J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2018 Oct;56(4):302-307. 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.4.302.
Full mouth rehabilitation of the patient with severe tooth loss and tooth wear with vertical dimension gaining: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. ykd@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2424030
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2018.56.4.302
Abstract
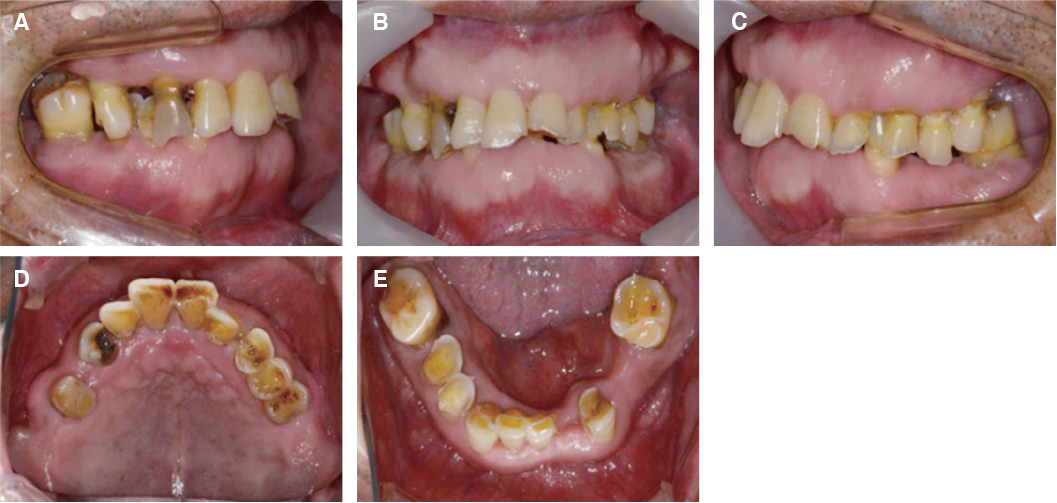
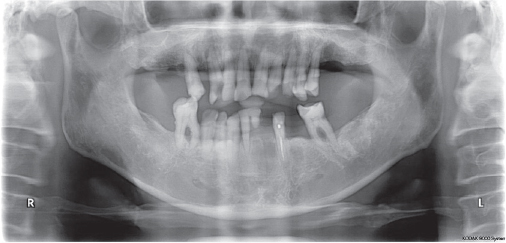
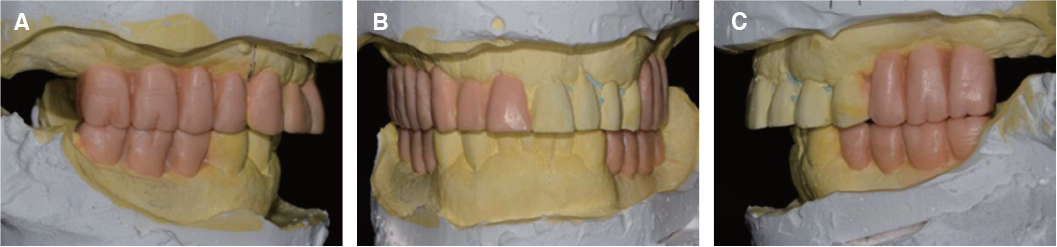
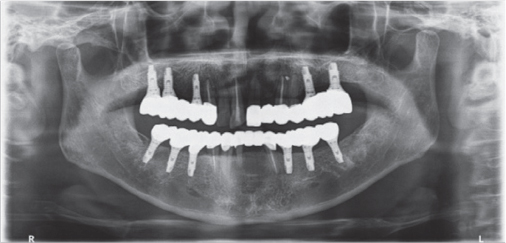
- Multiple tooth loss and excessive occlusal wear can result in damage to occlusal disharmony, functional disorders and esthetic problems, requiring comprehensive prosthetic treatments. Changing vertical dimension harmonized with surrounding muscle tissue is important. In this case, the patient with loss of vertical dimension caused by severe tooth loss and tooth wear was treated with the analysis of vertical dimension, such as diagnostic model, radiography and various clinical exams. the patient was satisfied with favorable functions and esthetics for 1 years of follow-up.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Full-mouth rehabilitation in a patient with inclined occlusal plane and reduced vertical dimension by an attrition: A case report
Ha-Rim Lee, Jae-Hoon Kim, Eun-Sun Jang, Gyeong-Je Lee
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2019;57(2):182-188. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2019.57.2.182.
Reference
-
1. Turner KA, Missirlian DM. Restoration of the extremely worn dentition. J Prosthet Dent. 1984; 52:467–474.
Article2. Rivera-Morales WC, Mohl ND. Relationship of occlusal vertical dimension to the health of the masticatory system. J Prosthet Dent. 1991; 65:547–553.
Article3. Thompson JR. The rest position of the mandible and its significance to dental science. J Am Dent Assoc. 1946; 33:151–180.
Article4. Ibbetson RJ, Setchell DJ. Treatment of the worn dentition: 2. Dent Update. 1989; 16:300–302. 305–307.5. Johnson A, Wildgoose DG, Wood DJ. The determination of freeway space using two different methods. J Oral Rehabil. 2002; 29:1010–1013.
Article6. Park JH, Jeong CM, Jeon YC, Lim JS. A study on the occlusal plane and the vertical dimension in Korean adults with natural dentition. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2005; 43:41–51.7. Mehta SB, Banerji S, Millar BJ, Suarez-Feito JM. Current concepts on the management of tooth wear: part 1. Assessment, treatment planning and strategies for the prevention and the passive management of tooth wear. Br Dent J. 2012; 212:17–27.
Article8. Mehta SB, Banerji S, Millar BJ, Suarez-Feito JM. Current concepts on the management of tooth wear: part 2. Active restorative care 1: the management of localised tooth wear. Br Dent J. 2012; 212:73–82.
Article9. Mehta SB, Banerji S, Millar BJ, Suarez-Feito JM. Current concepts on the management of tooth wear: part 4. An overview of the restorative techniques and dental materials commonly applied for the management of tooth wear. Br Dent J. 2012; 212:169–177.
Article10. Dawson PE. Functional occlusion: from TMJ to smile design. St. Louis; MO: Elsevier Health Sciences;2007. p. 430–452.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of full mouth rehabilitation with vertical dimension gaining in patient withseverely worn dentition and loss of vertical dimension due to loss of posterior support
- Full-mouth rehabilitation of the patient with severe tooth wear using all ceramic restorations
- Full mouth rehabilitation of patient with decreased occlusal vertical dimension due to severely worn dentition and posterior bite collapse
- Full mouth rehabilitation with vertical dimension increase in patient with loss of anterior guidance due to maxillary anterior teeth wear: A case report
- A case of full mouth rehabilitation with orthodontic treatment in patient with extensive tooth erosion and wear using monolithic zirconia prostheses