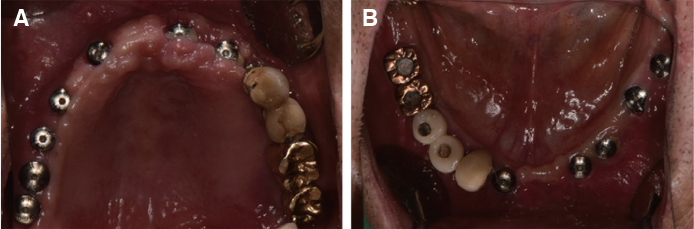
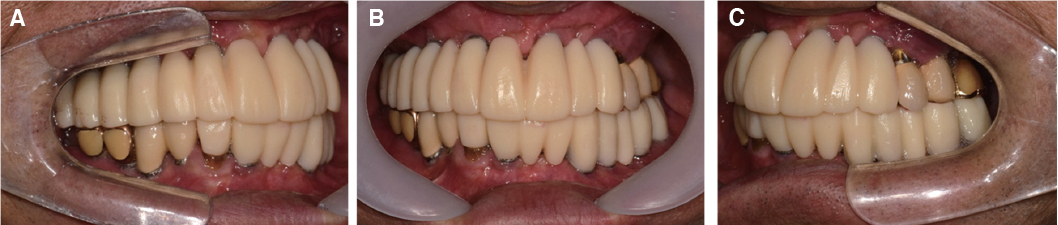
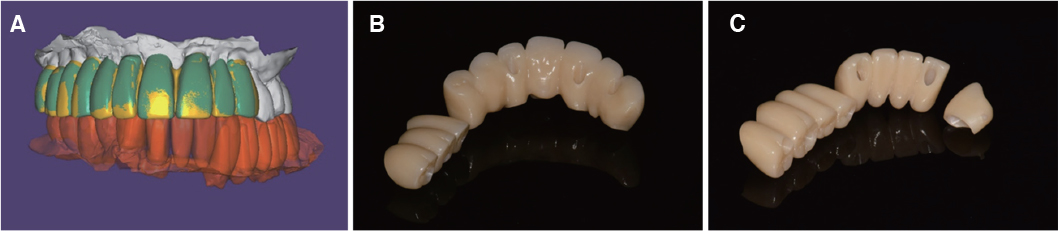
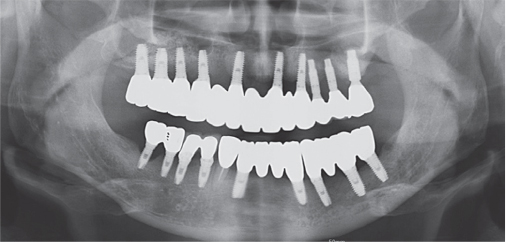
- Crossed occlusion can be treated either by overdenture and telescopic denture or by placing an implant at the edentulous area to reestablish the support on the occlusion. If alveolar bony support is sufficient and an the environment where an implant is inserted is favorable to restoring the masticatory and aesthetic function of a patient, the implant-supported fixed prosthesis can provide more definitive occlusal support and more aid for other oral functions. In this case report, a patient with a severe residual alveolar bone resorption following the extraction of teeth and who had a crossed occlusion was treated with sinus bone graft and alveolar bone augmentation in order to place the implants at prosthetically position. The definitive restoration was made to reflect the patient's occlusal and aesthetic function using the CAD/CAM double scanning method. Finally, the treatment had the masticatory and aesthetic function adequately restored, which is reported here.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Obana JI. Prosthodontic treatment for maxillary and mandibular teeth cross each other. 1st ed. Ishiyaku publishers;1994.2. Chikunov I, Doan P, Vahidi F. Implant-retained partial overdenture with resilient attachments. J Prosthodont. 2008; 17:141–148.
