Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2018 Aug;22(3):274-281. 10.14701/ahbps.2018.22.3.274.
Long-term complete response after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and stereotactic body radiation therapy in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma at the caudate lobe
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shwang@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2420617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2018.22.3.274
Abstract
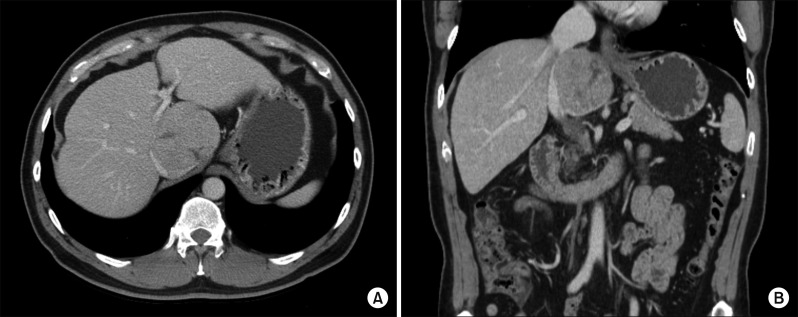
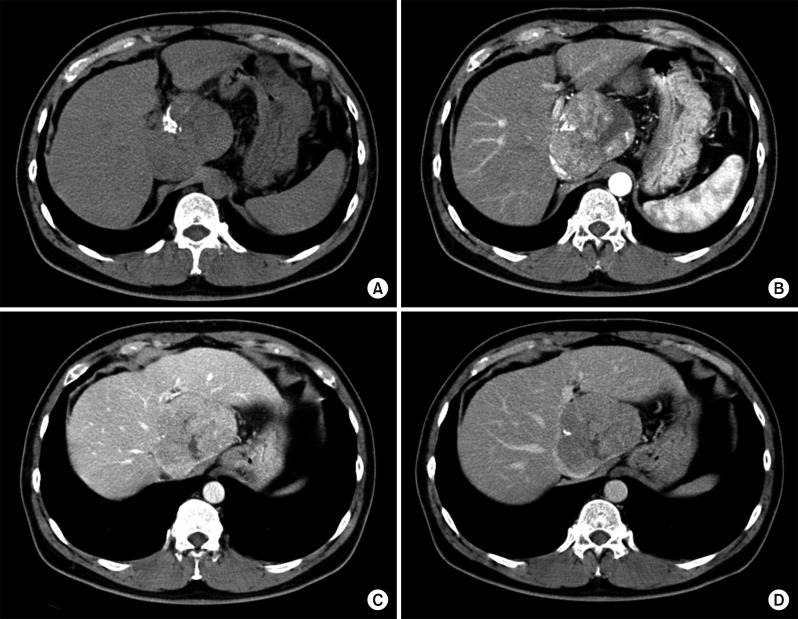
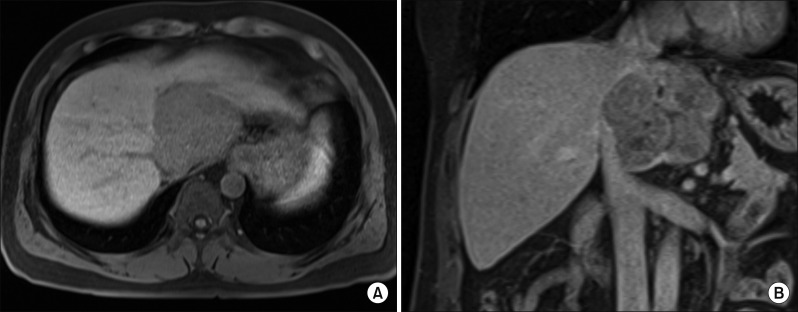
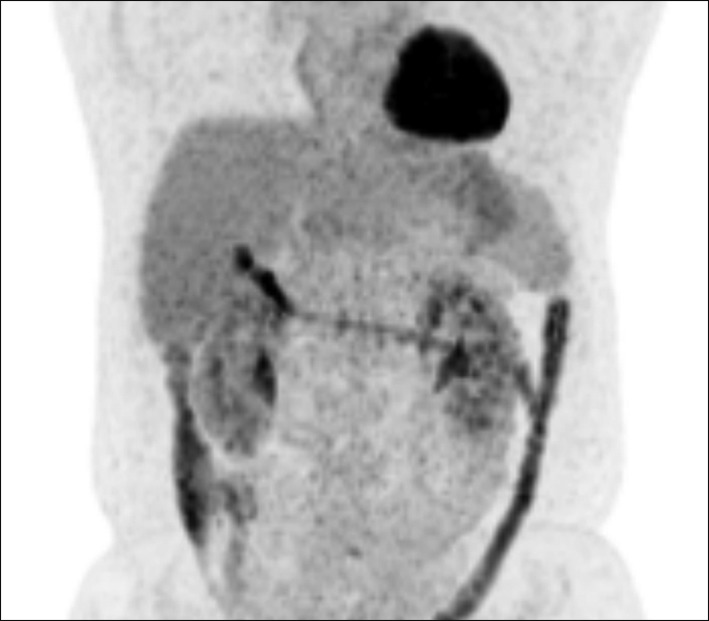
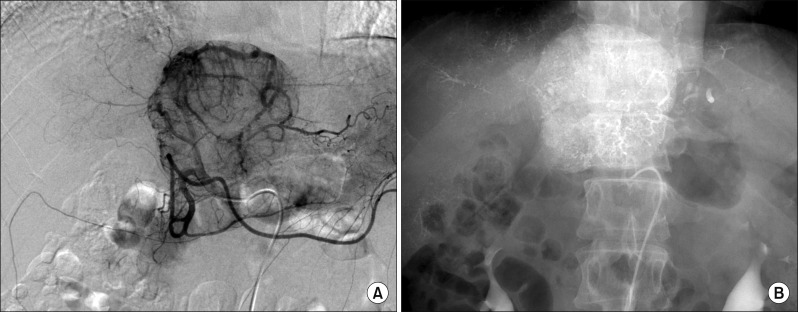
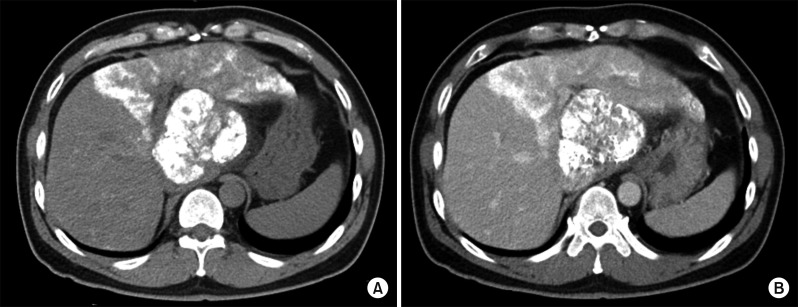
