J Korean Med Assoc.
2018 Sep;61(9):568-572. 10.5124/jkma.2018.61.9.568.
Antibiotic therapy for appendicitis treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. lettoyam@naver.com
- KMID: 2420368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2018.61.9.568
Abstract
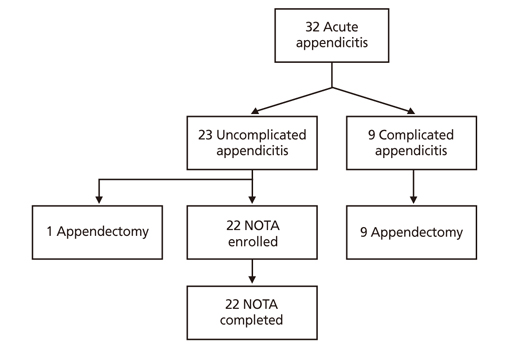
- Appendicitis is the most common diagnosis of acute abdominal pain that may require surgical treatment, and 8.6% for men and 6.9% for women are at risk for this illness over the course of their lives. During the past century, appendectomy was the standard treatment for acute appendicitis. However, laparoscopic appendectomy has been used as the first-line treatment choice for appendicitis since the introduction of laparoscopic surgery. In cases of perforation or abscess, interval appendectomy and percutaneous drainage are recommended. Treatment strategies have become more diverse. In recent years, in some European countries, non-surgical treatment has been used for simple appendicitis without complications, and nonoperative treatment of appendicitis has become increasingly common in adults and children. In this article, nonoperative treatment of appendicitis is introduced, and guidelines for the selection of antibiotics according to appendicitis classification are summarized.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korner H, Sondenaa K, Soreide JA, Andersen E, Nysted A, Lende TH, Kjellevold KH. Incidence of acute nonperforated and perforated appendicitis: age-specific and sex-specific analysis. World J Surg. 1997; 21:313–317.
Article2. Svensson JF, Hall NJ, Eaton S, Pierro A, Wester T. A review of conservative treatment of acute appendicitis. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2012; 22:185–194.
Article3. Vons C, Barry C, Maitre S, Pautrat K, Leconte M, Costaglioli B, Karoui M, Alves A, Dousset B, Valleur P, Falissard B, Franco D. Amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid versus appendicectomy for treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011; 377:1573–1579.
Article4. Hansson J, Korner U, Khorram-Manesh A, Solberg A, Lundholm K. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy versus appendicectomy as primary treatment of acute appendicitis in unselected patients. Br J Surg. 2009; 96:473–481.
Article5. Eriksson S, Granstrom L. Randomized controlled trial of appendicectomy versus antibiotic therapy for acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 1995; 82:166–169.
Article6. Styrud J, Eriksson S, Nilsson I, Ahlberg G, Haapaniemi S, Neovius G, Rex L, Badume I, Granstrom L. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis: a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial. World J Surg. 2006; 30:1033–1037.
Article7. Turhan AN, Kapan S, Kutukcu E, Yigitbaş H, Hatipoglu S, Aygun E. Comparison of operative and non operative management of acute appendicitis. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2009; 15:459–462.8. Salminen P, Paajanen H, Rautio T, Nordstrom P, Aarnio M, Rantanen T, Tuominen R, Hurme S, Virtanen J, Mecklin JP, Sand J, Jartti A, Rinta-Kiikka I, Gronroos JM. Antibiotic therapy vs appendectomy for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: the APPAC randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015; 313:2340–2348.
Article9. Wilms IM, de Hoog DE, de Visser DC, Janzing HM. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment for acute appendicitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (11):CD008359.
Article10. Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Safety and efficacy of antibiotics compared with appendicectomy for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2012; 344:e2156.
Article11. Antibiotic therapy for acute appendicitis in adults. Fewer immediate complications than with surgery, but more subsequent failures. Prescrire Int. 2014; 23:158–160.12. Sallinen V, Akl EA, You JJ, Agarwal A, Shoucair S, Vandvik PO, Agoritsas T, Heels-Ansdell D, Guyatt GH, Tikkinen KA. Meta-analysis of antibiotics versus appendicectomy for non-perforated acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2016; 103:656–667.
Article13. Harnoss JC, Zelienka I, Probst P, Grummich K, Muller-Lantzsch C, Harnoss JM, Ulrich A, Buchler MW, Diener MK. Antibiotics versus surgical therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis: systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials (PROSPERO 2015: CRD42015016882). Ann Surg. 2017; 265:889–900.14. Ehlers AP, Talan DA, Moran GJ, Flum DR, Davidson GH. Evidence for an antibiotics-first strategy for uncomplicated appendicitis in adults: a systematic review and gap analysis. J Am Coll Surg. 2016; 222:309–314.
Article15. Podda M, Cillara N, Di Saverio S, Lai A, Feroci F, Luridiana G, Agresta F, Vettoretto N. ACOI (Italian Society of Hospital Surgeons) Study Group on Acute Appendicitis. Italian Society of Hospital Surgeons) Study Group on Acute Appendicitis. Antibiotics-first strategy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults is associated with increased rates of peritonitis at surgery A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing appendectomy and non-operative management with antibiotics. Surgeon. 2017; 15:303–314.
Article16. Park HC, Kim MJ, Lee BH. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2017; 104:1785–1790.
Article17. Andersson RE, Hugander A, Thulin AJ. Diagnostic accuracy and perforation rate in appendicitis: association with age and sex of the patient and with appendicectomy rate. Eur J Surg. 1992; 158:37–41.18. Zingone F, Sultan AA, Humes DJ, West J. Risk of acute appendicitis in and around pregnancy: a population-based cohort study from England. Ann Surg. 2015; 261:332–337.19. Silvestri MT, Pettker CM, Brousseau EC, Dick MA, Ciarleglio MM, Erekson EA. Morbidity of appendectomy and cholecystectomy in pregnant and nonpregnant women. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 118:1261–1270.
Article20. Huang L, Yin Y, Yang L, Wang C, Li Y, Zhou Z. Comparison of antibiotic therapy and appendectomy for acute uncomplicated appendicitis in children: a meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017; 171:426–434.
Article21. Xu J, Adams S, Liu YC, Karpelowsky J. Nonoperative management in children with early acute appendicitis: A systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 2017; 52:1409–1415.
Article22. Georgiou R, Eaton S, Stanton MP, Pierro A, Hall NJ. Efficacy and safety of nonoperative treatment for acute appendicitis: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2017; 139. e20163003.
Article23. Hall NJ, Eaton S, Stanton MP, Pierro A, Burge DM. CHINA study collaborators and the Paediatric Surgery Trainees Research Network. Active observation versus interval appendicectomy after successful non-operative treatment of an appendix mass in children (CHINA study): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 2:253–260.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Computed Tomography Findings Associated with Treatment Failure after Antibiotic Therapy for Acute Appendicitis
- The Efficacy of Adding Postoperative Oral Antibiotics after Parenteral Antibiotic Therapy in Acute Appendicitis
- Pylephlebitis associated with appendicitis
- Optimal First-Line Antibiotic Treatment for Pediatric Complicated Appendicitis Based on Peritoneal Fluid Culture
- Routine Intraoperative Bacterial Culture May Be Needed in Complicated Appendicitis