Article3. Park NS, Choi DG, Leesungbok R. Prosthodontic treatment for maxillary and mandibular teeth cross each other. Seoul: Jisung Pub.;1996. p. 3–93.4. Kay KS, Kim YS, An JK. A clinical study on rehabilitation of vertical dimension in the patient with crossed occlusion. Oral Biol Res. 2001; 25:127–143.5. Zarb GA, Bolender CL, Eckert SE, Fenton AH, Jacob RF, Mericske-Stem R. Prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients: Complete dentures and implant-supported prostheses. 12th ed. St. Louise: Mosby;2003.6. Grossmann Y, Nissan J, Levin L. Clinical effectiveness of implant-supported removable partial dentures: a review of the literature and retrospective case evaluation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67:1941–1946.
Article7. Misch CE. Dental implant prosthetics. 2nd ed. St. Louise: Mosby;2015.8. Park JH, Jeong CM, Jeon YC, Lim JS. A study on the occlusal plane and the vertical dimension in Korean adults with natural dentition. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2005; 43:41–51.9. Kweon HS, Kim MJ, Moon IH. A clinical study on using Konus telescope removable partial denture in prosthetic treatment for maxillary and mandibular teeth cross each other. Oral Biol Res. 2000; 24:201–214.10. Beretta M, Cicciù M, Poli PP, Rancitelli D, Bassi G, Grossi GB, Maiorana C. A retrospective evaluation of 192 implants placed in augmented bone: Long-term follow-up study. J Oral Implantol. 2015; 41:669–674.
Article11. Lekovic V, Kenney EB, Weinlaender M, Han T, Klokkevold P, Nedic M, Orsini M. A bone regenerative approach to alveolar ridge maintenance following tooth extraction. Report of 10 cases. J Periodontol. 1997; 68:563–570.
Article12. Schliephake H, Neukam FW, Scheller H, Bothe KJ. Local ridge augmentation using bone grafts and osseointegrated implants in the rehabilitation of partial edentulism: preliminary results. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1994; 9:557–564.13. Mayfield L, Nobréus N, Attström R, Linde A. Guided bone regeneration in dental implant treatment using a bioabsorbable membrane. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997; 8:10–17.
Article14. Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1986; 1:11–25.15. Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003; 8:328–343.
Article16. Del Fabbro M, Testori T, Francetti L, Weinstein R. Systematic review of survival rates for implants placed in the grafted maxillary sinus. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2004; 24:565–577.
Article17. Hobo S, Ichida E, Garcia LT. Osseointegration and Occlusal Rehabilitation. Chicago; IL: Quintessence;1989. p. 159–162. p. 171–173.18. Orenstein JH, Appleby DC, Blitzer RM, Cohen SR. Twopiece occlusion rim for screw-retained implant prosthesis. J Prosthodont. 1998; 7:200–202.
Article19. Yang DH, Yang HS, Park SW, Lim HP, Yun KD, Vang MS. Full mouth implant rehabilitation with double scanning of provisional restoration. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2014; 52:252–257.
Article20. Karl M, Graef F, Wichmann M, Krafft T. Passivity of fit of CAD/CAM and copy-milled frameworks, veneered frameworks, and anatomically contoured, zirconia ceramic, implantsupported fixed prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 2012; 107:232–238.
Article21. Joo HS, Park SW, Yun KD, Lim HP. Complete-mouth rehabilitation using a 3D printing technique and the CAD/CAM double scanning method: A clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2016; 116:3–7.
Article22. Aparicio C. A new method for achieving passive fit of an interim restoration supported by Brånemark implants: a technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995; 10:614–618.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Full mouth rehabilitation of fully edentulous patient with implant-supported fixed prosthesis preceding bone graft: A case report
- Full mouth rehabilitation of edentulous patient with fixed implant prosthesis
- Full mouth rehabilitation of patient with severe dental caries with implant fixed prosthesis fabricated with milling and 3D printing method: A case report
- Full mouth rehabilitation of a partially edentulous patient with crossed occlusion using implant-retained RPD with zirconia occlusal table
- Full mouth rehabilitation of mandibular edentulous patient using implant hybrid prosthesis