J Breast Cancer.
2018 Sep;21(3):334-338. 10.4048/jbc.2018.21.e45.
Gasless Robot-Assisted Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. imgenius@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2421375
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2018.21.e45
Abstract
- Robotic surgical systems enhance surgical accuracy and efficiency by applying advanced technologies such as artificial arm joints to provide higher degrees of freedom of movement and high-quality three-dimensional images. However, the application of robotic surgical systems to breast surgery has not been widely attempted. The robotic system would improve cosmesis by enabling surgery using a single small incision. We report the first case of a gasless robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction in a patient with early breast cancer.
MeSH Terms
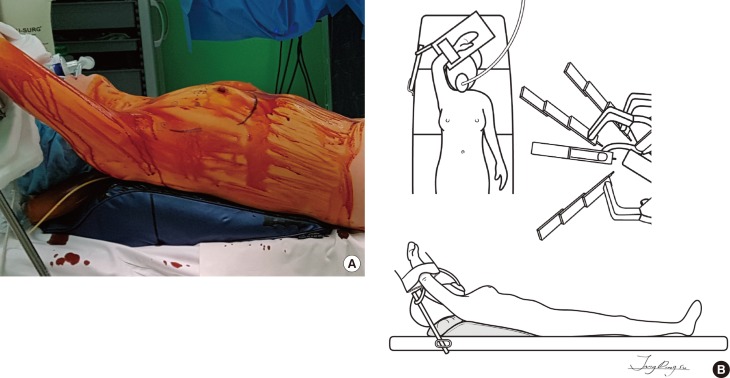
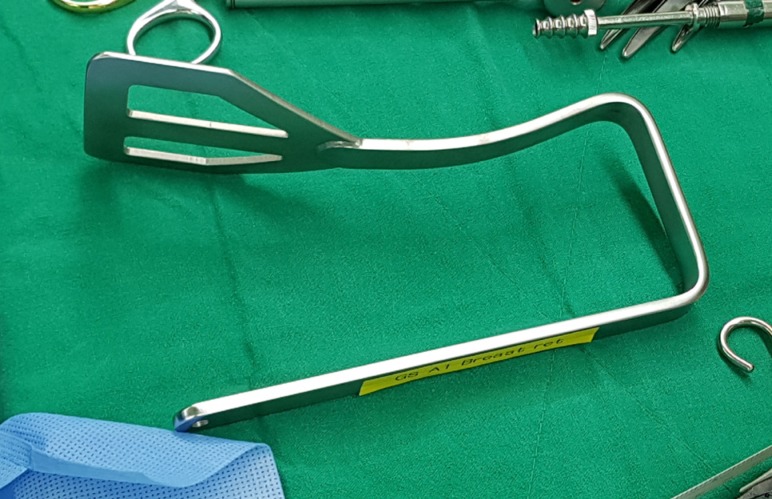
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Development of Robotic Mastectomy Using a Single-Port Surgical Robot System
Hyung Seok Park, Jeea Lee, Haemin Lee, Kwanbum Lee, Seung Yong Song, Antonio Toesca
J Breast Cancer. 2020;23(1):107-112. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2020.23.e3.
Reference
-
1. Tokin C, Weiss A, Wang-Rodriguez J, Blair SL. Oncologic safety of skin-sparing and nipple-sparing mastectomy: a discussion and review of the literature. Int J Surg Oncol. 2012; 2012:921821. PMID: 22848803.
Article2. Laronga C, Smith P. Nipple-sparing mastectomy: an oncologic and cosmetic perspective. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2014; 23:549–566. PMID: 24882350.3. Munhoz AM, Montag E, Filassi JR, Gemperli R. Immediate nipple-areola-sparing mastectomy reconstruction: an update on oncological and reconstruction techniques. World J Clin Oncol. 2014; 5:478–494. PMID: 25114861.
Article4. Peters BS, Armijo PR, Krause C, Choudhury SA, Oleynikov D. Review of emerging surgical robotic technology. Surg Endosc. 2018; 32:1636–1655. PMID: 29442240.
Article5. Toesca A, Peradze N, Manconi A, Galimberti V, Intra M, Colleoni M, et al. Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy for the treatment of breast cancer: feasibility and safety study. Breast. 2017; 31:51–56. PMID: 27810700.
Article6. Sarfati B, Honart JF, Leymarie N, Rimareix F, Al Khashnam H, Kolb F. Robotic da Vinci Xi-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy: first clinical report. Breast J. 2018; 24:373–376. PMID: 29251382.
Article7. Lee J, Chung WY. Robotic surgery for thyroid disease. Eur Thyroid J. 2013; 2:93–101. PMID: 24783046.
Article8. Toesca A, Peradze N, Galimberti V, Manconi A, Intra M, Gentilini O, et al. Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with implant: first report of surgical technique. Ann Surg. 2017; 266:e28–e30.9. Gottlieb A, Sprung J, Zheng XM, Gagner M. Massive subcutaneous emphysema and severe hypercarbia in a patient during endoscopic transcervical parathyroidectomy using carbon dioxide insufflation. Anesth Analg. 1997; 84:1154–1156. PMID: 9141952.
Article10. Yu J, Al Mushawah F, Taylor ME, Cyr AE, Gillanders WE, Aft RL, et al. Compromised margins following mastectomy for stage I-III invasive breast cancer. J Surg Res. 2012; 177:102–108. PMID: 22520579.
Article11. Cao D, Tsangaris TN, Kouprina N, Wu LS, Balch CM, Vang R, et al. The superficial margin of the skin-sparing mastectomy for breast carcinoma: factors predicting involvement and efficacy of additional margin sampling. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008; 15:1330–1340. PMID: 18246402.
Article12. Childs SK, Chen YH, Duggan MM, Golshan M, Pochebit S, Wong JS, et al. Surgical margins and the risk of local-regional recurrence after mastectomy without radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 84:1133–1138. PMID: 22543200.
Article13. Bryan ML, D'Agostino RB, Brown DR, Howard-McNatt MM. Is postmastectomy radiation therapy indicated in patients with close or positive margins? Adv Breast Cancer Res. 2016; 5:66–73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Single-port robot-assisted prosthetic breast reconstruction with the da Vinci SP Surgical System: first clinical report
- Comparison between Gasless and Gas-Inflated Robot-Assisted NippleSparing Mastectomy
- Development of Robotic Mastectomy Using a Single-Port Surgical Robot System
- Early experiences with robot-assisted prosthetic breast reconstruction
- Immediate Breast Reconstruction with TRAM Flap after Nipple-Areolar Sparing Mastectomy