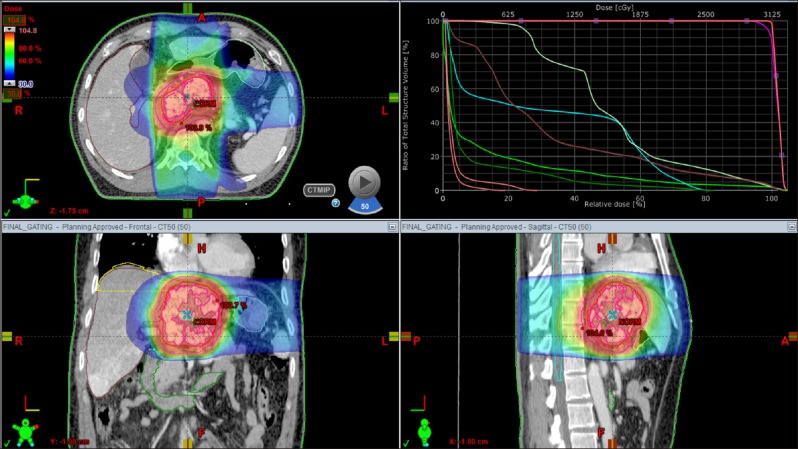
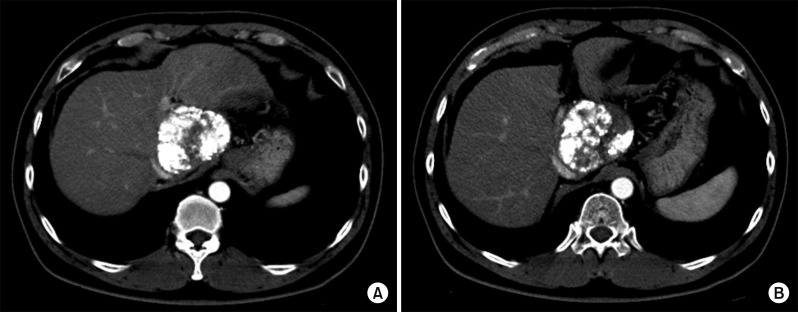
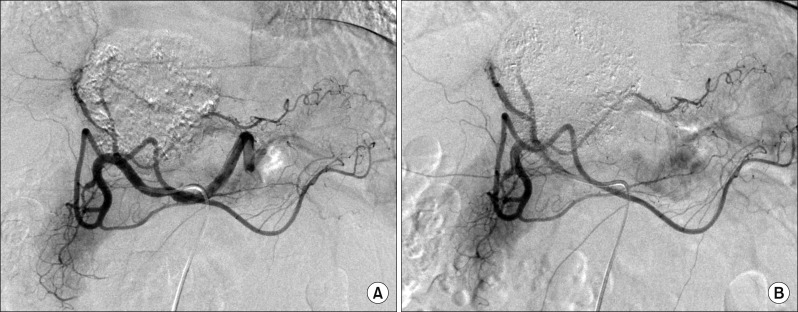
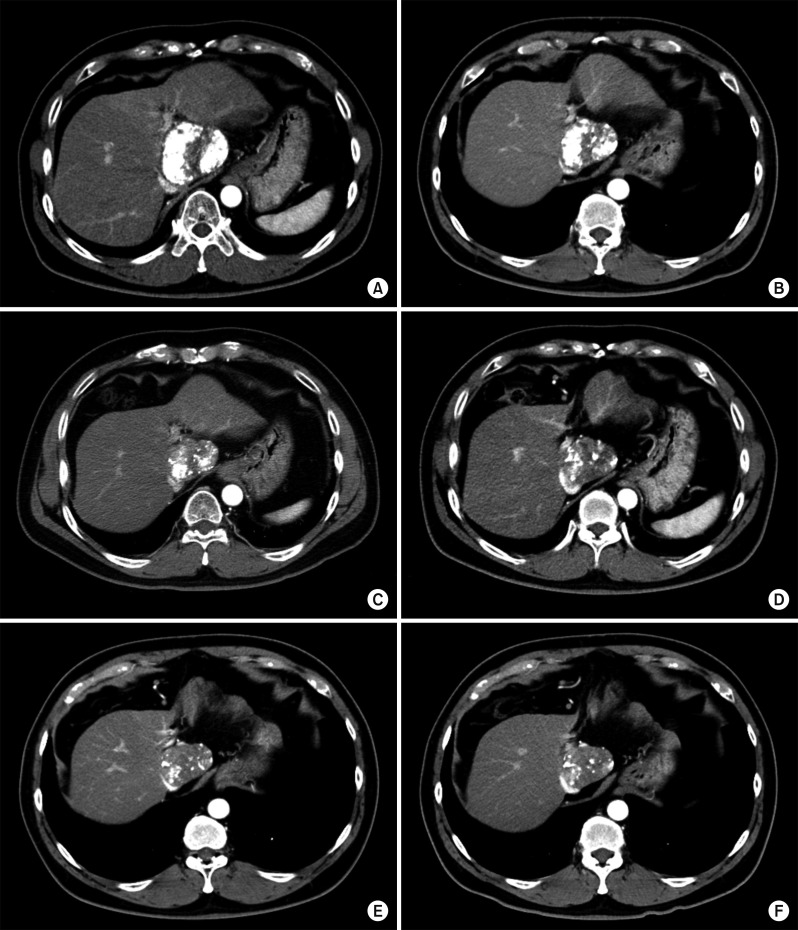
- It is expected that a combination of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) may induce synergistic therapeutic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which would result in a high rate of complete therapeutic response. In this study, we present the 5-year clinical course of a patient who had HCC at the caudate lobe, which was treated with TACE and SBRT. A 53-year-old male was diagnosed with an 8 cm-sized HCC at the caudate lobe with compression of the inferior vena cava (IVC). For fear of pulmonary metastasis, we decided to perform sequential TACE-radiotherapy instead of upfront hepatectomy, although the tumor appeared resectable. The first session of TACE, SBRT with 12 fractions, and the second session of TACE were sequentially performed. The patient was administered metformin for chemoprevention. Over the course of a 5-year follow-up, there was no evidence of HCC recurrence. We reported the clinical sequence of a patient showing complete therapeutic response of HCC at the caudate lobe after a combination of TACE and radiotherapy. This type of combined locoregional treatment can be a therapeutic option for HCC at the caudate lobe with marginal resectability.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012; 379:1245–1255. PMID: 22353262.
Article2. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:1118–1127. PMID: 21992124.
Article3. Wang ZG, Lau W, Fu SY, Liu H, Pan ZY, Yang Y, et al. Anterior hepatic parenchymal transection for complete caudate lobectomy to treat liver cancer situated in or involving the paracaval portion of the caudate lobe. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015; 19:880–886. PMID: 25759077.
Article4. Ahanatha Pillai S, Sathyanesan J, Perumal S, Ulagendra Perumal S, Lakshmanan A, Ramaswami S, et al. Isolated caudate lobe resection: technical challenges. Ann Gastroenterol. 2013; 26:150–155. PMID: 24714918.5. Liu P, Qiu BA, Bai G, Bai HW, Xia NX, Yang YX, et al. Choice of approach for hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma located in the caudate lobe: isolated or combined lobectomy? World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:3904–3909. PMID: 22876044.
Article6. Chaib E, Ribeiro MA Jr, Souza YE, D'Albuquerque LA. Anterior hepatic transection for caudate lobectomy. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2009; 64:1121–1125. PMID: 19936187.
Article7. Ha TY, Hwang S, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Ko GY, Ii Gwon D, et al. Absence of benefit of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with resectable solitary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2016; 40:1200–1210. PMID: 26666422.
Article8. Jeong Y, Jung J, Cho B, Kwak J, Jeong C, Kim JH, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy using a respiratory-gated volumetric-modulated arc therapy technique for small hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18:416. PMID: 29653562.
Article9. Ohri N, Dawson LA, Krishnan S, Seong J, Cheng JC, Sarin SK, et al. Radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: new indications and directions for future study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016; 108:djw133. PMID: 27377923.
Article10. Rim CH, Seong J. Application of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in current clinical practice guidelines. Radiat Oncol J. 2016; 34:160–167. PMID: 27730805.
Article11. Kang WH, Hwang S, Song GW, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Ahn CS, et al. Prognostic effect of transarterial chemoembolization-induced complete pathological response in patients undergoing liver resection and transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2017; 23:781–790. PMID: 28240808.
Article12. Yoon SM, Ryoo BY, Lee SJ, Kim JH, Shin JH, An JH, et al. Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization plus external beam radiotherapy vs sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018; DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5847. [in press].13. Im JH, Yoon SM, Park HC, Kim JH, Yu JI, Kim TH, et al. Radiotherapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumour thrombosis in a hepatitis B endemic area. Liver Int. 2017; 37:90–100.
Article14. Kwon JH, Bae SH, Kim JY, Choi BO, Jang HS, Jang JW, et al. Long-term effect of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma ineligible for local ablation therapy or surgical resection. stereotactic radiotherapy for liver cancer. BMC Cancer. 2010; 10:475. PMID: 20813065.
Article15. Wang JZ, Li XA, D'Souza WD, Stewart RD. Impact of prolonged fraction delivery times on tumor control: a note of caution for intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 57:543–552. PMID: 12957268.
Article16. Zheng XK, Chen LH, Yan X, Wang HM. Impact of prolonged fraction dose-delivery time modeling intensity-modulated radiation therapy on hepatocellular carcinoma cell killing. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:1452–1456. PMID: 15770720.
Article17. Ben Sahra I, Regazzetti C, Robert G, Laurent K, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Auberger P, et al. Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and cell-cycle arrest through REDD1. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:4366–4372. PMID: 21540236.
Article18. Chen HP, Shieh JJ, Chang CC, Chen TT, Lin JT, Wu MS, et al. Metformin decreases hepatocellular carcinoma risk in a dose-dependent manner: population-based and in vitro studies. Gut. 2013; 62:606–615. PMID: 22773548.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Showed Complete Response by Combined Therapy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
- A case of hepatocellular carcinoma in the caudate lobe successfully treated by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting beads
- Huge Hepatocellular Carcinoma Exhibiting a Complete Response after Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- A Case of Complete Remission in Ruptured Hepatocellular Carcinoma after One -time Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Extending to the Inferior Vena Cava and Right Atrium-A Case Report of 4 Years Survival after Repeated Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Therapy -